![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
261 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
MCS - 1 |

|
|
|
MCS - 2 |

|
|
|
MCS - 3 |

|
|
|
MCS Subcategory A |

|
|
|
MCS Subcategory B |

|
|
|
MCS Subcategory C |

|
|
|
DM - 0 |

|
|
|
DM - 1 |

|
|
|
DM - 2 |

|
|
|
DM - 3 |

|
|
|
ASA I |
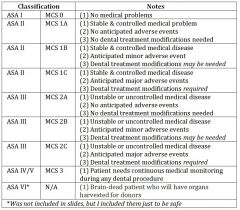
|
|
|
ASA II |
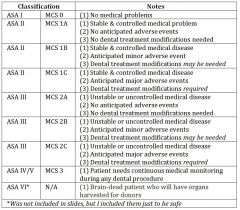
|
|
|
ASA III |

|
|
|
ASA IV |

|
|
|
potential problem of an abx allergy |
Potential Problem:
1) anaphylaxis 2) respiratory arrest ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
1) use alternative abx |
|
|
dental requirements of an abx allergy |
Potential Problem:
1) anaphylaxis 2) respiratory arrest ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
1) use alternative abx |
|
|
potential problem of warfarin |
Potential Problem:
1) bleeding ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
1) check INF before invasive procedures 2) if INR < 3.5, no need to alter 3) for surgical procedures, use local hemostatic measures (pressure packs etc.) |
|
|
dental requirements of warfarin |
Potential Problem:
1) bleeding ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
1) check INF before invasive procedures 2) if INR < 3.5, no need to alter 3) for surgical procedures, use local hemostatic measures (pressure packs etc.) |
|
|
potential problems for CD4 (viral load) if stable |
Potential Problem:
1) bleeding ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
1) check INF before invasive procedures 2) if INR < 3.5, no need to alter 3) for surgical procedures, use local hemostatic measures (pressure packs etc.) |
|
|
dental requirements for CD4 (viral load) if stable |
Potential Problem:
1) impaired immunity ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
1) monitor oral cavity for opportunistic infections 2) monitor loads every 6 months |
|
|
potential problems for HTN |
Potential Problem:
1) MI 2) CVA
Orthostatic Hypotension ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
for MI / CVA.... 1) vital signs every visit 2) minimize use of epi to ≤ 3 carpules 3) stress reduction
for orthostatic hyptension --> change chair position slowly |
|
|
dental requirements for HTN |
Potential Problem:
1) MI 2) CVA
Orthostatic Hypotension ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
for MI / CVA.... 1) vital signs every visit 2) minimize use of epi to ≤ 3 carpules 3) stress reduction
for orthostatic hyptension --> change chair position slowly |
|
|
potential problems for HAART Medications |
Potential Problem:
1) impaired liver function tests (LFT) 2) bleeding ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
1) monitor |
|
|
dental requirements for HAART Medications |
Potential Problem:
1) impaired liver function tests (LFT) 2) bleeding ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
1) monitor |
|
|
potential problems for xerostomia |
Potential Problem:
1) caries ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
1) frequent recalls 2) topical fluoride |
|
|
dental requirements for xerostomia |
Potential Problem:
1) caries ------------------------------
Dental Requirements:
1) frequent recalls 2) topical fluoride |
|
|
What is needed for diagnosis of HTN ? |
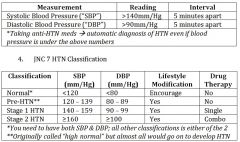
|
|
|
normal classification of BP |

|
|
|
pre-HTN classification of BP |
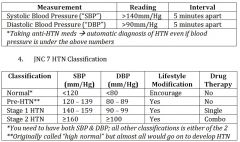
|
|
|
Stage 1 HTN |

|
|
|
Stage 2 HTN |

|
|
|
Guidelines on Controlled Hypertension |
< 60 years old ..... < 140/90
> 60 + diabetes mellitus or chronic renal disease ..... < 140/90
> 60 years old ..... < 150/90 |
|
|
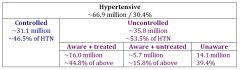
HTN Prevalence Among US Adults |

