![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why is studying crime important? |
Substantive importance! Sheds light on a key quality of life issue- crime in communities. People are concerned with danger violence. It's a macro level stressor that has been shown to affect micro physical and mental health. High crime neighborhoods also suffer negative outcomes over time. |
|
|
The sociological perspective |
The assertion that our lives are shaped by our environment; sociologists see general social behavior patterns in individuals. Sociological imagination (mills). The ability to link biography, experiences, and concerns if any one person into the overarching patterns of the society in which they live. In sum, it means we focus on factors outside the individual to explain behavior. |
|
|
Social disorganization theory |
Focuses on how the role of adverse neighborhood conditions such as poverty hinders a communities to control crime( residents law likely to intervene it look out for each other. Focuses on kinda of places instead of kinds of people. |
|
|
Crime |
A violation of society's rules of behavior as interpreted by criminal legal code created by people holding social and political power. individuals who violate these rules are subject to sanctions by state authority, social stigma, and loss of status. |
|
|
Concepts |
Abstract terms summarizing a set of mental images, observations, feelings, or ideas. have to explain what is meant by them |
|
|
Measurement |
Procedure for determining the value of a variable in a specific case. two steps: clarify concepts that we are interested in, and construct an operational definition. |
|
|
Operational definition |
How we are going to measure our concept. tangible and explicit |
|
|
Variable |
A means of measuring a concept where the values can vary |
|
|
Dependent variable |
Effect in a causal relationship. value of the dependent variable depends on the independent variable |
|
|
Independent variable |
Cause in a causal relationship. produces change in the dependent variable |
|
|
Reliability |
Stability and consistency of measurement over repeated trials |
|
|
Validity |
Are we measuring what we think we are measuring? |
|
|
External validity |
Whether results can be generalized to other populations |
|
|
Internal validity |
Whether measure is accurately measuring what we think it is |
|
|
What must happen for the crime to be counted in police reports? |
Why must happen, police must be notified of the crime, and police must record the crime |
|
|
Problems with definition of crimes |
The FBI (who decimates crime data) has some definitions for what crimes are but local jurisdictions might be more expansive. this is especially the case with sexual assault. UCR definition says the carnal knowledge of a female forcibly and against her will. assault or attempt to forcibly rape classified as attempt to commit forcible rape. The new definition now includes either male or female victims or offenders, includes instances in which the victim is incapable of giving consent because of temporary or permanent mental or physical incapacity (because of age or drugs), and reflects the various forms of sexual penetration understood to be rape. |
|
|
Ucr |
A large database compiled by the FBI on index crimes reported and arrests made each year throughout the US. part 1 index crimes are violent (murder and non negligent manslaughter, forcible rape, robbery, and aggravated assault) and property (burglary, larceny, theft, and motor vehicle theft). |
|
|
Strength of the UCR |
It is a large database, can compare across years, and has the most serious crimes |
|
|
Weakness of the UCR |
No federal crimes, reports are voluntary and vary in accuracy and completeness, not all police departments submit reports, relies on reported crimes - so what happens with unreported crimes? reflects police activity. Not Crime. |
|
|
Mis measuring crime |
Inconsistent coding (federal, state and local laws vary), non reporting by victims and police, incomplete and inaccurate data informs policy. |
|
|
Victimization surveys |
Generally designed to be representative surveys of particular location (state or county), ask about experiences regarding being the victim of a crime, get at crimes not reported to the police (avoids non reporting bias). self reports of victims and non victims. |
|
|
National Crime Victimization Survey (ncvs) |
The gold standard of surveys. how it works- each year data obtained from a nationally representative sample of about 90000 households comprising nearly 160,000 persons, on the frequency, characteristics, and consequences of criminal victimization in the United States. each household is interviewed twice during the year. the NCVS provides the largest national forum for victims to describe the impact of crime and characteristics of violent offenders. |
|
|
