![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Skeletal Muscle Cell
Peripheral Nuclei Striations (lightly staining I bands and more darkly staining A bands) reflect packing of myofibrils |
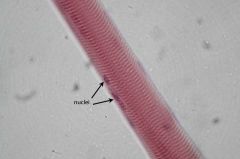
What is this?
What features distinguish this type of tissue? |
not the striations
|
|
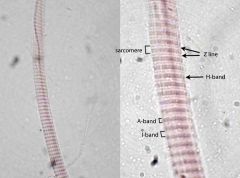
Label the features indicated by the arrows
|
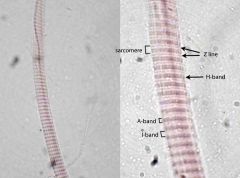
il immersion (right) image of a whole mount preparation, not a section, of a single muscle fiber (cell). Individual sarcomeres can be defined, extending from Z-line to Z-line. The Z-line is seen to bisect the lightly-staining I-band. Just a hint of the thin, lightly-staining H-band that bisects the dark A-band can be seen.
|
|
|

what type of cells are these? how can you tell
|
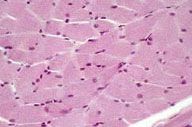
skeletal muscle, peripherally located nuclei
|
|
|
|
a myofibril within a skeletal muscle cell
|
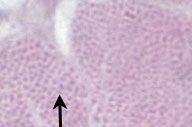
What is the dot that the arrow is pointing to?
|
|
|
|
epysium: connective tissue sheath surrounding entire muscle
|
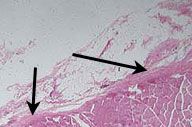
what structure are the arrows pointing to? what type of tissue is it made of?
|
|
|
|
At low power, the somewhat more delicate perimysium may be seen extending from the epimysium into the substance of the muscle. The perimysium will surround individual fascicles, each of which is comprised of numerous muscle fibers (cells).
|
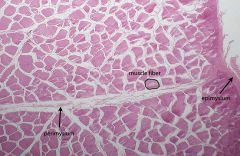
what structures are denoted by the arrows and circle? what type of tissue is this?
|
|
|
|
A medium power view through a section of skeletal muscle cut in cross section reveals a muscle spindle within the perimysial connective tissue. This structure, which provides proprioceptive information about the muscle in which it lies, is seen at higher power in the next image.
|
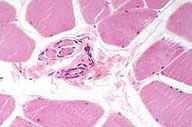
What is this structure?
Where is it found? What does it do? |
|

