![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Function |
Involvement in both innate and adaptive immunity Kills pathogens in blood |
|
|
Complement C3 |
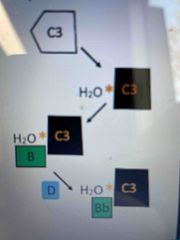
Most common complement factor (8th most common serum protein) Can be spontaneously activated by leakage of water to thioester bond - C3(H2O) Binds complement factor B which is cleaved to form C3(H2O)Bb C3Bb is a C3 convertase which cleaves C3 into 3a and 3b 3a is an anaphylotoxin 3b functions just like C3(H2O) C3b can covalently link to microbial surfaces
|
|
|
C3 thioester linkage |
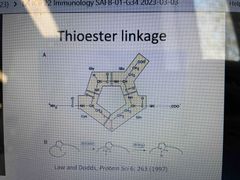
Inactive form of C3 is a ring consisting of Cys-Gly-Glu-Gln Thioester bond occurs between Cys and Gln Thioester CO can be nucleophilically attacked by OHs and NHs |
|
|
Opsonisation |

C3b on bacterial surfaces is recognised by the C3 receptor (C3R) on phagocytes |
|
|
C5 |
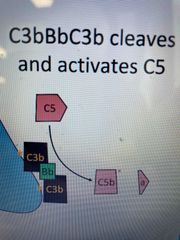
Multiple C3b molecules can bind factor B The resulting complex C3bBbC3b is a C5 convertase C5a is an anaphylotoxin and signals immature dendritic cells leading to formation of Th1 cells C5b recruits the membrane attack complex (C5bC6C7C8C9) |
|
|
Membrane attack complex |

C5b recruits C6 and C7 - the resulting complex binds to the membrane via C7 C8 binds this complex and inserts into the membrane C9 binds complex C5bC6C7C8 then recruits other C9 molecules to form pores The pores can kill bacteria by lysis |
|
|
Alternative Complement pathway |
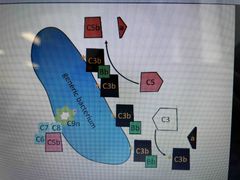
Spontaneous C3 activation C3b spontaneously bind surfaces Factor B binds C3b and cleaved to form C3bBb C3 activation is amplified - resulting surface C3b allows opsonisation Higher order C3bBbC3b can form and activate C5 C5b recruits the MAC which forms a C9 pore to kill the bacterium |
|
|
Complement C1 |
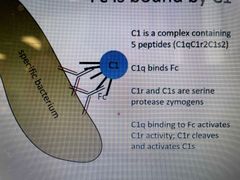
Complex of C1q, 2 C1r and 2 C1s C1q binds antibody Fc C1r and C1s are serine proteases C1r is activated by C1q binding Fc C1r cleaves and activates C1s |
|
|
C4 |
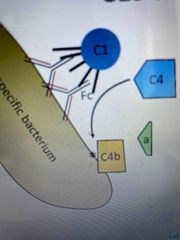
Activated upon cleavage by C1s, revealing a thioester bond like in C3 C4b binds bacterial surface and binds C2 which is also cleaved by C1s C4bC2a is a C4 convertase which activates the C3 alternative pathway |
|
|
Mannose binding lectin |
MBL binds mannose on some bacteria, fungi and Protozoa Recruits MASP1 (analogous to C1r) and MASP2 (analogous to C1s) MASP1/2 activates classical complement pathway C4 and C2 |
|
|
Control of complement |
Factor I is a serine protease which cleaves and inactivates C3b and C4b which kills complement activation amplification Factor H binds host glycosaminoglycans and recruits factor I |

