![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What broad categories can you divide movement into?
|
Involuntary - Automatic - Flexion - Withdrawal reflex
Voluntary - Conscious control - Voluntary - Reaching Spectrum |
|
|
What is the difference between Declarative and non-Declarative memory?
|
Declarative: Factual info, life events EASY FORMED/FORGOTTEN
Non -Declarative: Procedural memory - motor skills - Not available to consciousness - Less easily formed/forgotten |
|
|
What are the two strategies for controlling movements
|
Ballisitic
Visual feedback mechanisms |
|
|
What is a ballistic movement?
|
Movement based largely on preprogrammed instructions
Rapid but at expense of accuracy So little compensation time Smashing a ball with a limb/racket |
|
|
What is a visual feedback movement?
|
Motor command that receives continuous updates according to sensory feedback (e.g. visual)
Highly accurate but slower Modified in progress |
|
|
In practice most movements involve a bit of both
|
Agreed
|
|
|
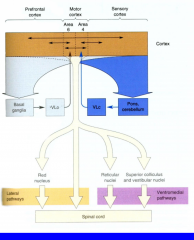
What are the areas involved in planning and instruction of voluntary movement?
|
Prefrontal cortex
AREA 6: SMA + PMA AREA 4: Motor cortex S1: Sensory cortex Area 5&7 |
|
|
How does the basal ganglia communicate within itself?
|
Input : PFC
Output: PMA Function: Initiation of movement Planning of complex movement |
|
|
What happens in the basal ganglia in Parkinson's disease?
|
Difficulty in initiating movement (tremor)
|
|
|
What happens in the basal ganglia in Huntington's disease?
|
Random involuntary movements
|
|
|
Which area of the motor input system rehearses the movement?
|
SMA
|
|
|
Which sensory systems provide information vital to movement?
|
Proprioception -SSC
Vision - VC Vestibular - Subcortical |
|
|
Cerebellum
Input: Output: Function: |
Cerebellum
Input: Sensory cortex Output: Primary motor cortex via thalamus Function: Co-ordination and smooth execution of meovements Motor learning, error detection Damage: Cerebellar ataxia = poor coordination |
|
|
What two groups of descending pathways are there?
|
Lateral - Corticospinal/rubrospinal
Ventromedial - Vestibulospinal, Reticulospinal, Tectospinal |
|
|
What is the main function of lateral pathways
|
Control of voluntary movements of distal limbs
Fine control |
|
|
What is the main function of the Ventromedial pathways?
|
Posture control of axial muscles
Synapse on MNs or INs in spinal cord |

