![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
353 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is DC offset? |
The offset of the wave from 0V
|
|
|
What are 3 ways analog and digital signals can be communicated? |
electrical conductors, optical fibre, air |
|
|
What is the traditional cable form for data communication? |
coaxial cable (coax) - generally made from copper |
|
|
What is the present-day standard cable form for Ethernet? |
Twisted pair |
|
|
What is the structure of coaxial cables? |
An inner conductor made of copper, an outer shield made of a copper mesh and/or tinfoil, plastic or foam insulation between inner core and outer shield, outside insulation |
|
|
What are important parts of a coax cable? |
The ratio of diameters (impedance), overall diameter (the bigger it is, the lower the losses) |
|
|
What do the two conductors in a coax cable do? |
Inner conductor is what the signal travels on, outer mesh is grounded. The outer mesh prevents the cable from radiating and shields it from interfering signals. |
|
|
What is the general structure of a twisted pair cable? |
Cable comes with one or more |
|
|
Why are the insulated copper wire pairs in a twisted pair cable twisted together? |
Each wire in a pair carries a complementary signal. Radiates little as signals cancel each other |
|
|
What is optical fibre made from? |
Glass or plastic |
|
|
What are benefits of using optical wire over other communication mediums? |
Cheap. Can be run for several km without amplifiers |
|
|
What are drawbacks of using optical wire over other communication mediums? |
More difficult to connect than copper wiring |
|
|
What is the general structure of optical fibre? |
An inner core, surrounded by an outer core, surrounded by insulation. |
|
|
What do the inner and outer cores of an optical fibre cable do? |
The outer core has a lower refractive index (i.e. light moves faster there) than the inner core. This means the light in the inner core is "trapped" by reflection/refraction. |
|
|
What is "graded refractive index" when referring to optical fibre? |
When the glass gets “faster” as the light moves away from the centre. When this happens, refraction is the means of transport. |
|
|
What is a multimode fibre? |
A fibre that we can send more than one light ray down a fibre by choosing different angles of incidence at the start. Usually often used for short distances only because it gets a bit difficult to keep the rays apart. Graded‐index fibre is best for this job |
|
|
Other than multimode fibres, what is another way to send more information in a fibre? |
send light in different colours (wavelength multiplexing) |
|
|
What is wavelength multiplexing? (optical fibre) |
Sending light through a fibre in different colours to send more information. |
|
|
What distance can optical fibres bridge without the need for repeaters? |
40km. Fibre repeaters are VERY expensive |
|
|
What are optical fibres used a lot for? |
Undersea cables and long distance overland because they're cheap. Usually come in pairs - one for each direction. |
|
|
What are radio signals commonly used for in recent times? |
Wi-fi, 3G/4G/LTE, Bluetooth, cellphones |
|
|
Received signal power drops to ... when the distance doubles? Why? |
a quarter |
|
|
Received signal voltage drops to ... when the |
a half |
|
|
How much smaller received signal can a typical radio system live with than the transmitted signal? |
10^11 times smaller |
|
|
How does wireless work? |
An antenna is a conductor that has electrons pumped in and out of it at one end with no connection at the other end. This means the conductor gets charged and discharged in rapid cycles. Thus we have an electric field that gets built up and collapses in cycles all the time.The electrons flowing in and out cause |
|
|
How fast do radio signals propagate? |
The speed of light. (300,000,000 m/s in free space) |
|
|
What is the wavelength of a signal? |
λ = cT where c = speed of light and T = cycle time. The wavelength is the distance the radio wave travels in one cycle. |
|
|
What is the frequency of a signal? |
f = 1/T. The cycles per second. |
|
|
What is the unit 'decibel's used for? |
Comparing voltage and power ratios. |
|
|
What is the decibel ratio formula for two voltage values? |
r (dB) = 20 log10(V1/V2) |
|
|
What is the decibel ratio formula for two power values? |
(dB) = 10 log10(P1/P2) |
|
|
A voltage ratio of 2:1 is approximately ...? |
6dB |
|
|
A power ratio of 2:1 is approximately ...? |
3dB |
|
|
Signal power is proportional to what voltage? |
Signal power is proportional to the square of the voltages. |
|
|
log y (x) = z |
x = y^z |
|
|
Just use the logarithm function you have and then divide by the logarithm of the base you want. |
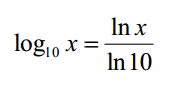
OK! |
|
|
y^a.y^b = y^(a+b) |
log y (y^a.y^b) = logy(y^a) + logy(y^b) |
|
|
logy(A/B) = ? |
logy(A/B) = logyA ‐ logyB |
|
|
logy (a^b) = ? |
b logy(a) |
|
|
X decibels in power ratio are X decibels in voltage ratio. Always! But: The power ratio (when not quoted in dB) is always the square of its corresponding voltage ratio |
kk |
|
|
How fast do signals in wire/cables propagate? |
Typically about 2/3rds of c |
|
|
How is signal lost in wire and fibre? |
Lost due to attenuation in the material (light or electrical power is converted into heat) |
|
|
What are geostationary satellites? |
Satellites that appear to be in the same spot in the sky 24hrs/day if viewed from earth |
|
|
What are Low/Medium Earth Orbit Satellites? |
LEO/MEO satellites are lower in the sky than geostationary satellites and don't appear to be in the same place. These can be used to cover more area but you need to track the satellite with steerable antenna to achieve large bandwidths |
|
|
What is the 'inclination' of LEO/MEO satellites? |
The angle between the equatorial plane and the orbital plane. Inclination determines highest/lowest latitude that the satellite can “cover” |
|
|
What is the 'footprint' of an LEO/MEO satellite? |
The area where the satellite is above the horizon |
|
|
What is a drawback of using satellites over cables/wire? |
Higher latency. Can be jammed easily unless spread‐spectrum technology is used |
|
|
What are some benefits of using satellites over cables/wire? |
Renting a transponder (satellite channel) can be much cheaper than running a cable over hundreds or thousands of km. Satellites don’t require landowner approval. Antennas can be used to “shape” footprints – deliver all your power into the area you want to cover |
|
|
What are shaped footprints (in terms of satellites)? |
Directional antennas (dishes) are used to spotlight a particular region of interest |
|
|
What is a 'one-to-one, simplex' communication channel? |
Only one way e.g. TV remote. No need to worry about receiver having to |
|
|
What is a 'one-to-one, full-duplex' communication channel? |
Both ways. Both parties can transmit and receive simultaneously. e.g. phone line, natural conversation |
|
|
What is a 'one‐to‐one, half‐duplex' communication channel? |
