![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
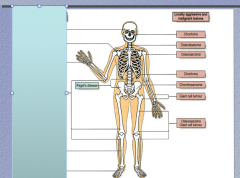
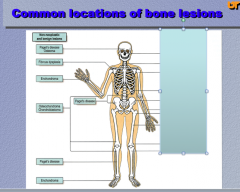
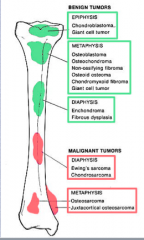
Identify the following non-neoplastic lesions:
Paget's disease, osteoma, fibrous dysplasia, enchondroma, osteochondroma, chondroblastoma
|
|
|
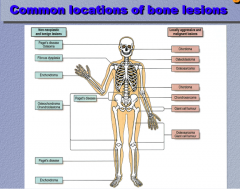
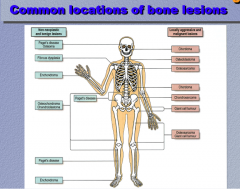
Identify the locations of the neoplastic conditions:
Osteoblastoma, chondroma, osteosarcoma, giant cell tumor |
|
|
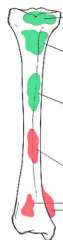
What benign tumors ar the epiphysis? |
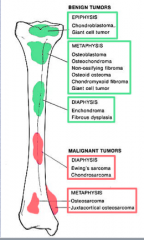
|
|
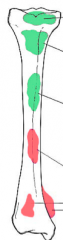
What benign tumors at the metaphysis?
|
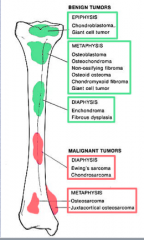
|
|
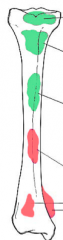
What benign tumors at diaphysis? |
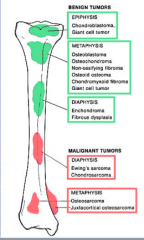
|
|
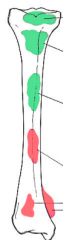
What malignant tumors at diaphysis? |
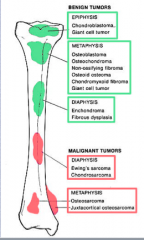
|
|
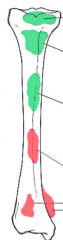
What malignant tumors at metaphysis? |
|
|
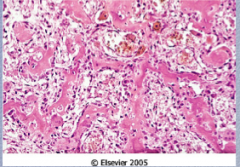
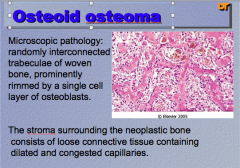
What condition shown here? Describe the microscopic pathology.
What does the stroma surrounding the neoplastic bone consist of? |
|
|
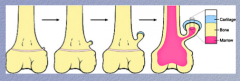
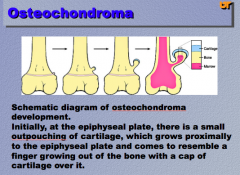
Osteochondroma:
Initially at the the epiphyseal plate, there is a small out pouching of ________, which grows proximally to the _________ and comes to resemble a finger growing out of the bone with a cap of cartilage over it. |
|
|
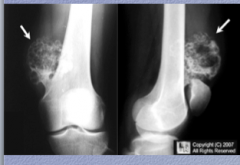
What is the condition? How do you know? |
|
|
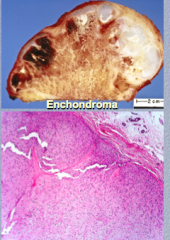
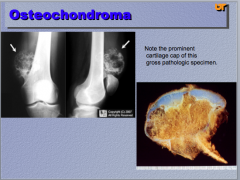
What do you notice (cap)? What does it look like?
You see numerous _______ closely packed to the periphery in the microscopic pathology. |
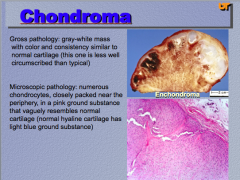
All vaguely resembles NORMAL cartilage! |
|
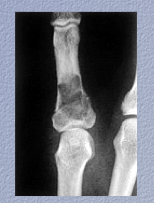
Disease?
Radiolucent nodule of __________ cartilage with scalloped endosteal surface. |
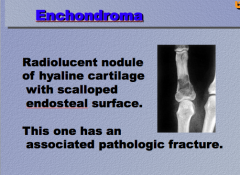
|
|
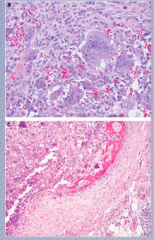
What do you see here? What type of cell is prominent? Activity of what? Formation what? What is the disease? |
|
|
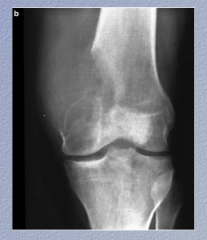
What is the neoplasm? Buzzword for the XR? What is it destroying? |
|
|
|
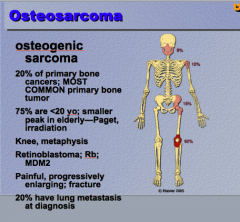
What is the most common primary bone tumor? What percent of primary bone cancers? What percent are less than 20 years old? Common two for this age group? What is most common location?
