![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Does not resemble any other tooth, looks primitive
|
Primary mandibular 1st molar
|
|
|
Resembles permanent maxillary 1st molar
|
Primary maxillary 2nd molar
|
|
|
Teeth having no deciduous predecessors
|
Accessional teeth (permanent molars)
|
|
|
From how many lobe/s does a peg lateral develop
|
1 lobe
|
|
|
What do you call the sixth cusp in the permanent mandibular 1st molar?
|
Tuberculum sextum
|
|
|
What do you call the 6th cusp when located in the distal marginal ridge (between distal cusp and DL cusp)
|
Tuberculim intermedium
|
|
|
When do the deciduous teeth develop in utero?
|
6 weeks
|
|
|
When do the deciduous teeth develop in utero?
|
6 weeks
|
|
|
When do primary teeth begin to calcify
|
4 mos in utero
|
|
|
When do the deciduous teeth develop in utero?
|
6 weeks
|
|
|
When do primary teeth begin to calcify
|
4 mos in utero
|
|
|
Aspirin, valium and dilantin are teratogens which cause what defect in the baby?
|
Cleft lip and palate
|
|
|
Excess in vitamin D causes what in dentofacial devt
|
Premature suture closure
|
|
|
How many line angles do all posterior teeth have?
|
8
|
|
|
How many line angles do all posterior teeth have?
|
8
|
|
|
How many line angles are there in anteriors?
|
6. There is no MI and DI line angle since they are rounded
|
|
|
Oblique ridge is found only what group of teeth?
|
Maxillary molars
|
|
|
Oblique ridge is found only what group of teeth?
|
Maxillary molars
|
|
|
A ridge formed by the union of the lingual triangular ridge of a buccal cusp and a buccal triangular ridge of a lingual cusp
|
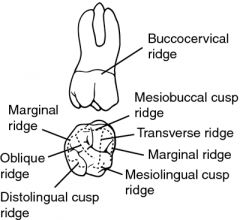
Transverse ridge
|
|
|
How many point angles do all teeth have?
|
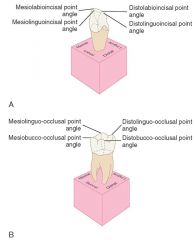
4
|
|
|
Buccal cusp ridge is more pronounced in what tooth
|
First premolars
|
|
|
A ridge found on all primary teeth and only on permanent molars
|
Cervical ridge
|
|
|
Primary centers of calcification
|
Lobes
|
|
|
Primary centers of calcification
|
Lobes
|
|
|
Small pinpoint depressions found at the junction of developmental grooves or at terminals of these grooves
|
Pit
|
|
|
Primary centers of calcification
|
Lobes
|
|
|
Small pinpoint depressions found at the junction of developmental grooves or at terminals of these grooves
|
Pit
|
|
|
Narrow channel or crevice formed at the depth of a developmental groove
|
Fissure
|
|
|
Second premolars have how many lobes?
|
3 buccal, 2 lingual
|
|
|
Second premolars have how many lobes?
|
3 buccal, 2 lingual
|
|
|
Where is the largest embrasure located?
|
Between max lateral and max canine
|
|
|
Second premolars have how many lobes?
|
3 buccal, 2 lingual
|
|
|
Where is the largest embrasure located?
|
Between max lateral and max canine
|
|
|
Does an embrasure contribute to arch stability?
|
No
|
|
|
Part of the crown which is covered by enamel
|
Anatomic crown
|
|
|
Lobes are separated by developmental depressions in anterior teeth. What separated lobes for the posterior teeth?
|
Developmental grooves
|
|
|
The smallest primary tooth
|
Primary mandibular central incisor
|
|
|
Crowns of primary molars are SHORTER and more NARROW MESIODISTALLY at the CERVICAL THIRD than the permanent. True or false?
|
True
|
|
|
Enamel ends more abruptly on the permanent teeth rather than becoming thinner. True or false?
|
False
|
|
|
Primary tooth whith the most noticeable morphological deviation from permanent teeth
|
Primary first molars
|
|
|
First deciduous tooth to erupt
|
Mand CI
|
|
|
First deciduous tooth to erupt
|
Mand CI
|
|
|
First permanent tooth to erupt
|
Mand 1st molar
|
|
|
Anterior teeth with a cingulum located in the CENTER if the lingual surface
|
Max 2 & 3
Mand 1 |
|
|
Anterior teeth with a cingulum located in the CENTER if the lingual surface
|
Max 2 & 3
Mand 1 |
|
|
Anterior teeth with a cingulum located OFF CENTER to the DISTAL
|
Mand 2 & 3
Max 1 |
|
|
Longest and widest anterior tooth
|
Max CI
|
|
|
Greatest axial inclination on relation to the occlusal plane and the tooth least likely to have a divided pulp canal
|
Max CI
|
|
|
Complication in root planning in maxillary lateral incisor is because of
|
Distolingual groove or palatogingival groove
|