Only one party can transmit at any one time, parties must negotiate handover of channel control, stick to a time slot regime, or manage collisions. e.g. walkie talkies |
|
|
What is a 'one‐to‐many, simplex (broadcast channel)' communication channel? |
One transmitter, many receivers e.g. radio, TV |
|
|
What is a 'one-to-one, shared channel' communication channel? |
One party communicating with several others, one at a time. e.g. Example: GSM cellphones (base station & handsets) |
|
|
What is a 'many‐to‐many, shared channel' communication channel? |
Participants act as both transmitters and receivers. Only one transmitter can access the channel at a time – participants must negotiate channel access, manage collisions, or stick to a timing scheme. Not every receiver may be able to hear every transmitter. Example: 802.11 WiFi |
|
|
What are ways we can split a resource (fibre, radio spectrum block, cable), into several simplex or duplex channels? |
Lay separate cables or fibres |
|
|
What is frequency? |
Frequency is the number of oscillation cycles |
|
|
What is power? |
The power is always proportional to the square of a voltage. It’s measured in watts (W) |
|
|
What is the phase of a sine wave? |
The phase of a sine wave is a measure for how |
|
|
What is fourier analysis? |
Fourier analysis lets us describe any continuous real‐valued function as a sum / integral of sine and cosine functions of different frequency, amplitude or phase |
|
|
Transitions between 0 and 1 are not instantaneous, how can we make them faster? |
The higher the frequencies we can include, the faster the transitions become. |
|
|
What is amplitude? |
The amplitude is the “height” of the signal |
|
|
What limits the number of different bits |
The transition time between bits |
|
|
How can we increase the bits per second we can |
Increasing the number of frequencies we can include. Reduce the transition time between bits. |
|
|
What is bandwidth? |
The difference between the highest and lowest frequency a communication channel can carry |
|
|
What is the frequency band? |
We use the width of the frequency band to measure bandwidth - the difference between the highest and lowest frequency a communication channel can carry |
|
|
What is bandwidth proportional to? |
(potential) bit rate |
|
|
What is a baseband signal? |
The signal in the band when the lowest frequency is 0Hz |
|
|
What does modulation allow us to do? |
Shift a baseband signal into a frequency band whose lowest frequency is (usually much) larger than 0 Hz |
|
|
What is the power spectrum of a signal? |
When frequency (Hz) is the horizontal axis and power is the vertical axis (i.e. we are in the frequency domain). |
|
|
What can we gather from the power spectrum of a signal? |
We can obtain the bandwidth. The difference between the highest and lowest (significant) |
|
|
What is modulation? |
The term for shaping an analog signal waveform in order to transmit analog or digital information. |
|
|
What current technologies use modulation? |
Radio and modem communications. |
|
|
What are the three basic types of modulation? |
amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, and phase modulation |
|
|
What is amplitude modulation? |
When we vary the amplitude of a carrier signal depending on the amplitude of the modulating signal that carries the information to be transmitted - crude example: for a binary (on or off) modulating signal, turn carrier on or off (Morse code on radio works that way) |
|
|
What are amplitude modulation sidebands? |
The frequencies on either side of the carrier frequency. The sidebands are at fc‐fm and fc+fm, where fc is the carrier frequency and fm the modulating signal’s frequency. Total bandwidth occupied by the signal is 2fm |
|
|
What is frequency modulation? |
When we vary the frequency of a sinusoidal carrier signal with the amplitude of the modulating signal |
|
|
What is amplitude modulation known as in the discrete case? |
Amplitude shift keying (ASK) |
|
|
What is frequency modulation known as in the discrete case? |
Frequency shift keying (FSK) |
|
|
How does frequency modulation compare to amplitude modulation? |
More robust modulation scheme if used on its |
|
|
What is phase modulation? |
When we vary the phase of carrier signal to follow the amplitude of the modulating signal |
|
|
How does frequency modulation compare to phase modulation? |
PM looks very similar to FM in many respects. In the analog case, FM receivers can generally be used to receive PM transmissions and vice versa. |
|
|
What is phase modulation known as in the discrete case? |
Phase shift keying (PSK) |
|
|
What does combining AM and PM do? |
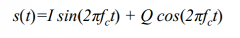
By choosing I and Q, we have states in a two‐dimensional state |
|
|
How can we combine AM and PM? |
Can modulate both amplitude and phase of a carrier signal by generating a linear combination of a sine and a cosine wave of the carrier frequency |
|
|
What is a constellation? |
A set of states in a two-dimensional state space |
|
|
What is BPSK? |
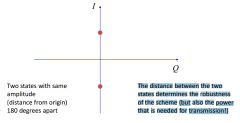
Binary phase shift keying. |
|
|
What is QPSK? |
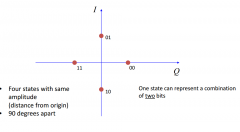
Quarternary phase shift keying. |
|
|
What is 16-QAM? |
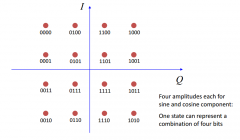
Quadrature AM |
|
|
What is gray coding? |
Look at the neighbouring constellation points in the 16‐QAM scheme. They all differ be exactly one bit. This is known as a Gray code. Using a Gray code means that if we end up decoding a |
|
|
What is a baud rate? |
The number of symbols (constellation points) we transmit per second. It is not normally the same as the bit rate, except when there are only two |
|
|
How may a signal lose amplitude? |
Through 'spreading', attenuation (light being absorbed by glass, heat coming off wire), distortion (some of its constituting frequency |
|
|
What is noise? |
Noise is a random signal that is added to |
|
|
What is white noise? |
Noise with a flat power spectrum. It often has |
|
|
What do we measure noise power in across a given bandwidth? |
In watts per hertz (W/Hz). |
|
|
What is additive white gaussian noise? |
(AWGN) Probability of an instantaneous noise amplitude falls off as amplitude grows. Actual received states looks like a “fuzzy cloud” around the true signal constellation point under AWGN (a bit like throwing darts at a target) |
|
|
What affects how much effect noise has? |
Two factors: |
|
|
What is the signal to noise ratio? |
(SNR) defines how close the detected signal |
|
|
How can we determine the area in which we can accommodate our constellation points? |
It is the square of the maximum sine and cosine amplitude we can transmit with (area of circle |
|
|
What is the Shannon Hartley capacity theorem for S much larger than N? |
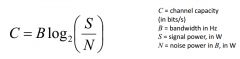
|
|
|
What is the Shannon-Hartley capacity theorem for S not much larger than N? |
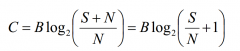
|
|
|
In what two contexts do we use error detection? |
When we can substitute the data (e.g. in photos we can do an interpolation), and when we can re-request the data from the transmitter |
|
|
What is ARQ? |
