![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
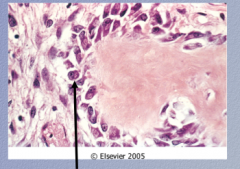
Identify the cell What is the matrix called? Is it mineralized? What is it made up of?
How you know osteoid is not bone? |
Osteoblast (mononuclear cells at edge of osteoid material)
Osteoid (not mineralized) = difference from bone
Collagen type I
Wavy, fibrillar due to collagen |
|
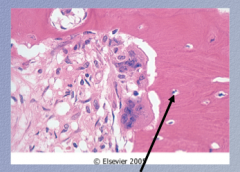
Identify the cell |
Osteocyte |
|
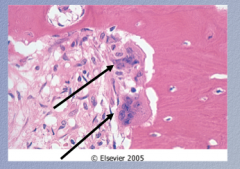
Identify the cells. How to differentiate from osteoblast?
What are the cup-shaped invaginations called? |
Osteoclasts
Multinucleated , live in cup-shaped invaginations into the bone
Halships lacunae (resorption pits) |
|
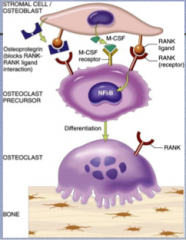
Describe the pathway.
Where is osteoprotegrin made? What does it do? |
Stromal cell/osteoblasts have RANK ligand and M-CSF. RANK-L activates NF-kB in osteoclast (RANK receptor) precursor => differentiation into osteoclast
Osteoprotegrin made in osteoblast, blocks RANK-L-RANK interaction |
|
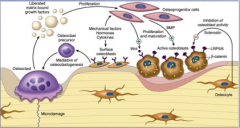
What if you have too much WNT?
|
Too much WNT = osteoporosis = too much bone growth
|
|
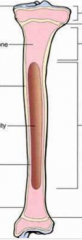
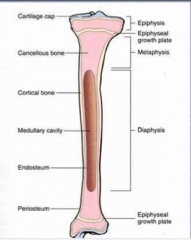
Identify the normal long bone structures.
(Metaphysis, diaphysis, epiphyseal growth plate, epiphysis, cancellous bone, cartilage cap, cortical bone, endosteum, periosteum, medullary cavity) |
|
|
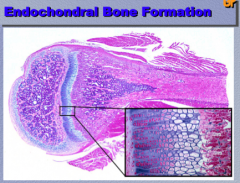
Where is bone formed?
How long does mineralization take? |
Epiphyseal bone plate
10-15 days (2 weeks) |
|
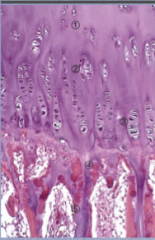
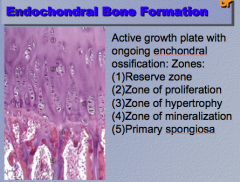
Identify the five labeled zones |
|
|
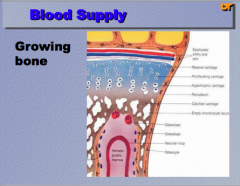
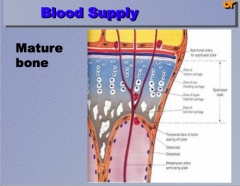
Note the difference in the blood supply and mature bone. Which group is more susceptible to vascular transmission of bone infection? |
Children through hematogenous spread of organisms
Can also occur from outside trauma/force, etc.
|
|
? |
? |
|
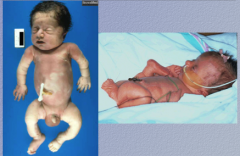
Identify the condition. Summarize the condition. What would an illness script have? |
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Brittle bone disease due to defect in type I collagen genes, most common disorder of connective tissue
"Adolescent who is prone to breaking bones..." |
|
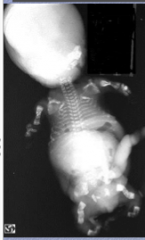
Osteogenesis imperfecta: What do you notice about each location?
Skull Long bones Ribs |

|
|
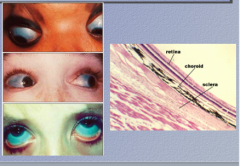
What color are the sclerae? What is the condition? What are sclerae made of?
What are the four diagnostic features? |
Osteogenesis imperfecta (sclerae made of type I collagen)
Blue sclerae, dentigenesis imperfecta, premature otosclerosis, blue sclerae |
|

