![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Coagulation |
• The chemical process of reducing the zeta potential and destabilization of particles (Hendricks 229) |
|
|
|
Flocculation |

|
|
|
|
Why Use Coagulation? |

|
|
|
|
Colloids |
• Small particles that do not settle due to an electric surface charge, usually negative.• The characteristic size range is 1 to 10 μm. |
|
|
|
Colloid System |
Colloid System is a sol dispersions of small solid particles in a liquid medium (Hendricks 230) |

|
|
|
Objectives of Coagulation |

|
|
|
|
Types of Coagulation |
• Conventional coagulation • Sweep-floc coagulation • Enhanced coagulation • Heterocoagulation |
|
|
|
Coagulation Mechanisms |
. Charge-Neutralization (pH < 6) • Sweep Floc (pH > 6) |
|
|
|
Charge-Neutralization |

|
|
|
|
Sweep Floc Coagulation |

|
|
|
|
Double Layers |
Stern layer + diffuse layer |
|
|
|
Stern Layer vs Diffuse Layer |

|

|
|
|
Particle Stabilization |

|
|
|
|
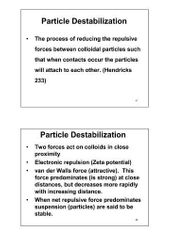
Particle Destabilization |
|
|
|
|
DLVO Theory |
• Combines the van der Waals intermolecular attractive forces with the electrostatic repulsive forces.• The “net” potential due to addition of these two forces determines the strength of the colloid interactions. |
|
|
|
Zeta Potential |

|
|
|
|
Particle Transport Mechanisms |
Brownian diffusion (perikinetic flocculation) Transport in laminar shear (orthokinetic flocculation) Differential settling Turbulent transport |
|
|
|
Destabilization Mechanisms |
Compression of the double layer (DLVO Theory) Counterions adsorption and charge neutralization Interparticle bridging Enmeshment in a precipitate Heterocoaguation |
|
|
|
How to Destabilize Colloids? |
Add coagulant(s) Mixing |
|
|
|
Coagulant |

|
|
|
|
Coagulant Aid |

|
|