Automatic repeat request. When we re‐request the correct data from the transmitter. This |
|
|
What are some examples of extra information we send for error detection? |
Parity bits, checksums |
|
|
When is error correction used? |
When we are not able to substitute or re‐request data, or when re‐requesting data is not feasible due to the turnaround time, or not |
|
|
What are some examples of extra information we send for error correction? |
- Hamming codes |
|
|
What is the data we wish to transmit called? |
Payload data |
|
|
What is the parity bit? |
An additional bit to each byte of the payload data. You can have even or odd parity. |
|
|
What is even parity? |
the parity bit is set such that the total number of |
|
|
What is odd parity? |
the parity bit is set such that the total number of |
|
|
What are CRCs? |
Cyclic redundancy checksums. Based on modulo 2 division of polynomials. |
|
|
what are digests |
Digests are like checksums, except that we presume that we want to guard the data against “intelligent interference” (i.e., when someone is deliberately trying to modify our data in transit). The algorithms for digests are generally more complex from a computational point of view |
|
|
What is the phase of a signal? |
The initial angle of a sinusoidal function at its origin. |
|
|
What is fourier synthesis? |
Adding sine waves together with different amplitudes, frequencies, and phases. |
|
|
What does fourier analysis tell us about making a perfect square wave? |
We'd need an infinite number of sine functions with infinitely high frequencies. |
|
|
What is 'spreading'? |
A form of signal degradation where the signal loses amplitude |
|
|
What is 'attenuation'? |
A form of signal degradation where the signal loses amplitude in the medium it propagates in. e.g. due to conversion to heat in a wire, or the light being absorbed by the glass in fibre. |
|
|
What does it mean for a signal to get distorted? |
A form of signal degradation where some of the signal's constituting frequency components (Fourier analysis) get attenuated by different amounts or propagate at different speeds or on different paths. Filtering can sometimes reverse this effect. |
|
|
What does it mean for a signal to get corrupted? |
A form of signal degradation where the signal is corrupted by additive noise on the medium it is propagating in. |
|
|
How can we determine the power per symbol in a constellation diagram? |
Total power = area of the circle around the origin going through the furthest constellation point around the origin. Divide the total power by the number of constellation points. |
|
|
When can we know when we'll routinely get symbol errors? |
When the power per symbol is lower than the noise power. |
|
|
How can we avoid routinely getting symbol errors? |
Choose a number of constellation points such that the noise power does not exceed the power per symbol within a given radius (amplitude) around the origin. |
|
|
How many parity bits are needed to detect a single data bit error? |
log2(number of data bits) + 1 |
|
|
What is the basic idea behind network coding? |
Don't transmit original set of messages if messages could get lost / corrupted. Instead: Form linear combinations of multiple messages from the set and transmit these. |
|
|
What is manchester coding? |
Code 0's and 1's as transitions from high to low and low to high respectively. |
|
|
What is bit stuffing? |
Insert a 0 after 5 consecutive 1's to keep clock synchronized. On the receiver end, remove the 0 after 5 consecutive 1's. |
|
|
What is differential manchester encoding? |
Code 0 as transition from opposite level to current level and 1 as transition from current level to opposite level. |
|
|
What are benefits of manchester encoding? |
No need for bit-stuffing. Easy clocking |
|
|
What are drawbacks of manchester encoding? |
signaling rate is twice the raw data rate, not very bandwidth‐friendly! |
|
|
What is the basic idea behind framing? |
Use bit-stuffing and mark the start and end of each frame by a byte 01111110 (six 1‐bits in series). Remember with bit stuffing we can only get 5 consecutive 1's so this is noticeable. Use a CRC checksum to differentiate noise from frames. |
|
|
What is the general structure of an ethernet frame? |
Marker > bit-stuffed payload > 4 byte CRC > Marker |
|
|
What are hamming codes? |
Those horrible multiple-parity bit things with parity matrices. ew. |
|
|
What is NZRI? |
0 is a change in level. 1 is no change in level. |
|
|
What is adaptive huffman encoding? |
When you don't know the probabilities, start with using a block code (all symbols have equal probability. Send a symbol and compute source statistics for all symbols send so far at the source and receiver. Generate huffman code for the new source probabilities at both ends. Use this code for the next symbol. Repeat. |
|
|
What is the input and output of LZ78 encoding? |
Input: String of bits. Output: an encoded tree (the vocabulary) |
|
|
What is the basic idea of LZ78 encoding? |
Series of parsing steps. Each step describes a substring as a reference to an earlier substring and a one bit innovation. |
|
|
What is LZ78 compression used in? |
ZIP files, compressing web pages on web servers before being transmitted to the browser. |
|
|
What are some facts about LZ78 compression? |
Cannot compress every string. Best at compressing long strings which may contain many repetitions of long substrings. |
|
|
What is IP? |
An unreliable datagram protocol where congestion or transmission errors cause lost packets. Multiple routes may lead to out-of-order delivery. |
|
|
What is UDP? |
An unreliable datagram protocol. Congestion or transmission errors may cause lost packets. Multiple route may cause out-of-order delivery. If senders send to fast, routers or receivers cannot keep up. |
|
|
What are found in UDP headers? |
Port numbers - used to find TCBs at each end. Source port is optional as there is no notion of a connection. Length - length in bytes of UDP header and data. Checksum - checksum. |
|
|
What does a day in the life of a UDP packet look like? |
User A: listen (portA) User B: send (addressA, portA, dataB) User A: receive (dataB) User A: listen (portA) |
|
|
What must UDP-applications include? |
Own timeout and own error recovery. |
|
|
What are some important UDP applications? |
DHCP, DNS, RIP, SNMP. Which can all survive lost packets. Each listen on a well-known port number. |
|
|
What is TCP? |
A protocol that fixes the issues of un-ordered data, and congestion/transmission issues. It does this using flow-control and retransmission after errors. |
|
|
What are the two approaches to flow-control and which does TCP use? |
Sliding Window and Rate Control. TCP uses sliding window. |
|
|
What is the Rate Control? |
An approach to flow-control where the sender determines the maximum safe sending rate and never exceeds it. |
|
|
What is the Sliding Window? |
An approach to flow-control where the sender sends up to a window full of data, but then pauses for acknowledgement. Window size is adjusted dynamically to match network capacity. A missing acknowledgement triggers a retransmission. |
|
|