|
|
|
controlled vs uncontrolled HTN |

|
|
|
aware vs unaware of HTN |
|
|
|
What is stepped care? |
“Stepped care for medical management of HTN can give you an estimate of patient’s level of CVD and its control based on:
the number and types of classes of medications” |
|
|
Dental treatment with respect to HTN and epinephrine |
“Numerous studies have shown that Stage 1 or Stage 2 HTN (SBP below 180mm/Hg and DBP below 110mm/Hg) is NOT an independent risk factor for perioperative cardiovascular complications.”
“The increased risk for adverse events among uncontrolled HTN patients was found to be LOW & the reported occurrence of adverse events in HTN patients associated with the use of epinephrine in local anesthetics was minimal.” |
|
|
referral to MD based on BP |

|
|
|
proposed treatment done depending on BP |

|
|
|
in a standard carpule of 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epi, what is the limit for a healthy adult? |
0.2mg (~12 carpules)
--> 0.017mg per carpule |
|
|
how much epi does adrenal medulla put out if stressed |
unstressed = 0.007 - 0.014mg / minute stressed = 0.28mg / minute |
|
|
how much epi does adrenal medulla put out if unstressed |
unstressed = 0.007 - 0.014mg / minute stressed = 0.28mg / minute |
|
|
how much epi in an epi-pen? |
0.3mg |
|
|
how should you limit epi? |
Healthy patients ≤ 0.051mg
Patients on non-selective β-blockers ≤ 0.034mg
Patients on digitalis (digoxin): avoid entirely |
|
|
epi for healthy patients w/ HTN |
Healthy patients ≤ 0.051mg
Patients on non-selective β-blockers ≤ 0.034mg
Patients on digitalis (digoxin): avoid entirely |
|
|
epi for patients using digoxin |
Healthy patients ≤ 0.051mg
Patients on non-selective β-blockers ≤ 0.034mg
Patients on digitalis (digoxin): avoid entirely |
|
|
epi for pts. on non-selective beta blockers |
Healthy patients ≤ 0.051mg
Patients on non-selective β-blockers ≤ 0.034mg
Patients on digitalis (digoxin): avoid entirely |
|
|
how do NSAIDs interact with anti-hypertensives? |
1) decreased renal blood flow
2) loss of anti-hypertensive effect **
--> use acetominophen instead !!! |
|
|
What can commonly cause a loss of anti-hypertensive effect in patients unknowingly? |
using NSAIDs
--> use acetominophen instead !!! |
|
|
BP meds - potential problems |
Orthostatic hypotension 1) change chair position slowly 2) wait 1 minute before letting pt. stand
xerostomia/caries 1) more frequent recalls 2) topical fluoride
NSAIDs & increasedBP 1) use alternative analgesic (i.e. acetominophen) |
|
|
BP meds - planned management |
Orthostatic hypotension 1) change chair position slowly 2) wait 1 minute before letting pt. stand
xerostomia/caries 1) more frequent recalls 2) topical fluoride
NSAIDs & increasedBP 1) use alternative analgesic (i.e. acetominophen) |
|
|
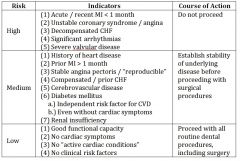
high risk for cardiovascular disease if... |

|
|
|
medium risk for cardiovascular disease if... |

|
|
|
low risk for cardiovascular disease if... |
|
|
|
when would an ejection fraction change? |
in congestive heart failure |
|
|
what blood test is the MOST important predictor of CVD? |
Hs-CRP |
|
|
nitrates |

|
|
|
beta-blockers |

|
|
|
calcium channel blockers |

|
|
|
anti-cholesterol drugs |

|
|
|
anti-platelet / aspirin |

|
|
|
why don't you give nitro to all patients? |
its a vasodilator...
if the pt is already hypotensive, it will make it worse |
|
|
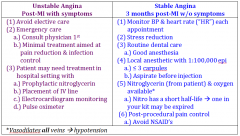
dental management with unstable angina |

|
|
|
dental management with stable angina |
|
|
|
what happens if chest pain develops? |

