![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Describe the role of the veterinarian technician in the laboratory |
To interpret and generate results |
|
|
|
Define technique |
You have to know what you are doing develop your own way of doing something correctly |
|
|
|
Identify the criteria needed for an efficient veterinarian laboratory and use of quality control |
Dedicated area, sink,storage electrical outlets, a centrifuge, a microscope, microhematocrit, and refractometer, pipettes electronic cell counter |
|
|
|
Identify the proper care and maintenance of various laboratory equipment and supplies |
Periodic calibration of the centrifuge is needed to ensure that the it is reaching the required speed Refractor meters must be calibrated on a regular basis to ensure diagnostic quality results Everything must be put in its proper place area needs to be neat and clean |
|
|
|
Describe the uses and benifits of hematology results |
To screen the general health of an animal to access its overall ability to transport oxygen and defend against infectious agents When combined with the history physical examination and other laboratory findings help to form diagnosis May also indicate a course of treatment for the animal |
An example is to differentiate between anemia caused by internal hemorrhage and that caused by bone marrow depression It has been said that a clinician who relies entirely on laboratory results to make a diagnosis is probably an experience and a clinician who claims not to need a laboratory is uninformed |
|
|
Describe the limitations of hematology results |
The collection and handling of the blood sample or any tissue sample should not be subjected to traumatic physical forces such as being forced rapidly through a small needle or violation or two extreme temperatures of heating or freezing avoid contaminating the sample with foreign materials such as dirt infectious agents chemicals are even water |
All counts of measurements should be done on a blind basis with no comparison to normals our expectations of changes that could lead to a bias in reported results it is imperative that all observations weather normal or abnormal be recorded |
|
|
State laboratory safety precautions |
All biological samples whether blood or other body tissues and fluids should be handled as if potentially infectious No drinking eating use of tobacco products or other hand to mouth activities nor any storage of food or beverages in the laboratory area a laboratory coat should be worn at all times long hair confined and sandals open toed shoes or I can this shoes should be avoided Laboratory gloves should be worn whenever potentially infectious samples are being handled all disposable pointed or cutting instrument should be placed in the appropriate sharps container |
|
|
|
State the functions of blood in the body |
Is to transport nutrition,oxygen, waste products, hormones, carbon dioxide, immune bodies, heat for temperature control, helps contain pH and water, electrolyte value, also helps homeostasis(regulating) and help prevent hemostasis(blood clotting) |
|
|
|
Describe the composition of blood |
Plasma, leukocytes, platelets |
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of blood include color volume and pH |
pH - 7.36(vein) 7.4 (artery) Will not have a nucleus and the cytoplasm is reddish to reddish orange the central pallor present(more prominent in dogs A RBC from the artery will be more of a bright redish color than a RBC from a vein Volume-5-11% of the body weight or 20-50 ml/lb |
The reddish color is caused by hemoglobin the greater the oxygen the brighter red the blood will be |
|
|
Define hematopoiesis |
Is the production of blood cells |
|
|
|
Describe the development of blood cells in the bone marrow |
Rubriblast, Prorubricyte, Rubricyte, Metarubricyte, polychromatophil(immature RBC) Erythrocytes |
|
|
|
Which cell is the father of all blood cells? |
Pluripotential |
Mack daddy cell |
|
|
Define hematocrit |
The percentage of RBCs relative to plasma To separating |
|
|
|
What is the abbreviations for hematocrit |
PCV |
|
|
|
Describe the laboratory use of a hematocrit test |
Looks at how many red blood cells you have can see if the animal is anemic, dehydrated, color Can also look at protein level normal plasma colors will be straw, yellow, or colorless which comes from bilirubin which is a breakdown of hemoglobin |
Cow and horse will have a darker color plasma than a dog our cat color should be described as clear and not cloudy |
|
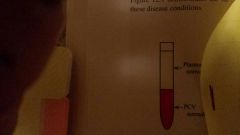
What is this PCV reading |
Normal |
|
|