Ncvs- types of information on event gathered (as many as have happened) |
Location of event (home, work etc) as well as geographical identifier like county, how many times event happened, time of day, where people present during event, information about offender if known ( age, race, sex, ethnicity, type of weapon used relationship- if more than one defender Asked Questions about "most of the offenders"), distress felt after the events such as being worried or anxious, whether the victim resisted, monetary loss, physical injury. |
|
|
Strengths of NCVS |
Accuracy and reliability, accounts for much more street crime, situational factors, characteristics of offenders, relationships, tells us about the dynamics of notifying the police. |
|
|
Predictors of reporting to police |
Completed offence, injury, stranger. |
|
|
Ncvs- reasons for not reporting |
Private matter, incomplete offense, property recovered, police ineffectiveness, no evidence |
|
|
Limitations of the NCvs |
Survey problems such as people not being candid, people over reporting or exaggerating interactions. institutionalized youth under represented. only captures offenses involving victims. drug and alcohol and white-collar offenses are excluded, murder excluded, interviewer/ respondent disconnected, missing cases a problem- excludes homeless persons and many other high-rate victims. juvenile victimization is under-reported and no data on less than 12 years of age |
|
|
NCVS survey summary |
Provides profile of incidents both reported and not reported to Police, provides contextual information on crimes but has inherent problems- does not cover all crimes, unverifiable, dependent on question wording and technical elements |
|
|
Self-report data |
People (mostly youth) are asked to discuss their legal activities often they are selected from schools |
|
|
Strengths of self report data |
People reveal information anonymously, indicate that crime much more prevalent than official statistics, can get information about other factors such as income, social ties, etc |
|
|
Weaknesses of self-report data |
People may exaggerate or forget their actions, missing cases a problem, institutionalized youth are underrepresented, often do not include serious delinquency |
|
|
Quantitative research |
Aims to find statistical patterns or trends in a population based on a sample |
|
|
Qualitative research |
Aims to find in-depth understanding of a social issue. focuses on nuances of behavior or experiences |
|
|
Major sources of qualitative data |
Participant observation, interviews |
|
|
Classical School of criminology |
Crime is a result of rational calculation that weighs the cost (pain )and benefit (pleasure) of committing the act. |
|
|
The basic idea behind classical criminology |
In every society people have free will to choose criminal or lawful solutions to meet their needs or settle their problems. criminal solutions maybe more attractive than lawful ones because they usually require less work for a greater pay off. a person's choice of criminals solutions may be controlled by his or her fear of punishment. the more severe, certain, and swift the punishment the better able it is to control criminal behavior. |
|
|
Positive school of criminology |
Two main elements of positivist school- positivists see human behavior as a function of internal or external forces that are often be on individual control. early positivists were influenced by the scientific method. view of criminal behavior- individuals are basically driven to criminal acts by complex forces over which they have little control. as the 19th century positivist said criminals go criminal as the insane go mad because they cannot help it |
|
|
National Incident based reporting system ( NIBRS) |
Designed to address hierarchy rule in the UCR. refers to the process of a multiple offense situation only in the most serious offense in the series is reported all others are ignored (house burglary or robbery). developed as a phase in program |
|
|
Incident types (UCR) |
8 ( with arson) part 1 offenses ( crimes known to the police). 20 part 2 offenses ( arrest data) |
|
|
Incident types (NIBRS) |
46 group a offences over 22 categories. 11 group b offenses (offenses that produced arrests). |
|
|
Early history of measuring crime |

|
|
|
History of measuring crime continued |

|
|
|
Problems with early UCR |

|
|
|
Problems with early ucr(continued) |

|
|
|
Picking the crimes to count UCR |

|
|
|
Early self-report |

|
|
|
Early victimization surveys |

|
|
|
Early victimization surveys continued |

|
|
|
Victimization surveys |

|
|
|
Unit of analysis |
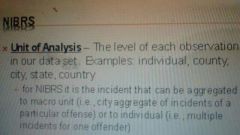
|
|
|
Problems with the NIBRS |

|
|
|
Problems with the NIBRS continued |
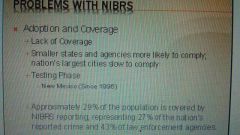
|
|
|
Adoption and coverage |

|
|
|
Summary of NIBRS- advantages |

|
|
|
Summary of NIBRS -disadvantages |

|