Why is the Sliding Window better than Rate Control? |
The Sliding Window approach works over an enormous range of speeds. Rate control works best in fixed speed networks. Sliding window works reasonably well as router load increases towards 100% (sharing between millions of TCP sessions is quite fair). Retransmission fits well into Sliding window. Rate control would have to break step to resend data. |
|
|
What are the three main phases of TCP connection? |
Establishment, data transfer, disconnection. |
|
|
How does a TCP connection initiate? |
The receiver has to be willing to accept incoming connections, while the sender has to choose to start. The listener listens to a specific port number which serves as a meeting point. |
|
|
What is a layer 4 address? |
IP address + port number |
|
|
How is a TCP connection established? |
Initiator sends a SYN. Listener returns with a SYN and ACK. Initiator returns with an ACK and determines that the connection is ok. When the listener receives the ACK, it too determines that the connection is ok. |
|
|
How is a TCP connection disconnected? |
A sends a FIN. B sends an ACK and FIN. A deems connection closed and sends an ACK. B deems connection closed. |
|
|
What's the deal with TCB's and TCP? |
During connection establishment, each end creates a TCB data structure which includes: local and remote port numbers for this connection, current send and receive window sizes, pointers into the send and receive buffers, status of send and receive sequence numbers. |
|
|
What does a TCB do? |
Links the user program at each end to the TCP process. |
|
|
What is the delay-bandwidth product? |
(bandwidth x RTT) / 2 |
|
|
What is the rough TCP window size? |
bandwidth x RTT |
|
|
What are some modern TCP techniques to avoid congestion? |
Slow start - start small and gently expand window. When duplicate ACKs indicate that later segments were lost, limit number of retransmissions. Fast recovery - after 3 duplicate ACKs, retransmit once and wait. If still no ACK revert to slow start. |
|
|
What does a day in the life of a TCP session look like? |
User A: Listen (portA) User B: (AddressA, portA) SYN/ACK exchange Data transfer phase: - User A: Send (dataA) - User B: Receive (dataA) - User B: Send (dataB) - User A: Receive (dataB) - repeat as required User B: close FIN/ACK exchange User A: Listen (portA) |
|
|
What is TLS? |
Transport Layer Security. It protects TCP sessions. Earlier versions known as SSL. |
|
|
How does TLS work? |
Uses a handshake procedure to negotiate crypto algorithm. The server presents a certificate to the client, including its public key. The certificate is cryptographically signed by a trusted certificate authority using its public key. After doing that, no third party can intercept or inject traffic. |
|
|
What is RTP? |
Real-time transport protocol. For audio/video streams. RTP data packets run over UDP on an even numbered port (usually above 16384). |
|
|
What is RTSP? |
RT Streaming Protocol is layered ontop of RTP. |
|
|
What is RTCP? |
RT Control Protocol runs over UDP on the next highest (odd-numbered) port number. |
|
|
What does RTP provide? |
Payload type identification. Sequence numbering. Time stamping for synchronisation and jitter management. Delivery monitoring. Because of unreliability, video/audio codecs must allow for this. |
|
|
What are the transmission modes? |
Parallel (many wires) or serial (single wire). Synchronous: uses a continuous clock. Isochronous: inserts gaps to match transmission rates |
|
|
What is in a TCP header? |
Sequence number - sequence number of first data byte in this segment (initialised in the SYN packet). Acknowledgement number - has the next sequence number the sender is expecting. Data offset, URG(urgent bit), ACK, PSH (push bit - kick received data to user),RST (reset bit - emergency disconnect), SYN, FIN, Window, Checksum, Urgent pointer, Options. |
|
|
What are some facts about the USB interface? |
Can support up to 127 connected devices. Provides power to devices with two power conductors and one twisted pair. Offers serial data transmission up to 400Mb/s. Uses differential NZRI signalling. |
|
|
What are the different types of USB connectors? |
Type-A (most common), Mini-A, Micro-A, Type-B, Mini-B, Micro-B. |
|
|
How many insert/remove cycles are Type-A usb connectors designed for? |
1,500. |
|
|
What is multiplexing? |
Carrying several different connections over a common link. Making one cable do the work of several different cables. |
|
|
Why is multiplexing useful? |
Long cables are expensive so they can be shared. |
|
|
What is Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM)? |
Streams take regular turns at being transmitted. Substreams from each source are grouped into frames and transmitted independently. (Have MUXes at each end). If a stream has nothing to send, its timeslot is wasted. |
|
|
What is statistical multiplexing? |
Similar to TDM but doesn't use regular time-slots. If A has more to send than B, it will use more of the available time than B. If a stream has nothing to send, another stream will use the channel. |
|
|
What needs to be done/considered when implementing/using statistical multiplexing? |
All streams need to get a fair share when load is heavy. Receiver must be able to identify incoming frames since there is no fixed time slot. |
|
|
How does multiplexing work with Radio Frequency signals? |
A combined signal consisting of frequencies from each channel (which have different bandwidths) is sent. A filter at the receiver end filters the signals out from each other. |
|
|
How does multiplexing with optical (light-wave) signals work? |
Wave division (WDM). Light consisting of multiple wavelengths is sent down the fibre and a prism is used at the receiver end to separate them out. Prism also can be used to combine them at the sender's end. |
|
|
What is flow control? |
Flow control manages the flow of data so that the sender doesn't send too fast for the receiver. Messages are broken into frames or packets. Flow control defines "the way frames are sent, tracked and controlled". |
|
|
What is the signalling method of Flow Control? |
The receiver signals the sender when it's ready to receive, or its buffer is getting full and needs to tell sender to stop sending. |
|
|
What is the "stop and wait" method of flow control? |
Send a frame and wait for an ACK. If you get a NAK back, send again and again until you get an ACK. Receiver receives frame and checks for errors. If there are errors, send NAK. Otherwise send ACK. No way to handle lost frames (No NAK or ACK). |
|
|
How can we calculate a protocol efficiency/effective data rate? |
Signal velocity in wire or fibre is 2/3rds speed of light (200,000,000m/s). Assume frame size is 1500Bytes = 1500x8 = 12000bits. Assume transmission rate is 10Mb/s = 10^7b/s. A frame would take 12000/10^7 = 1.2ms to output on the wire. Assume ACK is a 64byte frame -> 0.05ms to output. Auckland-Hamilton = 120km = 120,000m. 120,000/200,000,000 = 0.6ms. To send a frame and receive an ACK it takes 1.2 + 0.6 + 0.05 + 0.6 = 2.45ms. 12000/0.00245 = 4.9Mb/s = effective bit rate.
