![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are cognitive biases? |
Tendencies to think in certain ways that can lead to systematic deviation from a standard of rationality or good judgement. |
|
|
Ambiguity Effect |
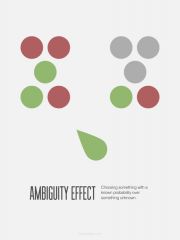
The tendency to avoid options for which missing information makes the probability seem "unknown". |
|
|
Anchoring Effect
|

The tendency to rely too heavily, or "anchor", on one trait or piece of information when making decisions (usually the first piece of information that we acquire on that subject) |
|
|
Anthropomorphism |

The tendency to excessively depend on automated systems which can lead to erroneous automated information overriding correct decisions. |
|
|
Availability Heuristic |
Estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory. If instances come readily to mind, we presume such events are common. (plane crashes/gun crime) |
|
|
Availability Cascade |

A self-reinforcing process in which a collective belief gains more and more plausibility through its increasing repetition in public discourse (or "repeat something long enough and it will become true") |
|
|
Backfire Effect |

When people react to disconfirming evidence by strengthening their beliefs. |
|
|
Base Rate Neglect/Fallacy |

The tendency to ignore base rate information (generic, general information) and focus on specific information (information only pertaining to a certain case) |
|
|
Cheerleader Effect |

The tendency for people to appear more attractive in a group rather than in isolation |
|
|
Choice-supportive Bias |

The tendency to retroactively ascribe positive attributes to one's choices or options they've selected. |
|
|
Confirmation Bias |

The tendency to search for, interpret on, focus on, and remember information that confirm's one's preconceptions. |
|
|
Contrast Effect |
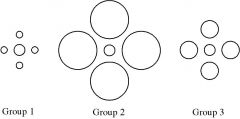
The enhancement or reduction of a certain perception's stimuli when compared with a recently observed, contrasting object |
|
|
Curse of Knowledge |

When better-informed people find it extremely difficult to think about problems from the perspective of lesser-informed people |
|
|
The Decoy Effect |

Preferences for either option A or B changes in favor of option B when option C is presented, which is similar to option B but in no way better |
|
|
Distinction Bias |

The tendency to view two options as more dissimilar when evaluating them simultaneously than when evaluating them separately |
|
|
Endowment Effect |

The tendency for people to demand much more to give up an object than they would be willing to pay to acquire it |
|
|
Forer Effect |

The tendency for people to accept vague and general personality descriptions as uniquely applicable to themselves, not realizing they can apply to anyone. |
|
|
Frequency Illusion |

The illusion in which a word, a name, or other thing that has recently come to one's attention suddenly seems to appear with improbable frequency shortly afterwards |
|
|
Gambler's Fallacy |

The tendency to think that future probabilities are altered by past events, when in reality they are unchanged. The fallacy arises from an erroneous conceptualization of the law of large numbers. For example, "I've flipped heads with this coin five times consecutively, so the chance of tails coming out on the sixth flip is much greater than heads." |
|
|
Hindsight Bias |

Sometimes called the "I-knew-it-all-along" effect, the tendency to see past events as being predictable at the time those events happened. |
|
|
Hot-hand Fallacy |
The "hot-hand fallacy" (also known as the "hot hand phenomenon" or "hot hand") is the fallacious belief that a person who has experienced success has a greater chance of further success in additional attempts. |
|
|
IKEA Effect |

The tendency for people to place a disproportionately high value on objects that they partially assembled themselves, such as furniture from IKEA, regardless of the quality of the end result. |
|
|
Illusion of Control |

Refers to people's belief that they influence over the outcome of uncontrollable events. |
|
|
Sunk Cost Fallacy |

The phenomenon where people justify increased investment in a decision, based on the cumulative prior investment, despite new evidence suggesting that the decision was probably wrong. |
|
|
The Mere-Exposure Effect |

The tendency to express undue liking for things merely because of familiarity with them. |
|
|
Moral credential effect |

The tendency of a track record of non-prejudice to increase subsequent prejudice. |
|
|
Negativity bias |

Psychological phenomenon by which humans have a greater recall of unpleasant memories compared with positive memories. |
|
|
Neglect of Probability |

The tendency to completely disregard probability when making a decision under uncertainty. |
|
|
Normalcy Biaas |

The refusal to plan for, or react to, a disaster which has never happened before. |
|
|
Omission Bias |
The tendency to judge harmful actions as worse, or less moral, than equally harmful omissions (inactions) Ex) In one scenario, John, a tennis player, would be facing a tough opponent the next day in a decisive match. John knows his opponent is allergic to a food substance. Subjects were presented with two conditions: John recommends the food containing the allergen to hurt his opponent's performance, or the opponent himself orders the allergenic food, and John says nothing. A majority of people judged that John's action of recommending the allergenic food as being more immoral than John's inaction of not informing the opponent of the allergenic substance. |
|
|
Optimism Bias |

