![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cognition |
The term cognition refers to all mental structures and processes involved in the reception storage and use of knowledge. |
|
|
Behaviourism |
the movement was based on the premise that mental processes could not be studied scientifically as these processes could not be observed. The psychologist who concentrated on scientific study of external behavior are known as behaviorists. |
|
|
Principles of the cognitive level of analysis |
Mental processes can and should be studied scientifically, Mental representations guide behaviour |
|
|
Schema theory |
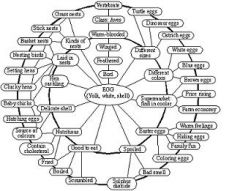
a schema is a cognitive structure that provides framework for organizing information about the world , events and people or actions. |
|
|
Scripts |
schemas which provide information about the sequence of events that occur in a more or less unchanging order in particular contact such as going to a restaurant, visiting the dentist or attending a class |
|
|
Self-schemas |
Organizes information we have about ourselves for example information stored in our memory about our strengths and weaknesses and how we feel about them. |
|
|
Social schemas |
Eg stereotypes represent information about groups of people for example Americans Egyptians women,accounts etc. |
|
|
What a schema does (well) |
- Organizes information in memory -can be activated to increase information processing efficiency -they enable the generation of expectations about objects, events and people -they regulate behavior -they are relatively stable and usually very resistant to change this ensuring continuity in the ways we process information |
|
|
what negatives does schema have? |
- Settings are unfamiliar and thus require novel approaches - The wrong schema become activated. |
|
|
Reliability of memory |
Witnesses recall can be inaccurate |
|
|
The multi-store model of memory (MsM) |
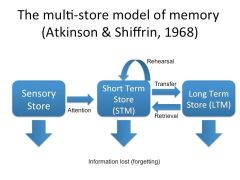
|
|
|
Leaves of processing |
Craik and lockhart 1972 (critisism towards MsM) - Structural level: Encodes physical features of stimulus - Phonological: processing information on how words sound - Semantic: extracts meaning related to stimulus object (salmon in this case) |
|
|
Appraisal theory of emotions |
Appraisal: evaluating the situation accordingly to the significant they have for us . Initially 2 major types of appraisal (Primary and secondary) later diversified to 3 sub types of each. |
|
|
Primary appraisal |
Situations that are personally relevant Motivational relevance Is the situation relevant to your goals Emotion only generated if they answer is yes congruence Situation favorable to my gola? positive emotion if yes positive if no negative. |
|
|
Secondary appraisal |
Provides information for an individual's options for coping with a situation. Problem focused coping: Can I cope with a situation by making it less threatening? Emotions focused coping: Can I change the situation by changing the way i feel about it if reevaluate the situation |