What is this PCV reading |
Polycythemia |
|
|
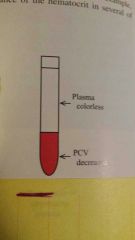
What is this PCV reading |
Bone marrow depression anemia |
|
|
|
Define erythropoiesis |
The formation or production of red blood cells, controlled by the tissue need for oxygen |
|
|
|
State the average lifespan of erythrocytes sites in dogs and cats |
110 days |
|
|
|
Define blood volume |
It's a total blood volume varies between species and depends on species, and breed, age, leanness or fat concentration |
|
|
|
State the effects of blood loss |
If the rate of blood loss is rapid body doesn't have time to react will have a state of shock If the rate of blood loss is chronic the body has time to adjust |
|
|
|
If the animal is anemic..will the hemoglobin be high or low? |
Hemoglobin concentration will be low. Meaning the cell will not be able to carry a lot of oxygen (hypoxia) |
|
|
|
What happens when you reach that level of hypoxia |
The kidneys will be stimulated to produce and release a hormone called erythropoetin will then go through the blood stream to the bone marrow and stimulates RBC's production |
|
|
|
Characteristics of erythrocytes |
Carry hemoglobin which turns into oxygen, transport CO2 back to the alveoli where it is released during exhalation, accumulate oxygen at the alveoli surface, transport and release oxygen to all cells of the body, replace the release oxygen with waste gas CO2 |
|
|
|
Function of RBC's destruction |
Some go through phagocytosis Hemo-iron is converted to ferritin then stored in the liver to be used for hemoglobin synthesis and bilirubin synthesis Globin-is degraded to amino acids |
|
|
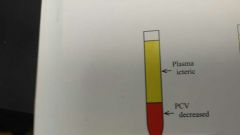
What is this PCV reading and what does is mean |
Hemolytic anemia- is when you have a high plasma and low PCV signs: mucous membrane pallor may be masked by icterus |
|
|
|
What is icterus |
A yellow orange color due to red cell breakdown products in the blood stream |
|
|
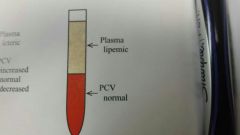
What is the PCV reading |
There is fat in the blood known as Lipemia - which is caused by obesity or not properly fasted before blood collection |
|
|
|
What does it mean when the plasma has a reddish tinge |
Hemolized |
|
|
|
What are the sings of anemia |
Pale mucous membranes, reduced exercise tolerance, tachycardia, and an increased inappropriate respiratory rate with exertional dyspnea |
|
|
|
What is anemia |
"No blood" means low total hemoglobin |
|
|
|
Define polycythemia |
Above normal percentage of erythrocytes in the blood |
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
PCV normal values for a dog |
37-55% |
|
|
|
PCV normal values for a cat |
30-45% |
|
|
|
PCV normal values for a horse |
32-57% |
|
|
|
PCV normal values for a cow |
24-42% |
|
|
|
Hemoglobin values of a dog |
12-18g/dL |
|
|
|