|
|
|
considerations and interactions for: calcium channel blockers |
monitor for ginigval hyperplasia |
|
|
considerations and interactions for: ACE-I |
1) scalded mouth 2) angioedema --> lips & tongue 3) altered taste |
|
|
considerations and interactions for: beta-blockers |
1) altered taste 2) interaction with epi --> HTN --> bradycardia 3) local with epi ≤ 2 carpules (0.034 mg) |
|
|
considerations and interactions for: diuretics |
lichenoid reactions |
|
|
what can cause lichenoid reactions? |
diuretics |
|
|
what can cause scalded mouth? |
ACE-inhibitors |
|
|
considerations and interactions for: amiodarone |
toxicity with lidocaine (use with caution) |
|
|
considerations and interactions for: digitalis/digoxin |
AVOID !!!!! - epi - azole antifungals |
|
|
considerations and interactions for: diuretics, ARBs, ACE-I & Dogixin |
AVOID use of NSAIDs !!! 1) decreased renal blood flow 2) reduced anti-hypertensive effects (up to 50%) 3) use of acetominophen instead |
|
|
aspirin |
if a MD prescribes it... it is NOT OTC... but is considered a cardiac drug !!! |
|
|
potential problem and planned management for aspirin |
Potential Problem:
1) bleeding ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) pressure packs 2) primary closure 3) atraumatic technique 4) local hemostatic measures 5) avoid NSAIDs |
|
|
potential problem and planned management for aspirin |
Potential Problem:
1) bleeding ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) pressure packs 2) primary closure 3) atraumatic technique 4) local hemostatic measures 5) avoid NSAIDs |
|
|
potential problem and planned management for angina / past MI |
Potential Problem:
1) 2nd MI ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) have nitro & 02 ready 2) make sure patient has taken meds & is asymptomatic 3) morning / early afternoon appointments 4) stress reduction |
|
|
potential problem and planned management for angina / past MI |
Potential Problem:
1) 2nd MI ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) have nitro & 02 ready 2) make sure patient has taken meds & is asymptomatic 3) morning / early afternoon appointments 4) stress reduction |
|
|
Coronary Artery By-Pass Graft (CABG) |
- cut out damaged piece of artery - excise piece of saphenous vein & anastomose it with artery
NO ABX PROPHYLAXIS NEEEDED !!!!! |
|
|
rules for PCTA with stent placement |
12 months of dual antiplatelet therapy --> usually aspirin & clopidogrel after placement of drug-eluding cardiac stents
**suggest delaying elective surgery rather than stopping either drug |
|
|
DE Stents < 1 year |
potential problem = thromboembolic event
planned management --> continue dual antiplateley therapy (clopidogrel & aspirin) |
|
|
potential problem and planned management for CHF |
Potential Problem:
1) pulmonary edema ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) monitor 2) adjust chair position as needed |
|
|
potential problem and planned management for CHF |
Potential Problem:
1) pulmonary edema ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) monitor 2) adjust chair position as needed |
|
|
right sided CHF |
RIGHT SIDED - systemic venous congestion - distended neck veins - enlarged liver - peripheral edema ascites
LEFT SIDED - pulmonary edema - dyspnea |
|
|
left-sided CHF |
RIGHT SIDED - systemic venous congestion - distended neck veins - enlarged liver - peripheral edema ascites
LEFT SIDED - pulmonary edema - dyspnea |
|
|
ejection fraction levels |

|
|
|
normal ejection fraction |

|
|
|
heart failure ejection fraction |

|
|
|
Heart Failure Class I |

|
|
|
Heart Failure Class II |

|
|
|
Heart Failure Class III |

|
|
|
Heart Failure Class IV |

|
|
|
compensated heart failure |

|
|
|
decompensated heart failure |

|
|
|
compensated vs. decompensated heart failure |

|
|
|
CHF & Clinical Predictors of Risk |

|
|
|
CHF & Clinical Predictors of Risk --> major |

|
|
|
CHF & Clinical Predictors of Risk --> intermediate |

|
|
|
CHF & Clinical Predictors of Risk --> minor |

|
|
|
what classes of compensated CHF can you do dental work? |
Class 1 --> routine dental work Class 2 --> medical consult
Class 3+4 --> NO routine dental tx.. need hospital setting |
|
|
what classes of compensated CHF can you NOT perform any dental work? |
Class 1 --> routine dental work Class 2 --> medical consult
Class 3+4 --> NO routine dental tx.. need hospital setting |
|
|
considerations for pts on digoxin |
1) avoid epinephrine 2) avoid gag reflex (very hyperactive) 3) avoid "the mycins" (erythromycin, clarithromycin) & azole antifungals |
|
|
classification of arrhythmias - supraventricular |