|
|
|
What is the idea behind the Sliding Window? |
Have i frames on the wire at any one time where i is the window size. Each frame has a sequence number. Window does not move until earliest frame has been ACK'ed. Then it slides down one place. |
|
|
If sequence numbers fit in a K-bit field, what is the maximum number of frames we can fit in the window? |
2^k. |
|
|
What is the 'bus' LAN topology? |
Each host shares the link by taking turns. |
|
|
What is the 'ring' LAN topology? |
access is controlled by passing a token around. |
|
|
What is the 'star' LAN topology? |
Each host is wired back to a hub. |
|
|
What type of LAN topology is Ethernet? |
Star |
|
|
What are the layers of LAN? |
Layer 1: physical layer Layer 2: link layer, where hosts talk to each other. Protocols here send frames (packets) to other hosts and receive frames in response. Layer 3: network layer. Used to pass packets between LANs |
|
|
What are the sublayers of the link layer? |
LLC - logical link control 802.2 MAC - medium access control 802.3 |
|
|
How is MAC different from multiplexing? |
MAC allows each sender full access to a channel, one at a time. Multiplexing shares Layer 1 channel between multiple pairs of senders and receivers. |
|
|
What is the Aloha protocol? |
Any host can broadcast messages to the Menehune (central station) at any time. If message is received correctly, the Menehune ACKs it on a different frequency. If two host transmissions overlap and interfere, the message is lost. If a message is not ACKed the host assumes it is lost, waits a random time, and resends. |
|
|
What is a downside of the Aloha protocol? |
Not an efficient use of the medium. |
|
|
What does CSMA stand for? |
Carrier Sense Multiple Access. |
|
|
How does CSMA work? |
Its like Aloha but listens to medium for any activity. If no activity, transmit, otherwise wait. Can still get collisions but there are ways to reduce them - slot time, random choice using probability of whether to transmit or wait for next slot. |
|
|
How does collision detection work in CSMA? (CSMA/CD) |
Start transmitting at any time but watch medium for collision. When collision is detected, stop transmitting and send jam signal. |
|
|
The minimum frame size for ethernet must...? |
Must be big enough to include the header and the FCS (frame check sequence). Must also be big enough to allow reliable collision detection - the collision signal must arrive before the frame has been completely transmitted. |
|
|
Why do we have a maximum frame size for ethernet? |
To stop a host from monopolising a medium. |
|
|
The gap sizes between ethernet frames must...? |
enough to ensure the electronics can switch from send to receive. It is specified as 96 bit periods. |
|
|
How do we calculate the time it takes for a collision signal to come back? |
T = 2 x (cable length) / (speed of signal) |
|
|
What is the minimum frame size for ethernet? |
Packet must take at least T = time it takes for a signal to come back. Multiply this by the transmission rate to get the minimum frame size. |
|
|
What are the different 10Mb/s physical implementations of ethernet? |
10Base5 - Thick coax 10Base2 - Thin coax 10BaseT - UTP (unshielded twisted pair) |
|
|
What is the max UTP cable length? |
100 metres |
|
|
What is the size of the collision domain for 10Mb/s ethernet? |
5 x 500m segments. |
|
|
What are some details about 100BaseTX ethernet? |
"Fast Ethernet". 100Mb/s. Can't use Manchester encoding as there is too much interference. Uses 4B/5B block encoding for each nibble. Uses MLT-3 signalling - multilevel line transmission. |
|
|
What is MLT-3 signalling? |
Multilevel line transmission - three signal levels -1, 0 and 1. For a 1-bit progress to the next state. For a 0 bit, maintain the same state. |
|
|
What are benefits of MLT-3 signalling? |
Uses 25% of max frequency compared to Manchester encoding. Works well over UTP. |
|
|
What is 100BaseFX and some facts about it? |
100Mb/s on multi-mode or single-mode FIBREEEE. Segment length of 412m if collisions can occur, 2km in full duplex. Uses 4B/5B encoding. Uses NRZI signaling instead of MLT-3. |
|
|
What is the collision domain for 100Mb/s or 100BaseTX? |
100m |
|
|
What is 1000BaseT and 1000BaseX? |
1000BaseT = Gigabit ethernet with a twisted pair. 1000BaseX = Gigabit ethernet with fibre or coax cable. Collisions are possible on both. |
|
|
What is the result of collisions being possible on gigabit ethernet? |
We need to use a longer minimum frame to keep the maximum segment length of 100m. Do this by padding shorter packets up to 4096 bits. |
|
|
What is a 'burst frame'? |
Sending a group of packets back to back as only the first packet needs to be 4096 bits long. |
|
|
What are some facts about 1000BaseX? |
It is gigabit ethernet on fibre or coax cable. Uses GMII. Has an 8-bit wide datapath and transmits 1bit (on all 8 lines) every 8 ns. Uses 8B/10B block encoding. |
|
|
What are some facts about 1000BaseT? |
Gigabit ethernet over category 5 UTP. Uses 4 twisted pairs to carry 250Mb/s each. Much harder for UTP than fibre because of its high signal frequencies. Does NOT support half-duplex. Full-duplex carried over each pair at the same time using hybrids to combine/separate signals. |
|
|
What is FHSS? |
Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum. Use a set of frequencies (channels) and hop between them in a pseudo random sequence. |
|
|
How many channels and hopping sequences does 802.11 use for FHSS? |
79 channels and 22 hopping sequences. |
|
|
What is DSSS? |
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum. For each transmitted bit, send a chip i.e. an n-bit pseudo-random sequence. |
|
|
How are collisions dealt with differently in 802.11 and ethernet? |
Ethernet works by collision detection and retrial. 802.11 works by collision avoidance - wait until channel is empty and send out a brief "im coming" signal first. |
|
|
What is the hidden stations RTS/CTS protocol? |
An access point can hear all base stations, but base stations can't hear each other so can't avoid collisions. Base station can send an RTS packet to which the access point replies with a CTS packet. The conflicting base stations can hear the CTS packet so stay quiet while the other base station can send without collisions. |
|
|
What's the difference between AP and Ad-hoc mode topologies? |
AP (Access point) or "Infrastructure mode" has an Access point that many user nodes connect to. Ad hoc mode (no AP) just has user nodes connecting to each other which is an "operational nightmare" - Neville 2014. |
|
|
What happens when you have multiple access points? |
Multiple AP's connect to form a single network. AP's must relay packets to one another. |
