![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does a normal endothelial cell release?
|
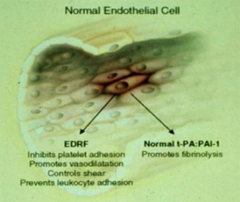
- EDRF: Endothelium-derived relaxing factor
- t-PA:PAI-1: Tissue plasminogen activator |
|
|
What is the normal action of EDRF (endothelium-derived relaxing factor)? Normal or dysfunctional?
|
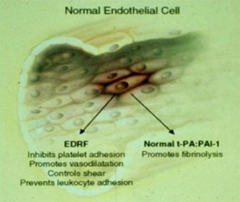
Normal endothelial cell function:
- Inhibits platelet adhesion - Promotes vasodilation - Controls shear - Prevents leukocyte adhesion |
|
|
What is the normal action of t-PA:PAI-1 (tissue plasminogen activator)? Normal or dysfunctional?
|
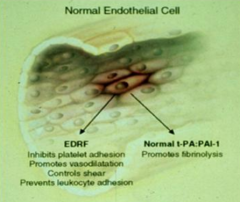
Normal endothelial cell function:
- Promotes fibrinolysis |
|
|
What does a dysfunctional endothelial cell release in hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis?
|
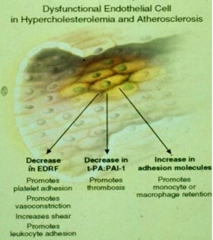
- Decreased EDRF: Endothelium-derived relaxing factor
- Decreased t-PA:PAI-1: Tissue plasminogen activator - Increase in Adhesion Molecules |
|
|
What are the results of a dysfunctional endothelial cell d/t hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis?
|
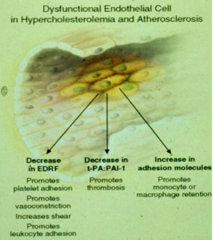
- ↓EDRF → platelet adhesion, vasoconstriction, ↑shear, leukocyte adhesion
- ↓t-PA:PAI-1 → promotes thrombosis - ↑Adhesion molecules → monocyte and macrophage retention |
|
|
What causes endothelial dysfunction?
|
Cardiac Risk Factors → ↑Reactive Oxygen Species and ↑Inflammation
|
|
|
What does endothelial dysfunction cause?
|
Vascular remodeling and atherosclerosis → ↑risk of coronary events and stroke
|
|
|
What are some invasive ways to measure vascular health?
|
- Intra-coronary measures
- Peripheral venous plethysmography |
|
|
What are some non-invasive ways to measure vascular health?
|
- Brachial artery reactivity
- Carotid IMT (intima media thickness) - Vascular tonometry |
|
|
Is brachial artery reactivity an invasive or non-invasive measure? What are you looking at in this screening?
|
- Non-invasive
- Use ultrasound to measure cross-section of brachial artery and can determine flow w/ doppler - Changes in vessel diameter after cuff release are measured to determine percent flow mediated dilation |
|
|
How do you do the brachial artery reactivity testing?
|
- Inflate BP cuff so that no blood can get through for 5 minutes
- Arm gets ischemic so the vessels dilate - When you release cuff, flow velocity will be extremely fast, causing shear forces on vessel - This should cause more dilation (peak 1-2 minutes after release) * Measure absolute change in diameter and relative change in diameter: determines percent Flow Mediated Dilation (FMD) |
|
|
How does the % Flow Mediated Dilation (FMD) change with BP?
|
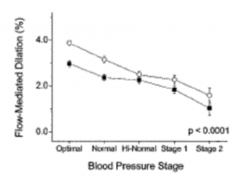
- Optimal BP, greater FMD
- As BP worsens, FMD decreases |
|
|
How does your risk score (takes into account age, BP, CV disease, etc) predict your Flow Mediated Dilation (FMD)?
|
The higher your risk score, the lower your FMD
|
|
|
Does improving your Flow-Mediated Dilation with therapy affect your risk of having an adverse event?
|
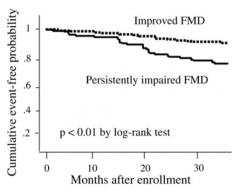
- Improved FMD increases your chances of living adverse event free
- A persistently impaired FMD is associated with more adverse events |
|
|
What are the advantages of measuring Flow-Mediated Dilation?
|
- Non-invasive
- Uses a pervasive technology - Correlates w/ function in coronary bed - Correlates w/ CV outcomes - Shows changes w/ therapy - High sensitivity |
|
|
What are the challenges of measuring Flow-Mediated Dilation?
|
- Technically difficult to perform (requires training)
- Protocol variations - Requires significant off-line analysis - No clear cut-off points for risk - Minimal data with respect to clinical improvements w/ alteration - Relatively low specificity |
|
|
What does Carotid IMT measure?
|
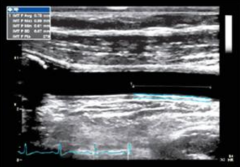
Structural changes in intima-media thickness
|
|
|
What are some independent determinants of carotid IMT?
|
- Age
- Pulse pressure - Diabetes - LDL cholesterol - Cigarette smoking |
|
|
What are the advantages of measuring Carotid IMT?
|
- Relative ease of performance
- Pervasive technology - Correlates w/ CV outcomes - High sensitivity - Correlates w/ presence and extent of coronary atherosclerosis |
|
|
What are the challenges of measuring Carotid IMT?
|
- Variations by age, sex, and race
- Study heterogeneity - Lack of specificity - Minimal data with respect to improvements with alteration also improve outcomes |