|
|
|
classification of arrhythmias - ventricular |

|
|
|
classification of arrhythmias - tachyarrhythmias |

|
|
|
classification of arrhythmias - bradyarrhythmias |

|
|
|
methods of treating arrhythmias |
1) pacemakers 2) medications 3) "zap out" node of His (ablation) |
|
|
How do anti-arrhythmic drugs such as sodium channel blockers and membrane stabilizers differ from other cardiac drugs? |
They DECREASE the excitability. |
|
|
concerns about amiodarone |
AVOID lidocaine !!! |
|
|
dental considerations for pts with arrhythmias |
significant or poorly controlled controlled arrhythmias --> not candidates for elective dental care
with stable (controlled) arrhythmias --> treat as NORMAL patient
**monitor blood pressure & pulse at each visit --> rate & rhythm for at least 60 seconds (get a sense of whether the rhythm is regular or irregular) |
|
|
are ABX prophylaxis necessary for pacemakers and AICD ? |
NO !!! |
|
|
how would you know if a pacemaker is shielded / what does that mean ? |
usually if it was placed within the past 5 years, they will be fully shielded |
|
|
unshielded pacemakers |

|
|
|
shielded pacemakers |

|
|
|
can you use electrosurgery on shielded pacemaker |
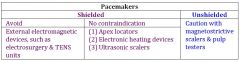
NO !!! |
|
|
potential problem of pt w/ atrial fibrilation |
Potential Problem:
1) exacerbation of rhythm
2) thromboembolic event
------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) - make sure pt. has taken meds - minimize stressful situations - be ready to treat emergency using vagal maneuver - AED available
2) continue warfarin |
|
|
planned management of pt. with atrial fibrillation |
Potential Problem:
1) exacerbation of rhythm
2) thromboembolic event
------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) - make sure pt. has taken meds - minimize stressful situations - be ready to treat emergency using vagal maneuver - AED available
2) continue warfarin |
|
|
potential problems of pt. taking amiodarone |
Potential Problem:
1) interaction with lidocaine
------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) limit 2% lidocaine 2) consider alternative anesthetic |
|
|
planned management of pt. taking amiodarone |
Potential Problem:
1) interaction with lidocaine
------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) limit 2% lidocaine 2) consider alternative anesthetic |
|
|
planned management of pt. taking calcium channel blockers |
Potential Problem:
1) gingival hyperplasia
------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) monitor 2) more frequent recalls if present |
|
|
what is a vagal maneuver |
push on carotid bodies on both sides or ask patient to hold their nose and blow --> lowers heart rate |
|
|
bioprosthetic valvular replacement |
- only lasts 10-15 years - lower thromboembolic risk - dont need anticoagulants after 3 months !!! |
|
|
mechanical valve replacement |
- lasts longer - pts need to be on HIGH doses of antivoagulants FOR LIFE |
|
|
ABX prophylaxis for valve replacement? |
- All dental procedures that involve gingival or periapical manipulation or perforation of mucosa - Doesn’t matter what the type of valve - Doesn’t matter which valve was replaced - Doesn’t matter how long ago valve was replaced - No time limit on the need for antibiotic prophylaxis |
|
|
when would you use abx prophy for ? |
- infectious endocarditis - prosthetic TOTAL joint replacement |
|
|
ABX prophylaxis is recommended for which cardiac conditions |
1) previous IE 2) prosthetic cardiac valve or prosthetic material used for cardiac valve repair 3) congenital heart disease 4) cardiac transplants who have cardiac valvulopathy |
|
|
when to prophylactically give antibiotics to cardiac patients |
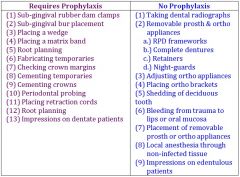
- when manipulating gingival tissue - when manipulating periapical region of teeth - when perforating the oral mucosa |
|
|
cardiac pt - requires prophy during these procedures |

|
|
|
cardiac pt - does NOT require prophy during these procedures |

|
|
|
prophylaxis is NEVER needed for: |
- cardiac stents - history of CABG - pacemakers / AICD - any cardiac murmur - history of RHD - valvular stenosis - cardiomyopathy - patent foramen ovale or atrial septal defect |
|
|
dose for abx prophy |

