![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Case Control Study:
Design and Measurements |

|
|
|
Cohort Study:
Design and Measurements |

|
|
|
Cross-sectional Study:
Design and Measurements |
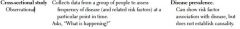
|
|
|
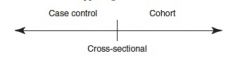
Time investigation of cohort, cross-sectional, and case-control studies
|
|
|
|
Twin concordance Study:
Design and Measurements |

|
|
|
Adoption Study:
Design and Measurements |

|
|
|
Clinical Trial: Definition
|

|
|
|
Clinical Trial: Phase I-- Study Sample and Purpose
|
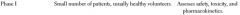
|
|
|
Clinical Trial: Phase II-- Study Sample and Purpose
|

|
|
|
Clinical Trial: Phase III-- Study Sample and Purpose
|

|
|
|
Meta-analysis
|

|
|
|
2 x 2 Table
|

|
|
|
Sensitivity
|

|
|
|
Specificity
|

|
|
|
Negative Predictive Value
|

|
|
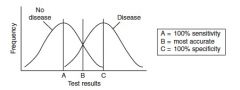
|
100 % specificity rules in the disease, while 100% sensitivity rules out the disease.
|
|
|
Positive Predictive Value
|

|
|
|
Prevalence vs. Incidence
|

|
|
|
Odds ratio, relative risk, attributable risk
|

|
|
|
Precision vs. Accuracy
|
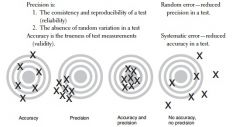
|
|
|
Bias types: selection, recall, sampling
|

|
|
|
Bias types: late-look, procedure, confounding
|

|
|
|
Bias types: lead-time, Pygmalion effect, Hawthorne effect
|

|
|
|
Statistical Distribution
|

|
|
|
Statistical Hypotheses
|

|
|
|
Type 1 and Type 2 error
|

|
|
|
Power
|

|
|
|
Standard Deviation and Standard Error
|

|
|
|
Normal Distribution
|
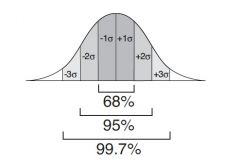
|
|
|
Confidence Interval
|

|
|
|
t-test, ANOVA, and chi-squared
|

|
|
|
Correlation coefficient
|

|
|
|
Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Disease Prevention
|

|
|
|
Disease Prevention Measures (some examples): diabetes, drug use, alcoholism, overweight, homeless/recent immigrant/inmate, high risk sexual behavior
|

|
|
|
Leading Cause of Death in the USA by age
|

|
|
|
Infant motor and cognitive/social milestones
|

|
|
|
Toddler motor and cognitive/social milestones
|

|
|
|
Preschool motor and cognitive/social milestones
|

|
|
|
Piaget's stages of cognitive development
|

|
|
|
Tanner stages of sexual development
|

|
|
|
Changes in the elderly
|

|
|
|
Grief (normal and pathologic)
|

|
|
|
Kubler-Ross Grief Stages
|

|
|
|
Stress effects
|

|
|
|
Body Mass Index (BMI)
|

|
|
|
Sleep Stages
|

|
|
|
REM sleep
|

|
|
|
Narcolepsy
|

|
|
|
Circadian Rhythm
|

|
|
|
Chromatin Structure
|

|
|
|
Heterochromatin
|

|
|
|
Euchromatin
|

|
|
|
"Beads on a String"
|

Term used to describe chromatin structure
|
|
|
Purines and Pyrimidines
|

|
|
|
GC Content
|

|
|
|
Relationship between cytosine and uracil
|

|
|
|
Uracil and Thymine
|
Uracil found in RNA, Thymine in DNA. THYmine contains a meTHYl group.
|
|
|
What amino acids are used to make purines?
|

Glycine, Aspartate, and Glutamine (GAG)
|
|
|
What is used to make pyrimidines?
|

|
|
|
Nucleoside vs. Nucleotide
|

|
|
|
De novo purine and pyrimidine synthesis
|
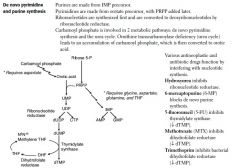
|
|
|
Purine Salvage Deficiencies
|
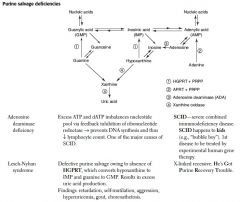
|
|
|
Transition vs. Transversion
|

|
|
|
Features of the genetic code
|

|
|
|
DNA mutations
|

|
|
|
DNA Replication!
|

|
|
|
Single Strand DNA repair
|

|
|
|
Double Strand DNA repair
|

|
|
|
DNA/RNA/Protein synthesis directions
|

Note: error in this diagram. The 3' OH is the attacking nucleophile. It attacks a triphosphate bond (depicted as a monophosphate here) in the incoming nucleotide.
|
|
|
Types of RNA
|

|
|
|
Start and Stop Codons
|

|
|
|
Functional Organization of the Gene
|

|
|
|
Gene expression regulation
|

|
|
|
RNA polymerases in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
|

|
|
|
RNA Processing (Eukaryotes)
|

|
|
|
pre-mRNA splicing in Eukaryotes
|

|
|
|
Introns vs. Exons
|

|
|
|
tRNA
|

|
|
|
tRNA wobble
|

|
|
|
Protein Synthesis: Initiation
|

|
|
|
Protein Synthesis: Elongation
|

|
|
|
Protein Synthesis: Termination
|

|
|
|
Prokaryote and Eukaryote Ribosome Subunits
|

|
|
|
Roles of ATP and GTP in protein synthesis
|

|
|
|
A, P, and E sites of ribosome
|

|
|
|
Antibiotics that interfere with protein synthesis
|

|
|
|
The eukaryotic ribosome
|

|
|
|
GTP and ATP requirements in translation
|

|
|
|
Posttranslational modifications of proteins
|

|
|
|
Cell cycle phases
|

|
|
|
Cell types with respect to cell cycle states
|

|
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
|

|
|
|
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|

|
|
|
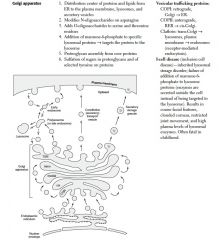
Golgi apparatus and vesicular trafficing
|
|
|
|
Microtubule
|

|
|
|
Cilia structure
|

|
|
|
Cytoskeletal elements
|

|