|
|
What happens when A can see the Access Point but A can't see B? |
The access point must relay packets. Indirect relay is when A relays through two or more access points to get to B. |
|
|
To allow for AP relaying, 802.11 frames have four address fields selected from which 5 address fields? |
1. Destination address (DA) 2. Source address (SA) 3. Sending wireless access point address 4. receiving wireless access point address 5. wireless network identifier (SSID) |
|
|
What is WEP? |
Wired equivalent privacy. a simple authentication/encryption scheme using RC4, a 40-bit security key and a 24-bit initialisation vector. Each message uses a different initialisation vector. |
|
|
What are some issues with WEP? |
It was broken in 2001. The initialisation vector sequence may be repeated often in heavy traffic and 40 bits is a short key. |
|
|
What is WPA? |
A 'quick fix' for WEP in 2003. Wi-Fi Protected Access. Also based on RC4. WPA2 is better. |
|
|
Web-based authorisation pages offer NO security to a wireless user. |
COOL BRah |
|
|
What does a repeater do? |
Reshapes, amplifies and sends on the signal. BONUS FACT: an ethernet repeater works in both directions! |
|
|
What does a hub do? |
Simply is a multi-port repeater. A signal coming in on any port is reshaped, amplified, and sent out on all other ports. |
|
|
What are some limits on hubs and repeaters? |
They both add slightly to the transmission delay. They are essentially cable extenders. In ethernet they form part of the collision domain calculation. |
|
|
What are disadvantages of hubs and repeaters? |
They don't avoid ethernet contention/saturation problems on shared LANs. |
|
|
What are advantages of hubs and repeaters? |
Nothing to configure, cheap, reliable, regenerate degraded signals |
|
|
What are bridges? |
A bridge pretends to be the destination on one network, and the source on another. Used when using a repeater or hub would exceed the collision domain limit. Any station that sees the packet sent from the bridge, will not be able to tell that it came from a bridge. |
|
|
How does a bridge know where/when to send a packet? |
Bridges know where every other ethernet station is and only sends packets in that direction. Each bridge needs a switching table. |
|
|
How do bridges learn? |
When bridges start up the switching table is empty. For each packet it sees on its ports, it adds entries of source addresses to its switching table. The bridge floods until it gets enough information. |
|
|
What is a problem we can encounter using multiple bridges? |
We may get cycles that never end. |
|
|
How do bridges avoid loops/bridges? |
They use spanning trees. Bridges send management packets to each other. One bridge is elected as the root. A designated bridge is elected and will send frames towards the root, based on distance from the root. Spanning tree does not optimise paths. Spanning tree is reconfigured upon a bridge failure. |
|
|
What are some disadvantages of bridges? |
Generally hard to operate and manage a large bridged network. Allow 'broadcast storms' despite using spanning trees. Suit old fashioned shared cable rather than star cable. Don't cure ethernet saturation on busy LANs |
|
|
What are some advantages of bridges? |
Fairly cheap and reliable. Self configuring. Overcome distance limit. Regenerate degraded frames. |
|
|
What is a switch? |
Multi-port bridge. |
|
|
What are some advantages of switches? |
Self configuring. Reliable. Overcome distance limit, regenerate degraded frames. Avoid ethernet contention/saturation problems on shared LANs or simple hubs. Suits modern UTP5 (modern) cabling. |
|
|
What is a disadvantage of switches? |
Requires systematic design and cable management. |
|
|
What are virtual LANs? (VLANs) |
Technique for mixing two or more usages of ethernet on one physical infrastructure (cables and switches). TWO LANS ON ONE SET OF CABLES AND SWITCHES |
|
|
When should VLANs be used? |
- When there are two populations of users mixed in the same area and there are serious privacy / security concerns. If one or both are generating a lot of traffic. - If you need to 'stretch' a LAN between buildings and theres no spare equipment - WILL IT ALWAYS BE AN ADVANTAGE? STILL SHARING SAME HARDWARE |
|
|
What are some routing problems? |
Real networks are massive and constantly changing. "Best" can mean a lot of things (cheapest, fastest, etc.) |
|
|
What are the two major approaches to dynamic routing? |
Distance vector routing - router informs neighbours of its best paths. Each router calculates best path for itself based on neighbours paths. Link state routing - router exchanges link status info with its neighbours. Each router relies on accuracy of its neighbours status info in calculating best paths through the whole map. |
|
|
What is distance vector routing? |
A form of dynamica routing where each router informs neighbours of its best paths. Each router calculates best path for itself based on neighbours paths. |
|
|
What is link state routing? |
A form of dynamic routing where each router exchanges link status info with its neighbours. Each router relies on accuracy of its neighbours status info in calculating best paths through the whole map. |
|
|
What algorithm is used for distance vector routing? |
Bellman-Ford algorithm |
|
|
Describe the basic idea of the Bellman-Ford algorithm. (High level details, not implementation details) |
Router computes a table of its distance to each other router and sends the table to its neighbours. Recomputes its own table from the info it receives from its neighbours. |
|
|
What is an issue with the Bellman-Ford algorithm? |
Sending complete tables of distances does not scale well. |
|
|
What algorithm is used for link state routing? |
Dijkstra's algorithm |
|
|
What is the Bellman-Ford algorithm? (implementation details) |
To calculate the distance from R1 to all Rn: Initialise all distances D(R1, Rn) to infinity except D(R1, R1) = 0.. For each edge Rx --> Ry in the graph: if D(R1, Ry) > D(R1, Rx) + 1 then D(R1, Ry) := D(R1, Rx) + 1. NOTE: the +1 can be +weighting of edge. W(x,y) <0 allowed but can lead to cycles. |
|
|
What is the dijkstra algorithm (implementation details)? |
Initialise each distance D(R1, Rn) as infinity and tentative except D(R1, R1) = 0 and marked as final. For each edge Rx --> Ry: D(R1, Ry) := D(R1, Rx) + W(x,y). |
|
|
What are the differences between link state routing and distance vector routing? |
Link state processes many fewer edges than the Bellman-Ford algorithm since once a distance is final, that node is no longer considered. |
|
|
What are 3 routing protocols we should know about? |