|
|
|
signs of infectious endocarditis |
- fever - chills - night sweats - weakness - shortness of breath - "splinter" hemmorhages under nails - joint pain - subconjunctival & soft palate petechiae - Osler's nodes (red & painful) in fingers and toes |
|
|
when would you see Oslers's nodes (red & painful) in fingers and toes & "splinter" hemmorhages under nails |
infectious endocarditis |
|
|
non - cardiac conditions that MAY require premedication for selected procedures |
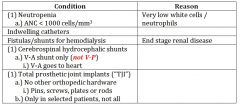
|
|
|
do you need to prophylax for pt with neutropenia? |
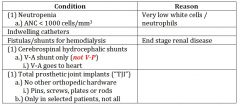
sometimes....
|
|
|
difference between prophylaxing NON-cardiac conditions.... |
ABX prophy for NON-cardaic is basically ONLY for perio procedures (including probing) + surgical procedures....
you DO NOT need a prophy for any restorative or prosth |
|
|
classes of bleedings |

|
|
|
class I bleeding |

|
|
|
class II bleeding |

|
|
|
class III bleeding |
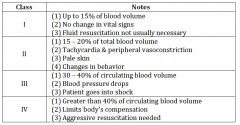
|
|
|
class IV bleeding |
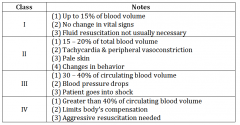
|
|
|
what conditions indicate "significant" bleeding ? |
- continue beyond 12 hours - doesnt stop within 30 minutes of firm pressure - requires blood transfusion |
|
|
which lab tests are NOT clinically relevant ? |
bleedign time / anti-platelet tests |
|
|
what do petechiae & ecchymosis indicate? |
petechiae & ecchymosis --> abnormal / low platelets
ecchymoses & hematomas --> coagulation problem |
|
|
what do ecchymoses & hematomas indicate? |
petechiae & ecchymosis --> abnormal / low platelets
ecchymoses & hematomas --> coagulation problem |
|
|
what lab test would you need for a pt on warfarin? |
warfarin --> IRN heparin --> PTT |
|
|
what lab test would you need for a pt on heparin? |
warfarin --> IRN heparin --> PTT |
|
|
risk categories for bleeding |

|
|
|
low risk category for bleeding |

|
|
|
moderate risk category for bleeding |
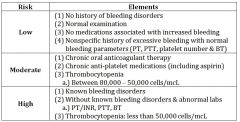
|
|
|
high risk category for bleeding |

|
|
|
pt with thrombocytopenis between 80,000-50,000 cells is ________ risk category |
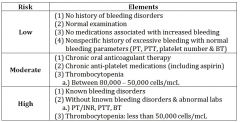
MODERATE |
|
|
management or ALL patients with potential bleeding problems |

|
|
|
when would you schedule patients with potential bleeding problems? |
- early in the day - early in the week |
|
|
what kind of suture is best for primary closure? |
silk > guy
- stays in mouth longer - gut degrades --> swells --> collects plaque, food & debris --> tissue inflammation |
|
|
dealing with potential problems and management of ptt with thrombocytopenia w/ a platelet count of 75,000 |
Potential Problem:
1) bleeding ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) currently 75,000 cells/ mcL 2) local hemostatic measures for invasive procedures 3) decrease local inflammation 4) careful soft tissue manipulation 5) avoid NSAIDs post-op |
|
|
most common way to get thrombocytopathy |
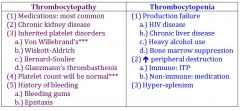
MEDICATIONS |
|
|
thrombocytopathy vs thrombocytopenia |
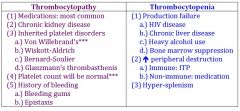
|
|
|
thrombocytopathy |

|
|
|
thrombocytopenia |
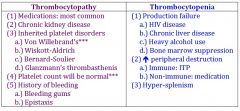
|
|
|
desmopressin (DDAVP) |
synthetic hormone
prevents / treats bleeding episodes in: - hemophilia A - vWD - platelet function defects (medication induced thrombocytopathy, chronic kidney disease, cirrhosis)
**induces release of von Willebrand factor from storage --> leads to increase in factor VIII & increases platelet adhesion |
|
|
what induces release of von Willebrand factor from storage --> leads to increase in factor VIII & increases platelet adhesion |
desmopressin (DDAVP) |
|
|
do hemophiliacs meed abx propy ? |
YES !!!! --> can compromise the immune system |
|
|
potential problems of pt with hemophilia A |
Potential Problem:
1) bleeding ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) hematology consult 2) determine need for factor transfusion 3) schedule early in the day/ week |
|
|
planned management of pt with hemophilia A |
Potential Problem:
1) bleeding ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) hematology consult 2) determine need for factor transfusion 3) schedule early in the day/ week |
|
|
potential problems of pt with total hip replacement |
Potential Problem:
1) joint infection ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) consider abx prophy for surgical and periodontal procedures |
|
|
planned management of pt with total hip replacement |
Potential Problem:
1) joint infection ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) consider abx prophy for surgical and periodontal procedures |
|
|
hemarthrosis |
bleeding into joints... may happen in pts with hemophilia A |
|
|
levels of factor VIII |

