![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Hypertension
|
persistent increased systemic arterial pressure
|
|
|
"Normal" range for BP?
Mild hypertension range? Moderate hypertension range? Severe hypertension range? |
Normal: 120/80
Mild: 140-150/90-100 Moderate: 160-170/100-110 Severe:>180/>110 |
|
|
What is aetiology and risk factors associated with Hypertension?
|
Primary (essential) HT
Smoking Obesity Diet (High Salt Exercise (lack of Genetics (unidentified components) Alcohol (J curve) Stress Secondary: Renal (Diabetes), Endocrine (Cushing's syndrome), Drugs (NSAIDS), Adrenal (Phaeochromocytoma) |
|
|
Describe the signs and symptoms of Hypertension
|
Signs: Presence of risk factors
Diagnostic BP Retinopathy Symptoms: Dyspnoea Visual changes Headache |
|
|
Describe the cardiac changes in Hypertension
|
Cardiac changes:
-Media:Lumen increases -Baroreceptors local and central adjust to new higher BP -Decreased density of vessels -Large vessel changes, less elastic and hardened, loss of arterial compliance -LV hypertrophy |
|
|
Describe renal changes in Hypertension
|
Renal
Change in renal vasculature leads to a decrease in Renal perfusion, GFR and decreased Na and Water excretion Activation of RAS |
|
|
Describe the consequence of persistent Hypertension
|
Atherosclerosis
Myocardial Infarction Stroke Heart failure Renal Failure Retinopathy |
|
|
List the 4 main treatment types of Hypertension
|
1) Block of sympathetic Nervous system - dec CO, VC
2) Kidney Action - reduce Blood Volume 3)Hormones - inhibit RAS system 4)Vasodilation of peripheral arterioles |
|
|
Beta Blockers (Propanolol, Atenolol)
Outline the following: Mode of action Effects Side Effects |
MOA: Competitive reversible antagonist of B1
EFFECTS: Dec. CO, HR, SV, renin release, symp tone SIDE EFFECTS: Exacerbate Asthma, Exercise intolerance, hypoglycaemia, vivid dreams |
|
|
Alpha blockers (Phentolamine, Doxazosin)
Outline the following: Mode of action Effects Side Effects |
MOA: Competitive reversible antagonist of A1
EFFECT: Dec. symp tone on arterioles, peripheral resistance SIDE EFFECTS: Reflex tachycardia, postural hypotension (loss of symp venoconstriction) |
|
|
ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Enalopril)
Outline the following: Mode of action Effects Side Effects |
MOA: Blocks the action Angiotensin Converting Enzyme on vascular endothelial cells, which means Ang II is not produced
EFFECT: Dec TPR, Dec BV (loss of Aldosterone production so less Na and Water reabsorbed) SIDE EFFECTS: Cough (ACE breaks down bradykinin in lungs), sudden drop of BP on first dose |
|
|
Ang II R blockers (Candesartan, Losartan)
Outline the following: Mode of action Effects Side Effects |
MOA: AT1 block as it mediates vasoconstriction and Ang II directed Aldosterone release
EFFECT: Dec. TPR and BV SIDE EFFECTS: Good profile, expensive |
|
|
Diuretics (Thiazides)
Outline the following: Mode of action Effects Side Effects |
MOA: Reduce renal absorption of Na and water, with possible vasodilation
EFFECT: Dec. TPR and BV Side Effect: Decrease K+> arrythmias |
|
|
Calcium Channel blockers (Diltiazem, Verapamil)
Outline the following: Mode of action Effects Side Effects |
MOA: Block of L-type voltage gated Ca2+ ion channels
by 1) open channel block and 2) allosteric modulation (preventing channel opening) EFFECT: Dec TPR (block of ca2+ entry in SMCs reduce vasoconstriction) Dec CO (Block of Ca2+ reduces HR and SV) SIDE EFFECTS: Constipation, negative dysrhytmias (decreased chronotropic and dromotropic effect) |
|
|
What does NICE have to say on Hypertension drugs?
|
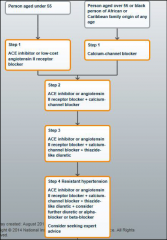
We'll see
|
|
|
Describe Postural hypotension
|
When seated or laying down
Gravity induced blood pooling in lower extremities Compromises venous return Dec. CO and Dec. BP Insufficient blood perfusion to upper extremities |

