![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How is own-price elasticity of demand defined? |
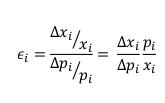
It is the percentage change in quantity demanded for a given percentage change in price. |
|
|
When is a demand elastic or inelastic? |
If a good has -An elasticity of demand greater than 1 in absolute value: elastic demand -An elasticity of demand less than 1 in absolute value: inelastic demand |
|
|
What is cross-price elasticity? |
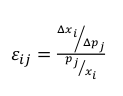
Changes in the price of a good or service may also affect demand for other goods and services. |
|
|
What does the sign of the cross-price elasticity say about two goods? |
If eij is, positive, then good i and j are substitutes negative, then good i and j are complements zero, then good i and j are independent |
|
|
What is the problem of health insurance coverage with respect to medical care? |
Health insurance reduces the price of health care services when personal health care services are consumed and thereby creating a higher demand for treatment. |
|
|
What are the different aspects of moral hazard for health insurances? |
-Health care providers are relatively uninformed about a client's health risk and health related behavior. -The patient is relatively uninformed about health care treatments but the health practitioner is relatively informed. |
|
|
What are the different kinds of health insurances? |
- fixed dollar subsidy - Ad valorem subsidy or coinsurance - deductible - Co-pay - Combinations of the above |
|
|
What is the fixed dollar subsidy? What are the advantages and disadvantages? |
The insurance policy specifies a fixed amount that the insurer will pay per unit of service for a particular type of service. The subsidy does not change with the price of service. +: less distortions than other types of subsidies -: low expenditure risk protection |
|
|
What is a Coinsurance? What are the advantages and disadvantages? |
Health insurance pays a certain percentage of the price. +: better expenditure risk protection -: fixed limit value of price of certain care according to region |
|
|
What are deductibles? What are the advantages and disadvantages? |
Minimum amounts of total expenditure that insured person must bear before the insurer subsidizes care. +: full expenditure rick protection for large expenses (above deductible) - : no coverage on small expenses, so risk of not getting care |
|
|
What are copays? What are the advantages and disadvantages? |
Insured pays a fixed amount per unit of service +: reduction of unnecessary medical care -: may act as a barrier for needed care |
|
|
How is the full price of consultation derived? |
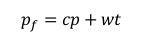
c is the coinsurance rate p is the physician's fee t is the total time of a visit w is the value of person's time |
|
|
What are the different types of data used to realize empirical studies? |
- Observational data - Data from randomized control trials (RCTs) -> avoids selection problem - Natural experiments |
|
|
What are stop loss insurance programs? |
They represent the maximum dollar expenditure an insurance company is willing to pay. |
|
|
What are the main results from the Health insurance Experiment? |
For 94% of persons having health insurance didn't have an effect on health. 3 to 5 years isn't sufficient to determine the relationship between health services use and health |
|
|
What are the effects of cost sharing on urgency and effectiveness? |
- Cost-sharing lead to lower emergency room utilization. - Difference in emergency room visits between plans with cost-sharing compared to the free plan - 23% for more urgent diagnoses - 47% for less urgent diagnoses -Both effective and ineffective services reduced by cost-sharing |
|
|
How is capitation defined? |
Health plans pay providers a fixed amount per enrolee. Providers bear full costs of treatment and thus try to reduce treatment costs or select healthier subjects |
|
|
What is the goal of a welfare analysis? |
Economists perform welfare analysis to determine whether e.g. a policy change increase or decreases societal well-being or "welfare" |
|
|
What is consumer surplus? |
Net value attached to the purchase of the quantity at the price by consumer. The area below demand curve and above the constant price of health care is the consumer surplus |
|
|
How is the wellfare loss defined? |
The welfare loss is given by thetriangle BFE where consumerwillingness to pay is lower thanmarginal costs of production. The area below the constant price of health care and above the demand curve is the wellfare loss. |