The tendency to be over-optimistic, overestimating favorable and pleasing outcomes (see also wishful thinking, valence effect, positive outcome bias) |
|
|
Ostrich effect |
Ignoring an obvious (negative) situation. |
|
|
Overconfidence Effect |
When someone's subjective confidence in their judgements is reliably greater than their objective accuracy. |
|
|
Pareidolia |

A vague and random stimulus (often an image or sound) is perceived as significant, e.g., seeing images of animals or faces in clouds, the man in the moon, and hearing non-existent hidden messages on records played in reverse. |
|
|
Parkinson's Law of Triviality |

The tendency to give disproportionate weight to trivial issues. Also known as bikeshedding, this bias explains why an organization may avoid specialized or complex subjects, such as the design of a nuclear reactor, and instead focus on something easy to grasp or rewarding to the average participant, such as the design of an adjacent bike shed |
|
|
Pessimism Bias |
The tendency for some people, especially those suffering from depression, to overestimate the likelihood of negative things happening to them. |
|
|
Planning Fallacy |

The tendency to underestimate task-completion times. |
|
|
Post-purchase rationalization effect |
The tendency to persuade oneself through rational argument that a purchase was a good value. |
|
|
Reactive Devaluation |

Devaluing proposals only because they purportedly originated with an adversary. |
|
|
Restraint Bias |

The tendency for one to overestimate one's ability to show restraint in the face of temptation. |
|
|
Rhyme as Reason Effect |
Rhyming statements are perceived as more truthful. A famous example being used in the O.J Simpson trial with the defense's use of the phrase "If the gloves don't fit, then you must acquit."
|
|
|
The Peltzman Effect |
The tendency to take greater risks when perceived safety increases. |
|
|
Selective Perception |
The tendency for expectations to affect perception. |
|
|
Semmelweis reflex |

The tendency to reject new evidence that contradicts a paradigm (established norms/firmly held beliefs) |
|
|
Social Comparison Bias |
The tendency, when making hiring decisions, to favour potential candidates who don't compete with one's own particular strengths |
|
|
Social Desirability Bias |

The tendency of survey respondents to answer questions in a manner that will be viewed favorably by others. It can take the form of over-reporting "good behavior" or under-reporting "bad", or undesirable behavior. |
|
|
Subjective Validation |

The tendency for a person will consider a statement or another piece of information to be correct if it has any personal meaning or significance to them. |
|
|
The Survivorship Bias |

Concentrating on the people or things that "survived" some process and inadvertently overlooking those that didn't because of their lack of visibility. |
|
|
Time-saving Bias |
Underestimations of the time that could be saved (or lost) when increasing (or decreasing) from a relatively low speed and overestimations of the time that could be saved (or lost) when increasing (or decreasing) from a relatively high speed. |
|
|
Well-Traveled Road Effect |
Underestimation of the duration taken to traverse oft-traveled routes and overestimation of the duration taken to traverse less familiar routes. |
|
|
Fundamental Attribution Error |
The tendency for people to over-emphasize personality-based explanations for behaviors observed in others while under-emphasizing the role and power of situational influences on the same behavior |
|
|
Defensive Attribution Bias |
Sometimes referred to as the self-serving bias. Our successes are attributed to internal factors whereas our failures are attributed to external factors. |
|
|
Egocentric Bias |

Occurs when people claim more responsibility for themselves for the results of a joint action than an outside observer would credit them with. (Obama- "I killed bin Laden during my presidency") |
|
|
Extrinsic Incentive Bias |
An exception to the fundamental attribution error, when people view others as having (situational) extrinsic motivations and (dispositional) intrinsic motivations for oneself |
|
|
False Consensus Effect |

The tendency for people to overestimate the degree to which others agree with them |
|
|
Group Attribution Error |

The biased belief that the characteristics of an individual group member are reflective of the group as a whole or the tendency to assume that group decision outcomes reflect the preferences of group members, even when information is available that clearly suggests otherwise. |
|
|
Halo Effect |

The tendency for a person's positive or negative traits to "spill over" from one personality area to another in others' perceptions of them (see also physical attractiveness stereotype) |
|
|
Illusion of Transparency |
People overestimate others' ability to know them, and they also overestimate their ability to know others. (Ex- 'everyone knows im teaching in Thailand) |
|
|
Illusory Superiority |
Overestimating one's desirable qualities, and underestimating undesirable qualities, relative to other people. (Also known as "Lake Wobegon effect", "better-than-average effect", or "superiority bias".) |
|
|
Ingroup Bias |

The tendency for people to give preferential treatment to others they perceive to be members of their own groups. |
|
|
Just-World Fallacy |