RIP, OSPF, BGP |
|
|
What does RIP stand for? |
Routing information protocol not Rest In Peace lol |
|
|
What is IGP? |
Interior Gateway Protocol. Any site-wide routing protocol used within a campus or company network or within a single ISPs network. |
|
|
What is EGP? |
Exterior Gateway Protocol. Any wide-area routing protocol used to interconnect sites and ISPs. Sometimes known as IDR (inter-domain routing). |
|
|
Is RIP an IGP or EGP? |
IGP yo |
|
|
Is OSPF an IGP or EGP? |
IGP yo |
|
|
Is BGP an IGP or EGP? |
EGP yo |
|
|
Does RIP use distance vector routing or link state routing? |
Distance vector routing |
|
|
What number does RIP use as a distance of infinity and why? |
16. Real networks shouldn't be designed so that any normal path exceeds 16 hops. |
|
|
What is in RIP messages? |
Command (request or response). Route tag to say if route is within the RIP domain or outside it (wide area route). Address and mask. Next hop address (0 means default route via current router). Metric. |
|
|
How does RIP operate? |
Each router sends its full DV in one or more response messages on startup, every 30 seconds, on request, and whenever something changes. Each router recalculates its DV whenever it receives a response using Bellman-Ford algorithm. |
|
|
What are some interesting things to note about RIP? |
It doesn't work well in large, complex networks. RIP messages are noisy with lots of unused bits. |
|
|
What does OSPF stand for? |
Open Shortest Path First |
|
|
What is OSPF? |
A common Internet LS protocol for IGP use. Uses dijkstra's algorithm. |
|
|
What are the OSPF message types? |
1. Hello (discover / maintain neighbours) 2. Database description (summarise database contents) 3. Link state request (request database download) 4. Link state update (send database update) 5. Link state ACK (acknowledge an update) |
|
|
How does OSPF work? |
Each router sends its LSAs in one or more Link State Update messages - when timer expires, whenever an LSA changes, whenever an LS request message is received. Each router recalculates its LSAs whenever an LSU response is received (including running dijkstra's algorithm) |
|
|
What does BGP4 stand for? |
Border Gateway Protocol v4. |
|
|
What is BGP4? |
The only external gateway protocol in use today. It is a modified distance vector protocol and provides routing between autonomous systems which are networks running their own IGP internally. |
|
|
What are the BGP4 message types? |
Open - Sent when a link to a neighbour BGP speaker comes up Update - routing information Notification - sent when a link to a neighbour BGP speaker is intentionally closed. Keepalive |
|
|
What are two application architectures we should know of? |
Peer to peer, client-server |
|
|
What is meant by 'self-scalability' when referring to p2p architectures? |
New peers bring new service capacity as well as new service demands. |
|
|
What are two ways processes communicate? |
Inter-process communication and messages. Inter-process communication is when the two processes are within the same host. |
|
|
What is the difference between a client process and a server process? |
Client process: process that initiates communication. Server process: process that waits to be contacted |
|
|
What is a socket? |
Processes send/receive messages to/from its socket. |
|
|
What does a process identifier consist of? |
IP address and port number |
|
|
What does an application layer protocol define? |
Types of messages, message syntax, message semantics, rules for when and how processes send and respond to messages. |
|
|
What transport service does an app need? |
data integrity, timing, throughput, security |
|
|
What type of application uses the SMTP application layer protocol and what is the underlying transport protocol? |
Email. TCP |
|
|
What type of application uses the Telnet application layer protocol and what is the underlying transport protocol? |
Remote terminal access. TCP |
|
|
What application layer protocol(s) is used for streaming multimedia and what is the underlying transport protocol(s)? |
HTTP (youtube) or RTP. TCP or UDP. |
|
|
What application layer protocol does internet telephony use and what is the underlying transport protocol? |
SIP, RTP, proprietary (e.g. Skype). UDP or TCP |
|
|
What does SSL provide? |
TCP and UDP offer no security. Plain text passwords passed around. SSL provides an encrypted TCP connection, data integrity, and end-point authentication. SSL is at the application layer. |
|
|
What does it mean by HTTP being a 'stateless' protocol? |
Server maintains no information about past client requests. |
|
|
What does 'non-persistent' HTTP mean? |
At most one object is sent over TCP connection, the connection is then closed. Downloading multiple objects requires multiple connections. |
|
|
What does persistent HTTP mean? |
Multiple objects can be sent over a single TCP connection. |
|
|
What is the definition of RTT? |
Round trip time: time it takes for a small packet to travel from client to server and back. |
|
|
What is the HTTP response time in terms of RTT's? |
One RTT to initiate TCP connection. One RTT for request and first few bytes of HTTP response to return. File transmission time (not in terms of RTT). Non-persistent HTTP response time: 2RTT + file transmission time |
|
|
What are some issues/outcomes with non-persistent HTTP? |
Requires two RTT per object. OS overhead for each TCP connection. Browsers often open parallel TCP connections to fetch referenced objects. |
|
|
What are some issues/outcomes with persistent HTTP? |
Server leaves connection open after sending response. Subsequent HTTP messages between same client/server send over open connection. Client sends request as soon as it encounters a referenced object. As little as one RTT for all the referenced objects. |
|
|
What are the types of HTTP messages? |
Request and response (OMG REALLY??) |
|
|
In an HTTP request message, what indicates the end of the header lines? |
\r\n \n = line-feed |
|
|
Where in an HTTP request message is the request line? |
The very beginning before the header lines. |
|
|
How can we upload form input? |
POST method. Input is uploaded to server in entity body. OR URL method. Uses the GET method and input is uploaded in URL field of request line |
|
|
What HTTP methods were in the HTTP/1.0 version? |
GET, POST, HEAD |
|
|
What HTTP methods are in the HTTP/1.1 version? |
GET, POST, HEAD, PUT, DELETE |
|
|
Where is the status line located in a HTTP response message? |
At the very beginning. |
|
|
What separates the header from the body in an HTTP response message? |
\r\n \r = carriage return \n = line-feed |
|
|