20% have what metastasis at diagnosis? |
|
|
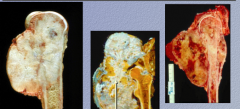
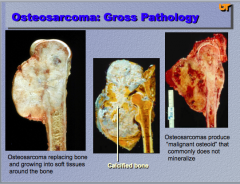
What is the neoplasm?
What does the arrow indicate? What do osteosarcomas produce that DOES NOT COMMONLY mineralize? |
|
|
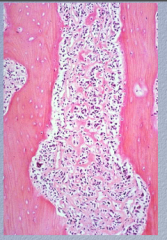
Neoplasm? When it invades the bone what does it normally form? What type of cells? WHAT IS DIAGNOSTIC OF THIS NEOPLASM? |
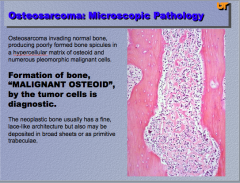
|
|
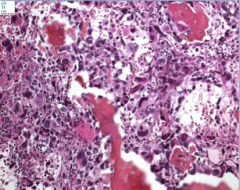
What is the neoplasm? Do you see any pattern here? What bizarre cells are common? What else common (think rapid division)? |
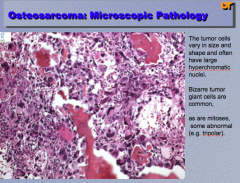
|
|
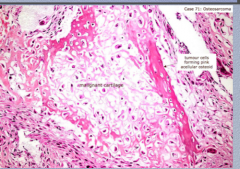
What is being made in this malignant sarcoma? |
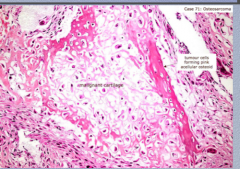
|
|
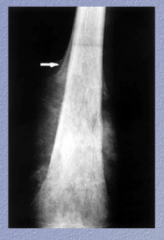
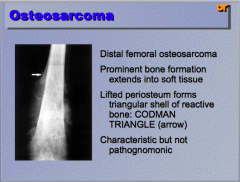
Neoplasm? What extends into soft tissue? What is the name for the structure the arrow is pointing to? Is this pathognomonic? |
|
|
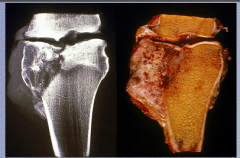
What type of neoplasm? Location? What is characteristic of malignant bone neoplasms with regard to joint space? |
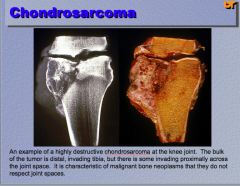
|
|
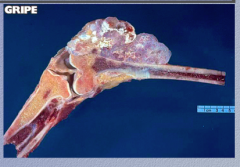
What type of neoplasm? |
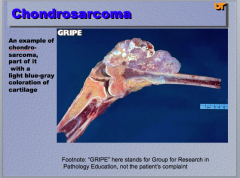
|
|
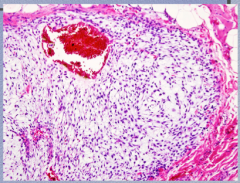
What type of neoplasm? What do the cells mimic and appear to float on?
Comment on size of nuclei, nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio, and mitotic figures (numbers of each) |
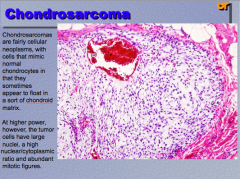
|
|
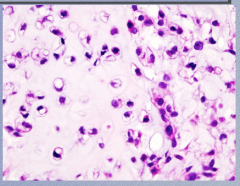
What type of neoplasm? What type of chondrocytes? |
Malignant chondrocytes in a chondrosarcoma |
|
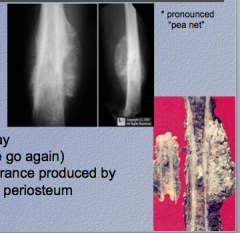
What type of tumor (fancy name and common name)? What is the characteristic appearance produced by layers of reactive periosteum and neoplasm? |

|
|
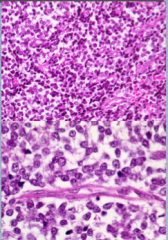
PNET:
Size, shape, color of cells, Many or few mitoses Glycogen rich cytoplasm may appear ______. Typically in _______ sheets of cells. May have prominent ________ in a geographic pattern. |
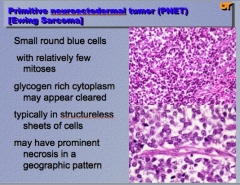
|
|
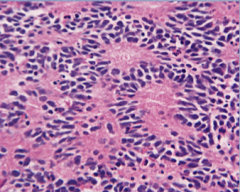
What is the neoplasm? What is the name of the rosettes? Which cells are tumor and which is the fibrillar material? What does this suggest? |
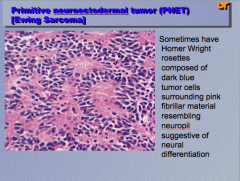
|
|
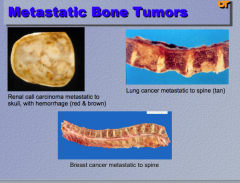
Common cancers to metastasize to bone? |
Renal, lung, breast |