What is the condition? Describe |
Achondroplasia
Genetic disorder of the growth of the long bones => chondrocytes don't work properly (reduction at growth plate) |
|
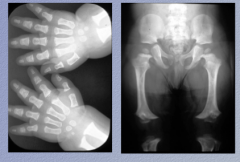
What is the condition? Describe |
Achondroplasia
Poor bone formation, don't have a lot of cartilage in the places that you should |
|
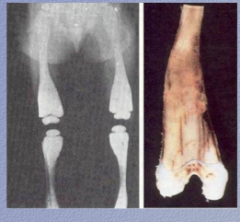
Long bones without cavities but with misshapen bulbous ends. What is the condition? Are the bones strong or brittle? What else do they suffer from? |
Osteopetrosis
Brittle
Hearing loss (cranial nerve paralysis), pancytopenia due to lack of hematopoiesis due to lack of bone marrow space |
|
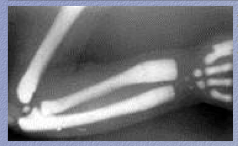
What do you notice in the X-ray? What is the condition? |
Bones are diffusely "sclerotic;" distal metaphases of ulna and radius are poorly formed and have bulbous ends
Osteopetrosis |
|
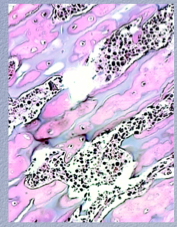
What is shown here? Comment on trabeculae, cartilage. Number of osteoclasts? What is in the marrow cavities? |

