![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 stages that everyone goes through when acquiring their FIRST LANGUAGE (L1)? |
1. BABBLING: 6 mos. - 1 yr. |
|
|
What are the 5 SECOND LANGUAGE (L2) PROFICIENCY LEVELS? |
1. BEGINNING (B): know a few words & can write a few words |
|
|
What are BICS and CALP |
Levels of fluency described by Cummins. BICS (Basic Interpersonal Communicative Skills) is fluency on a social level which should not be mistaken by a teacher to be the same as CALP (Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency) which is a level of fluency that allows for classroom learning. |
|
|
What are 8 STRATEGIES learners use in developing a 2nd language? |
1. Repetition |
|
|
What are 5 characteristics of BICS? |
1. social conversation |
|
|
What are 5 skills taught in CALPS? |
1. higher-order thinking |
|
|
What are the "ONE-BALLOON" & "TWO-BALLOON" theories? |
ONE-BALLOON: CUP (language is developed in "1 area" & there is a connection bet. L1 & L2) |
|
|
Whar are 3 PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS that influence intstruction? |
1. BACKGROUND FACTORS: validate name; age of EL; L1 proficiency; type of bigingualism (limited, partial, proficient; L2 experience; CELDT - access L2 level;prior academic success; likes & dislikes |
|
|
What are SOCIOCULTURAL FACTORS that influence instruction? |
1. FAMILY ACCULTURATIN & USE OF L1 & L2 (visit student's home & encourage parent involvment) |
|
|
What is the Constructivism Theory? |
People construct their own understanding and knowledge of the world, through experiencing things and reflecting on those experiences.The learner is an information constructor. (Vygotsky)
|
|
|
What is Vygotsky's Theory? |
Learning begins as interpersonal communication. Studied incremental gains in learning that take place in the zone of proximal development and are helped along by scaffolding. |
|
|
What is the zone of proximal development? |
The zone of proximal development, often abbreviated as ZPD, is the difference between what a learner can do without help and what he or she can do with help.
(Vygotsky) |
|
|
What are Piaget's Stages of Development? |
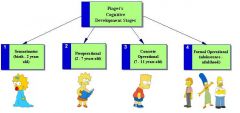
|
|
|
What is Chomsky's Theory? |
Chomsky argues that human brains have a language acquisition device (LAD), an innate mechanism or process that allows children to develop language skills. According to this view, all children are born with a universal grammar, which makes them receptive to the common features of all languages. (Nativist Model) |
|
|
What is the Behaviorist Model? |
Skinner: Learn in response to stimuli. |
|
|
What is the Social Interactionist Model of Language acquisition? |
The child will learn to speak in the manner and syntax of those people who speak to him. |
|
|
What is the Acquisition-Learning Model? (Krashen) |
Language learned in 2-step process: Acquisition= subconcious absorbtion of language Learning= formal education
Language learned mainly by long-term exposure that can be sped up with formal learning. |
|
|
How is the Acquisition-Learning Theory applied in the classsroom? |
According to this theory, the optimal way a language is learned is through natural communication. As a second language teacher, the ideal is to create a situation wherein language is used in order to fulfill authentic purposes. This is turn, will help students to ‘acquire’ the language instead of just ‘learning’ it. |
|
|
What is the Monitor Hypothesis? (Krashen) |
The formal learning of a language (grammar etc) causes the learner to monitor their speaking. The ‘monitor’ can sometimes act as a barrier as it forces the learner to slow down and focus more on accuracy as opposed to fluency. |
|
|
How is the Monitor Hypothesis applied in the classroom? |
As an SL teacher it will always be a challenge to strike a balance between encouraging accuracy and fluency in your students. This balance will depend on numerous variables including the language level of the students, the context of language use and the personal goals of each student. This balance is also known as Communicative competency. |
|
|
What is The Natural Order hypothesis? (Krashen) |
For any given language, there is a natural order of learning (that should be adhered to) in order to learn the language |
|
|
How is the Natural Order Hypothesis applied in the Classroom? |
According to this hypothesis, teachers should be aware that certain structures of a language are easier to acquire than others and therefore language structures should be taught in an order that is conducive to learning. |
|
|
What is the Input Hypothesis? (Krashen) |
Language acquisition occurs when learners receive messages that they can understand, a concept also known as comprehensible input. However, Krashen also suggests that this comprehensible input should be one step beyond the learner’s current language |
|
|
How is the Input Hypothesis applied in the classroom? |
The Input hypothesis highlights the importance of using the Target Language in the classroom. Self-Instruction & scaffolding also important. Can be difficult to tailor to individual student needs. (Slightly above ability level.) |
|
|
What is The Affective Filter hypothesis? (Krashen) |
One obstacle that manifests itself during language acquisition is the affective filter; that is a 'screen' that is influenced by emotional variables that can prevent learning. Anxiety, self-confidence, motivation and stress can influence a student's ability to learn. |
|
|
How is the Affective Filter Hypothesis applied in the classroom? |
In any aspect of education it is always important to create a safe, welcoming environment in which students can learn. In language education this may be especially important since in order to take in and produce language, learners need to feel that they are able to make mistakes and take risks |