The tendency for people to want to believe that the world is fundamentally just, causing them to rationalize an otherwise inexplicable injustice as deserved by the victim(s). |
|
|
Moral Luck |
The tendency for people to ascribe greater or lesser moral standing based on the outcome of an event (Ex-There are two people driving cars, Driver A, and Driver B. They are alike in every way. Driver A is driving down a road, and, in a moment of inattention, runs a red light as a child is crossing the street. Driver A slams the brakes, swerves, in short does everything to try to avoid hitting the child – alas, the car hits and kills the child. Driver B, in the meantime, also runs a red light but, since no one is crossing, gets a traffic ticket but nothing more.If a bystander were asked to morally evaluate Drivers A and B, there is very good reason to expect them to say that Driver A is due more moral blame than Driver B.) |
|
|
Naive Realism |

The belief that we see reality as it really is – objectively and without bias; that the facts are plain for all to see; that rational people will agree with us; and that those who don't are either uninformed, lazy, irrational, or biased. |
|
|
Projection Bias |
The tendency to unconsciously assume that others (or one's future selves) share one's current emotional states, thoughts and values.
|
|
|
Self-Serving Bias |

The tendency to claim more responsibility for successes than failures. It may also manifest itself as a tendency for people to evaluate ambiguous information in a way beneficial to their interests |
|
|
System Justification (Status Quo Bias) |
The tendency to defend and bolster the status quo. Existing social, economic, and political arrangements tend to be preferred, and alternatives disparaged, sometimes even at the expense of individual and collective self-interest. |
|
|
Ultimate Attribution Error |

The tendency to make more favorable and flattering attributions about member's of one's group than about members of other groups. (Self-serving Attributional Bias at group level) |
|
|
Bizarreness Effect |
Bizarre material is better remembered than common material. |
|
|
Change Bias |
After an investment of effort in producing change, remembering one's past performance as more difficult than it actually was |
|
|
Consistency Bias |

Incorrectly remembering one's past attitudes and behaviour as resembling present attitudes and behaviour |
|
|
Cryptomnesia |
A form of misattribution where a memory is mistaken for imagination, because there is no subjective experience of it being a memory |
|
|
Generation Effect (Self-generation effect) |
That self-generated information is remembered best. For instance, people are better able to recall memories of statements that they have generated than similar statements generated by others. |
|
|
Google Effect |
The tendency to forget information that can be found readily online by using Internet search engines. (using internet as memory storage in a way) |
|
|
Misinformation Effect |

Memory becoming less accurate because of interference from post-event information |
|
|
Mood-congruent memory bias |

The improved recall of information congruent with one's current mood. |
|
|
Next-in-line Effect |

That a person in a group has diminished recall for the words of others who spoke immediately before himself, if they take turns speaking. |
|
|
Part-list cueing Effect |
That being shown some items from a list and later retrieving one item causes it to become harder to retrieve the other items |
|
|
Peak-end Rule |
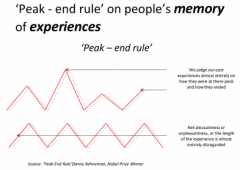
We judge our past entirely on how they were at their peak (pleasant or unpleasant) and how they ended |
|
|
Primacy effect, Recency effect &Serial position effect |
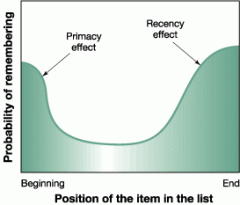
That items near the end of a sequence are the easiest to recall, followed by the items at the beginning of a sequence; items in the middle are the least likely to be remembered. |
|
|
Processing-difficulty Effect |
That information that takes longer to read and is thought about more (processed with more difficulty) is more easily remembered. |
|
|
Rosy Retrospection Effect |
The remembering of the past as having been better than it really was. |
|
|
Self-Relevance Effect |
That memories relating to the self are better recalled than similar information relating to others. |
|
|
Source Confusion Effect |
Confusing episodic memories with other information, creating distorted memories |
|
|
Spacing Effect |
That information is better recalled if exposure to it is repeated over a long span of time rather than a short one. |
|
|
Spotlight Effect |

tendency to overestimate the amount that other people notice your appearance or behavior. |
|
|
Suffix Effect |
Diminishment of the recency effect because a sound item is appended to the list that the subject is not required to recall |
|
|
Telescoping Effect |
The tendency to displace recent events backward in time and remote events forward in time, so that recent events appear more remote, and remote events, more recent. |
|
|
Testing Effect |
The fact that you more easily remember information you have read by rewriting it instead of rereading it |
|
|
Verbatim Effect |
That the "gist" of what someone has said is better remembered than the verbatim wording.[109] This is because memories are representations, not exact copies. |
|
|
Von Restorff Effect |
That an item that sticks out is more likely to be remembered than other items |

