![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where is actin often localized to? |
Cell cortex |
|
|
What are actins functions in muscle cells vs nonmuscle cells |
•in muscle cells: contraction • in non muscle cells: formation of contractile ring, cell movement, structural integrity of cytosol • in nucleus: it stabilizes chromatin and nuclear structure |
|
|
Describe two ends of f actin |
+ and - ends, G actin monomer with GTP being added, and then g actin monomer with ADP being subtracted |
|
|
3 steps of generation |
1) lag 2) polymerization 3) steady state 1) nucleation site for chain to build, 3 g monomers with ATP 3) rate of rxn between two ends is the same. Equilibrium |
|
|
Where is Phalloidin from and what does it do? |
Poisonous mushroom It inhibits depolymerization of actin proteins, by binding tightly to F actin polymer. Also inhibits hydrolysis of ATP |
|
|
What is spectrin? |
It is an actin binding protein. It is important for actin binding in RBCs because it helps with flexibility of cells through small blood vessels, flow of laminar fluid, and concave nature of cell to allow for more oxygen carrying |
|
|
What is dystrophin? |
Actin-binding protein. This protein if defected can lead to muscular dystrophy because it is needed for tensile strength for muscle cell diners |
|
|
What are each group of Intermediate filament used for? |
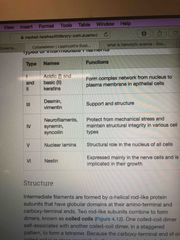
I and II - acidic and basic keratins III - Desmin, vimentin IV - neurofilaments, synemin, syncoilin V - nuclear lamina VI - nestin |
|
|
What are microtubules major functions? |
Chromosomal movement during nuclear division, intracellular transport, formation of flagella/cilia for some cells |
|
|
What do centrosomes do? Where are they found? |
They coordinate and regulate the radiation of microtubules. Found in one corner of the nucleus |
|
|
What is the basic unit for microtubules? |
Alpha-beta tubulin heterodimer, with beta oriented away from the centrosome. |
|
|
What is dynamic instability seen in microtubule formation? |
The tubules experience switching between growing and shrinking phases |
|
|
What is the difference between kinesin and dynein? What are they? |
Microtubule-binding proteins. ATP binding heads, and cargo tail Kinesin takes cargo away from centrosomes, so toward + end of microtubule. Dynein takes cargo toward centrosomes, so to - end of microtubule |