Hemoglobin values of a cat |
8-15g/dL |
|
|
|
Hemoglobin values of a horse |
10.5-18g/dL |
|
|
|
Hemoglobin values of a cow |
8-14g/dL |
|
|
|
List the laboratory test that comprise the CBC |
Indexx Lasercyte and Abaxis |
|
|
|
What are the four words you use to describe plasma |
Yellow, straw, hemolized, or colorless |
You would only use clear to describe plasma color in a cow and a horse |
|
|
What equation do you use to get your hemoglobin estimate |
PCV÷3=_g% |
|
|
|
What equation do you use to get your RBC count estimate |
PCV÷6=_×10^6/mm^3 |
|
|
|
What can a large buffy coat indicate |
That an increase in circulating white blood cells and possibly infection ex. Leukocytosis |
|
|
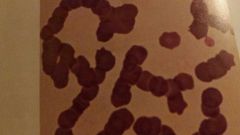
What is happening in this picture
|
Rouleaux-are linear and sometimes branching chains of RBC's may be seen in increased amounts associated with inflammatory disease |
|
|
|
describe the reticulocyte as seen in a peripheral blood smear with the use of special stains |
punctate, aggergate |
|
|
|
explain the use of erthrocytes indices in assessment of anemias |
by cell size and cell color MCV, MCHC, MCH |
|
|
|
MCV (Mean Cell Volume) |
it expresses the average volume of the individual erythrocyte and is calculated (PCV(whole numbers)x10)/RBC count |
|
|
|
MCH( Mean Cell Hemoglobin) |
is used to demonstrate the amount of hemoglobin, by weight, in the erythrocyte (Hb(g/dL)x10)/RBC count |
|
|
|
MCHC (Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration) |
is the concentration of hemoglobin in the average erythrocyte (Hgb.x100)/PCV |
|
|
|
if the MCHC is low what would it be called |
Microcytic Hypochromic |
|
|
|
what are punctate |
they have been around for a while will only have two little dots |
there want be many because they are punks only 2 in a group |
|
|
what are aggregate |
large clumps of reticulum, will eventually mature into punctate in 12-14 hrs and last 10-14 days |
|
|
|
when counting reticulocytes which ones will you count and why |
only the aggeragate because you want to know what the bone marrow is doing and how it is reasoponding |
|
|
|
What are macrocytes |
Are usually juvenile RBC and may indicate a regenerative response to anemia, may be seen with cell maturation disorders |
|
|
|
What are microcytes |
Often associated with deficiencies of essential erythrocytes nutrients (iron) |
|
|
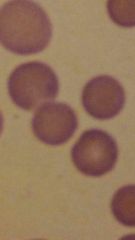
Described these cells |
Spherocytes- will be spherical with a lack of central pallor may be present in low numbers when there is a non immune mediated damage to the RBC formed by macrophages |
|
|
|
What are crenated cells |
Notching and projections on the surface of RBC |
|
|
|
What is a Leptocyte cell |
RBC typically larger with excessive thin membrane and folds two types: target and bar cells Possible liver disease |
|
|