|
|
|
what level of factor VIII would a MILD hemophiliac have? |

|
|
|
what level of factor VIII would a MODERATE hemophiliac have? |

|
|
|
what level of factor VIII would a SEVERE hemophiliac have? |

|
|
|
what is the NORMAL level of factor VIII ? |

>50%
|
|
|
management for hemophiliacs |

|
|
|
management for MILD hemophiliac |

|
|
|
management for MODERATE hemophiliac |

|
|
|
management for SEVERE hemophiliac |

|
|
|
how do you administer dasmopressin (DDAVP) ? |
- parenterally or via nasal spray 1 hour before surgery (can be prescribed by dentist) |
|
|
what is the most common inherited bleeding disorder? |
vWD |
|
|
potential problems with pt with vWF disease |
Potential Problem:
1) bleeding ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) schedule appt early in the day/week 2) decrease local inflammation 3) careful soft tissue manipulation 4) DDAVp pre-op (post-op as needed) 5) local hemostatic measures 6) use EACA post-op (anti-fibrinolytic mouth rinse) |
|
|
planned management for pt with vWF disease |
Potential Problem:
1) bleeding ------------------------------
Planned Management:
1) schedule appt early in the day/week 2) decrease local inflammation 3) careful soft tissue manipulation 4) DDAVp pre-op (post-op as needed) 5) local hemostatic measures 6) use EACA post-op (anti-fibrinolytic mouth rinse) |
|
|
types of vWD |
Type I - "quantitative" - most common (70-80% of cases) - shortage of vWF
Type II - "qualitative" - flawed vWF
Type III - rarest form - deficiency in vWF - usually have low Factor VIII levels - clinically similar to Hemophilia A |
|
|
type I vWD |
Type I - "quantitative" - most common (70-80% of cases) - shortage of vWF
Type II - "qualitative" - flawed vWF
Type III - rarest form - deficiency in vWF - usually have low Factor VIII levels - clinically similar to Hemophilia A |
|
|
type II vWD |
Type I - "quantitative" - most common (70-80% of cases) - shortage of vWF
Type II - "qualitative" - flawed vWF
Type III - rarest form - deficiency in vWF - usually have low Factor VIII levels - clinically similar to Hemophilia A |
|
|
type III vWD |
Type I - "quantitative" - most common (70-80% of cases) - shortage of vWF
Type II - "qualitative" - flawed vWF
Type III - rarest form - deficiency in vWF - usually have low Factor VIII levels - clinically similar to Hemophilia A |
|
|
treating a vWD patient |

|
|
|
treating type I vWD pt. |

|
|
|
treating type II vWD pt. |

|
|
|
treating type III vWD pt. |

|
|
|
you prescribed an azole to treat candidiasis on a pt. who is on warfarin... and she has uncontrollable blelding... why? |
azole antifungals inhibit cytochrome p450 receptor(needed for coumadin to be deactivated) |
|
|
anti-coagulants vs anti-platelets |
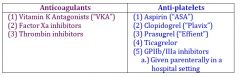
|
|
|
anti-platelets |
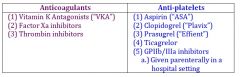
|
|
|
anti-coagulants |

|
|
|
cyclooxogenase inhibitors |
1) aspirin (irreversible) 2) NAIDs (variable reversible) |
|
|
P2Y12 inhibitors |
1) Prasugrel ("Effient" 2) Ticagrelor ("Brilinta") 3) Clopidogrel ("Plavix") **most common** |
|
|
phosphodiesterase inibitors |
1) dipyrimadamole ("persantine" / "Aggrenox" ) |
|
|
GPIIb / IIIa inhibitors (IV drugs) |
1) abciximad 2) tirofiban 3) eptifibatide |
|
|
irreversible vs reversible anti-platelet drugs |