|
|
|
What is the pathophysiology of osteopetrosis? |
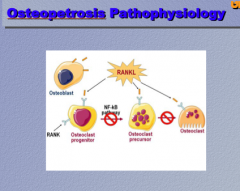
Not enough osteoclasts or osteoclasts that you have don't work very well. |
|
|
Disorder: Give gene involved and phenotype
BRACHYDACTYLY
Defect in TRANSCIPTION FACTORS => mesenchymal condensation and related cell differentiation |
Gene: HOXD13
Clinical Phenotype: Short, broad terminal phalanges of thumbs and first toes |
|
|
Disorder: Give gene involved and phenotype
CAMPOMELIC DYSPLASIA
Defect in TRANSCIPTION FACTORS => mesenchymal condensation and related cell differentiation
|
Gene: SOX9
Clinical Phenotype: Short bowing long bones, small chest cavity, respiratory failure, sex reversal (46XY with female phenotype) |
|
|
Disorder: Give gene involved and phenotype
CLEIDOCRANIAL DYSPLASIA
Defect in TRANSCIPTION FACTORS => mesenchymal condensation and related cell differentiation |
Gene: RUNX2
Clinical Phenotype: Hypoplastic clavicles, Wormian (divided skull) bones, supernumerary teeth |
|
|
Disorder: Give gene involved and phenotype
HOLT-ORAM SYNDROME
Defect in TRANSCIPTION FACTORS => mesenchymal condensation and related cell differentiation |
Gene: TBX5
Clinical Phenotype: Thumb, wrist and forearm bone hypoplasias, cardiac atrial septal defect |
|
|
Disorder: Give gene involved and phenotype
NAIL-PATELLA SYNDROME
Defect in TRANSCIPTION FACTORS => mesenchymal condensation and related cell differentiation |
Gene: LMX1B
Clinical Phenotype: Hypoplastic nails, hypo- or aplastic patellas, dislocated radial head, progressive nephropathy |
|
|
Disorder: Give gene involved and phenotype
WAARDENBURG SYNDROME
Defect in TRANSCIPTION FACTORS => mesenchymal condensation and related cell differentiation |
Gene: PAX3
Clinical Phenotype: Hearing loss, partial albinism, different colored eyes, patches of white hair or early graying, constipation |
|
|
Disorder: Give gene involved and phenotype
THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA ("death bearing")
Defect in HORMONES AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PROTEINS => abnormal proliferation or maturation of osteoblasts, osteoclasts, or chondrocytes |
Gene: HFGFR3
Clinical phenotype: Severe limb shortening and bowing, small chest cavity, respiratory failure |
|
|
Disorder: Give gene involved and phenotype
ACHONDROGENESIS TYPE 2
Defects in EXTRACELLULAR STRUCTURAL PROTEINS |
Gene: COL2A1 (type II collagen)
Clinical phenotype: Short trunk |
|
|
Disorder: Give gene involved and phenotype
METAPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA (SCHMID TYPE)
Defects in EXTRACELLULAR STRUCTURAL PROTEINS |
Gene: COL10A1 (type X collagen)
Clinical phenotype: short stature |
|
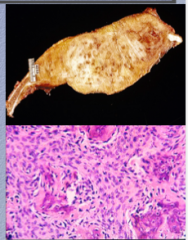
What is the condition?
Gross pathology?
Microscopic pathology?
What surrounds islets?
Can they be any size? |
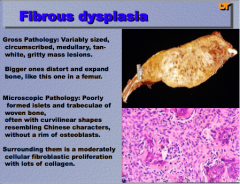
Yes, can be any size. |
|
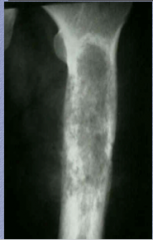
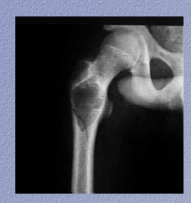
What is shown?
What is the descriptor? |
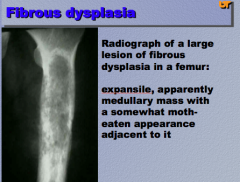
MOTH EATEN! |
|
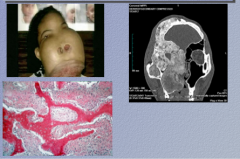
What is the condition? Is it benign? |
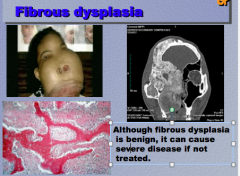
Fibrous dysplasia Benign (cannot invade) Expansile mass of poorly formed bone and fibroblasts |
|
|
What is Mazabraud syndrome? (Combination |
Fibrous dysplasia (usually polyostotic) plus soft tissue myxomas |
|
|
What is McCune Albright syndrome? |
Polycystic fibrous dysplasia plus cafe-au-lair skin pigmentations and endocrine abnormalities, especially precocious puberty |
|
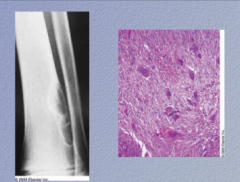
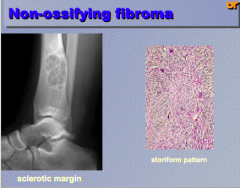
What is shown here?
What would you call it if it was bigger than 5cm? |
Fibrous cortical defect
Fibroma! |
|
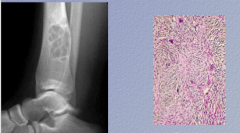
What is the disease? What is pattern on left and pattern on right? |
Woven pattern |
|
What is shown here? Describe. |

|
|
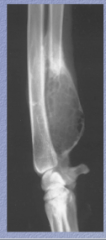
What is this? Filled with what? What are two complications? |

Not a neoplasm, probably developmental (USP6 protease excess) |
|
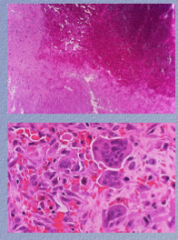
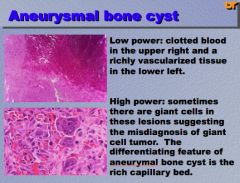
Condition? What do you see in the top?
Bottom? What cells are present? Is this misleading?
What is the DIFFERENTIATING FEATURE of this condition? |
Age, sex, location, radiographic diagnosis |