What are the HTTP response status codes and what do each mean? |
200 - OK 301 - moved permanently- new location later in the message 304 - not modified 400 - Bad request 404 - Not found 505 - HTTP version not supported |
|
|
What can cookies be used for? |
Shopping carts, authorization, recommendations, user session state |
|
|
What is a conditional-get? |
When you send a "If-modified-since" HTTP message specifying the date of the copy you have in your cache. The server responds with a 304: not modified or with an updated copy. |
|
|
What is FTP? |
F da police. Nah tricks, File Transfer Protocol. Transfer file to/from remote host. |
|
|
Is the remote host the client or the server in FTP? |
Server - the client initiates the transfer. |
|
|
What port number is the FTP server? |
21 |
|
|
Explain the difference between the control and data connections in FTP plz |
Control connection: FTP client contacts FTP server over port 21 and browses the remote directory. The client sends commands over this connection. Data connection: Upon receiving a file transfer command the server opens a second TCP connection (data connection) to the client. After transferring one file over this connection, the server closes the data connection. |
|
|
What is the FTP return code for "Username OK, password required"? |
331 |
|
|
What is the FTP return code for "data connection already open; transfer starting"? |
125 |
|
|
What is the FTP return code for "can't open data connection"? |
425 |
|
|
What is the FTP return code for "error writing file"? |
452 |
|
|
What are the three major components of electronic mail? |
- user agents - mail servers - simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP) |
|
|
What does SMTP stand for? |
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol |
|
|
What is a "user agent" when talking about electronic mail? |
The "mail reader". E.g. Outlook, Thunderbird etc. |
|
|
What are the components of a mail server? |
Message queue - outgoing messages Mailbox - contains incoming messages for user SMTP - between mail servers to send emails |
|
|
What port does SMTP electronic mail use? |
Port 25 |
|
|
What format are commands in for electronic mail/SMTP? |
ASCII text |
|
|
What format are the responses for electronic mail/SMTP? |
Status code and phrase. |
|
|
How many bit ASCII must messages be in for SMTP? |
7-bit ASCII |
|
|
What type of connections does SMTP use? |
persistent connections |
|
|
How does an SMTP server identify the end of a message? |
CRLF (carriage return, line-feed) |
|
|
How does SMTP compare to HTTP? |
SMTP: push. HTTP: pull. Both have ASCII command/response interaction and status codes. In HTTP each object is encapsulated in its own response message. In SMTP multiple objects are sent in a multipart message. |
|
|
What is the difference between SMTP and a mail access protocol? |
SMTP is involved with the delivery and storage to a receiver's server whereas the mail access protocol is concerned with the retrieval of the mail from the server. |
|
|
What are some different Mail Access Protocols? |
POP (post office protocol) - authorisation and download IMAP (internet mail access protocol) - more features, including manipulation of messages on server HTTP - gmail, hotmail etc. |
|
|
In POP3 what are the client commands available in the authorisation phase? |
user & pass - for declaration of username and password to server. e.g. user bob |
|
|
In POP3 what are the server responses used in the authorisation phase? |
+OK & -ERR |
|
|
In POP3 what are the client commands available in the Transaction phase? |
list: list message numbers retr: retrieve messages by number dele: delete quit |
|
|
In POP3 what does download and delete mode mean? |
Once a message is downloaded, it is deleted. You cannot re-read the downloaded message if you change clients. |
|
|
What is the idea behind IMAP? |
Keeps all messages in one place: the server and allows users to organise into folders. Keeps user state across sessions. |
|
|
POP3 is stateless across user sessions. What does this mean? |
You can't organise messages into folders? I think? |
|
|
How many root name servers are there worldwide? |
13 |
|
|
What is TLD? |
Top-level domain servers. Responsible for com, org, net, edu, aero, jobs, museums, and all top-level country domains (uk, fr, ca, etc.) |
|
|
What are authoritative DNS servers? |
Organisations own DNS server(s) which can be maintained by organisation or service provider. |
|
|
What is a local DNS name server? |
Each ISP has one, does not strictly belong to a hierarchy. WHen a host makes a DNS query, query is sent to the local DNS server. Has a local cache of recent mappings. Forwards query to hierarchy. |
|
|
What is an iterative query (DNS)? |
The server contacted comes back with the name of a server to contact. "I don't know this name, but ask this server". |
|
|
What is a recursive query (DNS)? |
Puts burden of name resolution on contacted server. |
|
|
What is the format of resource records (RR) in DNS? |
(name, value, type, ttl) |
|
|
In type A RR, what is the name and value? |
name = hostname value = IP address |
|
|
In type NS RR, what is the name and value? |
name = domain value =hostname of authoritative name server for this domain |
|
|
In type CNAME RR, what is the name and value? |
name = alias for real canonical name value = canonical name |
|
|
In type MX RR, what is the name and value? |
value = name of mail server associated with name |
|
|
Is there a difference between message formats for request and replies in DNS? |
No |
|
|
Do peers change IP addresses in P2P? |
yes |
|
|
How long does it take to distribute F to N clients using a client-server approach? |
max{NF/us, F/dmin} dmin = minimum client download rate |
|
|
How long does it take to distribute F to N clients using a P2P approach? |
max{F/us, F/dmin, NF/(us + ∑ui)} where ui = upload speed of ith client us = upload capacity of server dmin = minimum client download rate |
|
|
What is a torrent? |
Group of peers exchanging chunks of a file |
|
|
What is a tracker (P2P)? |
Tracks peers participating in a torrent |
|
|
How does requesting chunks work in torrenting? |
Periodically a peer will request a list of chunks from each peer. The rarest chunks are requested first. |
|
|
How does sending chunks work in torrenting? |
A peer will send chunks to four peers who are sending them chunks at the highest rate. None to anyone else. Top 4 are reevaluated every 10 seconds. Every 30 seconds randomly select another peer and start sending them chunks. |
|
|
What is "peer churn" in P2P? |
When peers come and go. |
|
|
Internet traffic measurement? Socket programming? ye |
yeah nah no idea |