|
|
|
irreversible anti-platelet drugs |

|
|
|
irreversible anti-platelet drugs |

|
|
|
advantages of new anticoagulants |
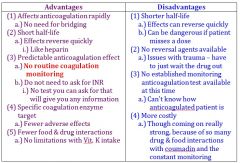
|
|
|
disadvantages of new anticoagulants |

|
|
|
how do antibiotics affect pts on warfarin? |
broad spectrum antibiotics kill off gut flora needed to produce vitamin K --> nothing for warfaran to antagonize & act with --> you have unmetabolized warfarin
==> lower metabolism of warfarin... higher INR & bleeding |
|
|
how do azoles affect patients on warfarin ? |
inhibit cytochrome p450 receptor, which is needed for coumadin to be deactivated
==> lower metabolism of warfarin... higher INR & bleeding |
|
|
where is erythropoietin produced? |
95% --> renal cortex 5% --> liver |
|
|
bleeding and anemia |
bleeding can cause anemia... but anemia can NOT cause bleeding !! |
|
|
symptoms of mild/moderate anemia |
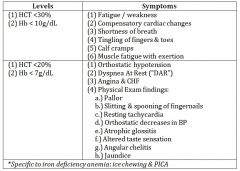
|
|
|
symptoms of moderate/severe anemia |

|
|
|
examples of microcytic anemia |

|
|
|
examples of normocytic anemia |

|
|
|
examples of macrocytic anemia |
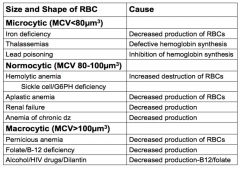
|
|
|
plummer-vinson syndrome |
- severe & chronic iron deficiency anemia - dysphagia (esophageal stenosis & webbing) - koilonycha ( spoon-shaped nails) - sore mouth (atrophic glossitis & angular chelitis)
****PREDISPOSITION TO DEVELOP CANCER OF ORAL CAVITY & ESOPHAGUS |
|
|
what is commonly associated with a predisposition to development of cancer of the oral cavity? |
plummer-vinson syndrome
- severe & chronic iron deficiency anemia - dysphagia (esophageal stenosis & webbing) - koilonycha ( spoon-shaped nails) - sore mouth (atrophic glossitis & angular chelitis)
****PREDISPOSITION TO DEVELOP CANCER OF ORAL CAVITY & ESOPHAGUS |
|
|
diagnostic lab tests for pernicious anemia |
- elevated homocysteine & methylmalonic acid (MMA) - positive schilling test |
|
|
-elevated homocysteine & methylmalonic acid (MMA) is typical of what |
pernicious anemia |
|
|
positive schilling test |
pernicious anemia
--> checks if b12 can be absorbed orally or needs to be injected |
|
|
hemolytic anemia --> RBC membrane |

|
|
|
hemolytic anemia --> enzyme deficiencies |

|
|
|
hemolytic anemia --> hemoglobin synthesis |

|
|
|
potential problems with a patient with sickle cell anemia |

|
|
|
planned management for a patient with sickle cell anemia |

|
|
|
what is moderate neutropenia |
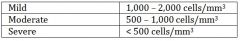
normal is 1500-8000 |
|
|
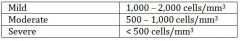
what is severe neutropenia? |
normal is 1500-8000 |
|
|
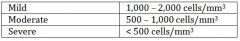
what is mild neutropenia? |
normal is 1500-8000 |
|
|
for which WBC conditions would you NOT treat a patient? |
total WBC < 1,000
OR
ANC < 500 |
|
|
when would you give pre-operative abx for invasive procedures with pts with WBC disorders? |
WBC < 2,000 or ANC < 1,000
consult physicial about regimen (usually penicillin if not allergic)
start 30-60 minutes before the procedure and then continue for 7-10 days |
|
|
autologous stem cell transplant |
autologous stem cell transplant = own stem cells
synegenic stem cell transplant = identical twin's stem cells
allogenic stem cell transplant = relative / donor's stem cells (HLA antigen matching) |
|
|
synegenic stem cell transplant |
autologous stem cell transplant = own stem cells
synegenic stem cell transplant = identical twin's stem cells
allogenic stem cell transplant = relative / donor's stem cells (HLA antigen matching) |
|
|
allogenic stem cell transplant |
autologous stem cell transplant = own stem cells
synegenic stem cell transplant = identical twin's stem cells
allogenic stem cell transplant = relative / donor's stem cells (HLA antigen matching) |
|
|
identical twin's stem cells |
autologous stem cell transplant = own stem cells
synegenic stem cell transplant = identical twin's stem cells
allogenic stem cell transplant = relative / donor's stem cells (HLA antigen matching) |
|
|
own stem cells |
autologous stem cell transplant = own stem cells
synegenic stem cell transplant = identical twin's stem cells
allogenic stem cell transplant = relative / donor's stem cells (HLA antigen matching) |
|
|
donor's stem cells |
autologous stem cell transplant = own stem cells
synegenic stem cell transplant = identical twin's stem cells
allogenic stem cell transplant = relative / donor's stem cells (HLA antigen matching) |
|
|
pts with leukemia |
high risk -> hospitalization & IV abs
moderate --> plan dental tx around chemotherapy or when WBC >35,000 cells and platelets >60,000 (abx prophy when WBC < 2000 or ANC < 1000) |
|
|
autologous vs. allogenic HSCT |

