![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
METHODS OF URINE COLLECTION |
-Bottle method-Gauze-pad method-Catheterization-SPA-Mid-stream catch method/ Clean catch method |
|
|
TYPES OF URINE SPECIMEN |
-Random -Cytology studies-FAS-Timed |
|
|
Urine specimen must be evaluated in terms of its _________________ before performing any examination. |
acceptability and integrity |
|
|
is essential to prevent microbiologic decomposition and inherent chemical changes. |
Preservation of Urine Specimen |
|
|
When a specimen is to be transported over a long distance and refrigeration is impossible, ______________________ may be added. |
chemical preservatives |
|
|
glass, plastic wide mouth container |
Bottle method |
|
|
use for infants |
Gauze-pad method |
|
|
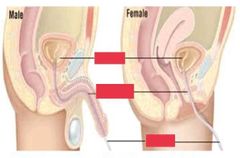
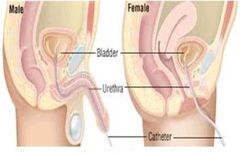
catheter is inserted in the urethra & urine is obtained from the bladder. |
Urethral catheter |
|
|
urine may be collected by external introduction of needle through the abdomen into the bladder. |
SPA (Suprapubic Aspiration) |
|
|
Because the bladder is sterile under normal conditions, SPA provides a sample for |
Bacterial culture |
|
|
Can be used for cytologic examination. It involves putting a needle through the skin just above the pubic bone into the bladder. |
SPA |
|
|
It is typically used as a method to collect urine in children less than 2 years of age who is not yet toilet trained in an effort to diagnose a urinary tract infection. |
SPA |
|
|
Collecting urine in the middle part of urination. Free from contamination. |
Mid-stream catch method/ Clean catch method |
|
|
Urine collected at any timeUSES: Routine screening |
Ramdom |
|
|
with prior hydrationYou may need to hold your first morning urine in your bladder for a few hours prior to a cystoscopy. |
Cytology studies |
|
|
First urine voided after sleep (= 6 to 8 hours). Most concentrated urine. |
FIRST MORNING/FIRST AVAILABLE SPECIMEN (FAS) |
|
|
USES: Routine screening; good recovery of cells and casts to confirm postural or orthostatic proteinuria |
FIRST MORNING/FIRST AVAILABLE SPECIMEN (FAS) |
|
|
Collect all urine during a specific timed interval. |
TIMED |
|
|
USES: Quantitative chemical analysis, Clearance tests, Cytology studies, Evaluation of fistula |
Timed |
|
|
Will prevent bacterial growth, instability of urinary solutes, and degradation of organized sediments. |
Preservation |
|
|
_________is converted to ammonium carbonate (alkaline fermentation) by _________splitting organisms, thus urine becomes alkaline. |
Urea |
|
|
False positive albumin test due to the presence of |
Bacterial protein |
|
|
Diacetic acid is converted to __________ |
Acetone |
|
|
Bilirubin is oxidized to _______________ |
Biliverdin. |
|
|
Urobilinogen is oxidized to______________ |
Urobilin |
|
|
Two methods of urine preservation |
-Refridgeration -Chemical preservatives |
|
|
most commonly used and precipitates amorphous phosphates & urates |
Refrigeration |
|
|
Preserves glucose & sediments well |
Thymol |
|
|
Preserves protein & formed elements well. Does not interfere with routine analyses other than pH |
Boric acid |
|
|
Does not interfere with routine tests |
Phenol |
|
|
Acts as reducing agent interfering with chemical tests for glucose, blood, leukocyte esterase, & copper reduction |
Formalin |
|
|
Does not interfere with routine tests |
Toluene |
|
|
Prevents glycolysis. Good preservative for drug analyses |
Sodium Fluoride |
|
|
Convenient when refrigeration not possible. Have controlled concentration to minimize interference |
Commercial preservative tablets |
|
|
inhibits bacterial growth, Aldosterone. Causes change in the characteristics of the cellular sediments. |
Chloroform |
|
|
prevents bacterial growth & useful as a glucose preservative. |
Chlorhexidine |
|
|
for Vanil Mandelic Acid/VMA |
6N hydrochloric acid |
|
|
for Cathecholamines |
Sulfuric acid |
|
|
Sample stable at RT for 48 hrs. Preserves bacteria. Decreases pH. |
Uses of Gray C&S tube |
|
|
Use on Automated instruments. Refrigerate w/in 2 hours. |
Uses of yellow plain tube |
|
|
Stable for 72 hours at RT. Preservative is sodium propionate. |
Uses of cherry red tube |
|
|
A 75-year-old bedridden patient has an acute urinary retention. |
Type of Urine: Random Method: Catheterization/Midstream clean catch |
|
|
A 6-month-old febrile patient with a bladder outlet obstruction and urethral catheterization is not possible. |
Type of urine: random Method: SPA |
|
|
A 24-year-old male patient is having recurrent UTI, the doctor requested for a urine culture and routine urinalysis |
Type of urine:Random/First morning Method: mid-stream clean catch |
|
|
One year old patient is suspected of UTI, the doctor requested for a routine urinalysis. |
Type of Urine Specimen: Random or First MorningCollection Technique: Gauze Pad Method |
|
|
A 30 year old female came in the laboratory at noon time and have a request for routine urinalysis for her annual physical exam
|
Type of Urine Specimen: RandomCollection Technique: Midstream Clean Catch |
|

|
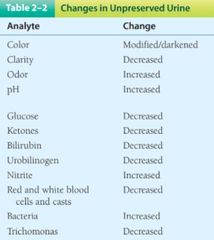
Modified/Darkened- color Increased- Odor, pH, Nitrite, Bacteria The rest decreased |
|
|
|