|
|
|
what is the time it takes for autologous HSCT before immune system is functional again |

|
|
|
what is the time it takes for allogenic HSCT before immune system is functional again |

|
|
|
acute GVHD |
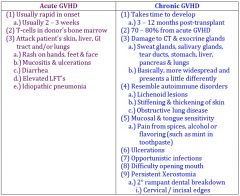
Acute GVHD = 1st 100 days Chronic GVHD = 100 days - 3 years |
|
|
Chronic GVHD |
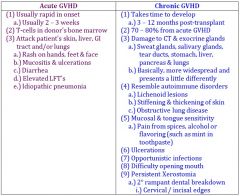
Acute GVHD = 1st 100 days Chronic GVHD = 100 days - 3 years |
|
|
which type of HSCT is considered to be "rescue treatment" ? |

|
|
|
which type of HSCT is considered to be "curative treatment" ? |
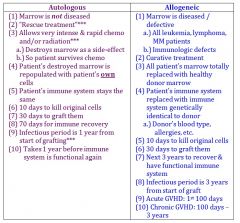
|
|
|
treatment of GVDH |
- higher dose of immunosuppressants |
|
|
immune system - b-cell deficiencies |
- bacterial infections - chemotherapy |
|
|
immune system t-cell deficiencies |
- viral - fungal - parasitic infections - HIV infection |
|
|
how do you confirm HIV ? |
ELSIA/western blot (positive test twice) |
|
|
viral load |
rate of viral replication (how fast the car is going) |
|
|
CD4+ count |
ability to fight viruses, fungi & parasites (NOT BACTERIA.... thats neutrophil count)
"how much distance there is between you and the wall" |
|
|
when does a HIV pt have AIDS |
ONE of the following:
- CD4+ cell count < 200 cells/mm3 - CD4+ percent of total lymphocytes < 14% |
|
|
NON- AIDS defining oral manifestations |
- candidiasis (oralpharyngeal) - oral hairy leukoplakia - oral herpes zoster |
|
|
AIDS-defining illnesses |
- candidiasis (esophageal) - herpes simplex: chronic ulcers > 1 month duration - kaposi's sarcoma - TB |
|
|
when is viral load highest? |
highest during 1st 3 months after initial infection AND late stages |
|
|
do viral load or CD4 count have any direct impact on the delivery of dental care? |
NO |
|
|
HAART Guidelines |
- CD4+ counts < 500 - SYMPTOMATIC !!!!!!!!!
regardless of CD4+ - all pregnant pts. - HIV-associated nephropathy - need tx for Hep B |
|
|
treatment planning considerations for pts with AIDS |
CD4+ < 300 - more freq recalls - monitor opportunistic infections
CD4+ < 100 - always get a neutrophil count |
|
|
difference in pts with HIV |
xerostomia - increased risk for caries and periodontal disease
post-surgical complications - prolonged bleeding, delayed healing, dry socket |
|
|
potential problems for pts with low CD4+ |

|
|
|
planned management for pts with low CD4+ |

|
|
|
potential problems for pts with high viral load |

|
|
|
planned management for pts with high viral load |

|
|
|
potential problems for pts on HAART |

|
|
|
planned management for pts on HAART |

|