What is this picture showing |
Aggulation- a clump of RBC'S that is usually caused by cross-linking RBC's surface associated with antibodies |
|
|

The pen is pointing at a.. |
Ghost cell-remnant members of RBC'S that undergo intravascular lysis |
|
|

|
Howell-Jolly- are fragments of nuclei |
|
|

What is the pen pointing to |
Basophilic stippling- retained RNA and are most commonly seen during regenerative response in ruminants (lead poisoning) |
|
|
|
What is anisocytosis |
used to describe variation in size of RBC ex. Macrocytes or microcytes |
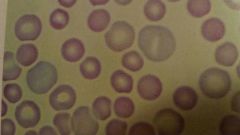
|
|

What word would you use to describe these cells |
Poikilocytosis-any abnormal shape RBC in circulation |
|
|
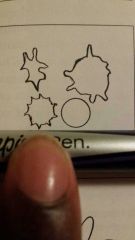
What word describes these cells |
Acanthocyte- RBC with multiple variable size irregular membrane projections that are caused by alterations in the ratio of membrane cholesterol to phospholipids |
|
|
|
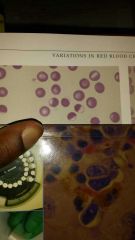
Echinocytes- cells with multiple small delicate regular shaped spines distributed evenly around RBC membranes (vitro artifacts) |
|
|
|
Eccentrocytes- RBC with a cresent shaped clear area that is eccentrically placed "oxidant-induced membrane damage" |
|
|
|
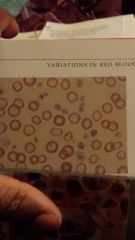
Hypochromasia- a RBC in circulation that has a increased central pallor and decreased staining intensity of membrane "iron deficiency" |
|
|
What are these cells |
Target cells- also known as "codocytes" have an extra round out folding of the membrane in the middle of the cell |
|
|
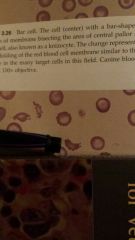
What type of cell is the pen pointing to |
Bar cell- RBC with a central bar shaped out folding also known as "knizocyte" |
|
|
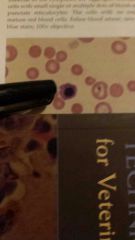
What is the cell that the pen is pointing to |
Schistocytes- are fragments of RBC results from mechanical damage to RBC in circulation ex. microvascular abnormalities, or presence of fibrin strands in the microvasculature |
|
|

What cell Is the pen pointing to |
Ovalocytes- also known as "elliptocytes" cells that are oval with an oval region of central pallor seen with RBC membrane defects |
|
|
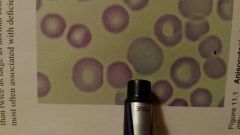
What is the cell that the pen is pointing to |
Nucleated read blood cell- RBC with a nucleus usually lysed before the reticolocytes stage of RBC maturation |
|
|
What cell is the pen pointing to |
Polychromasia - larger cell with a grayish blue tinge, the presence of polychromatophils in the blood |
|
|
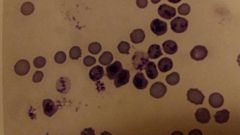
What are these cells |
Reticulocyte- an immature RBC that contains clumps of ribosomal RNA and mitochondria |
|
|
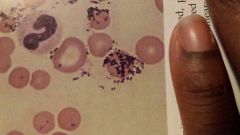
|
Stain precipitate- present as small variable sized or purple granular material |
|
|
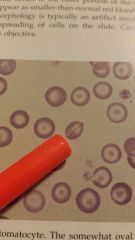
The cell that the pen is pointing to |
Stomatocyte-RBC with a central pallor that is oval to enlongated and take a on the appearance of a mouth |
|
|
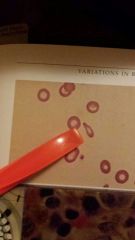
What cell is the pen pointing to |
Teardrop cell- also known as "dacryocyte" results for the failure of the cell to resume it's normal shape after passing through the capillaries |
|
|
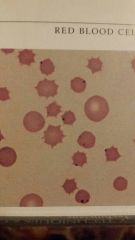
What are the cells with the inclusions in them |
An aphasia marginale- a intracellular blood parasite that causes anaplasmosis in cattle and wild ruminate appears as small dark staining coccia |
Blood parasite |
|
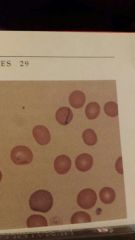
What are the cells that have rod shaped blue structures in them |
Mycoplasma haemacains |
|
|
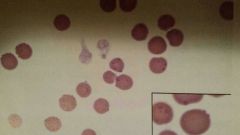
What are the cells with small blue coccoid,rod, and ring shaped organisms |
Mycoplasma haemofelis- also known has feline infectious anemia and stain dark purple |
|
|
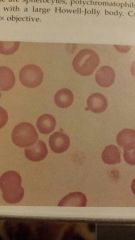
The cell that has a round projection from the surface of the RED are called what |
Heinz bodies |
|
|
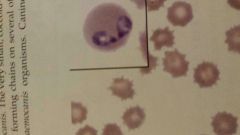
|
Babesia canis |
|
|
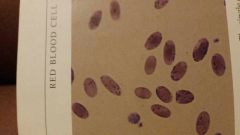
|
Eperythrozoon- organisms can appear coccoid, rod, or ring shaped structures on the surface of the RBC |
|
|
|
What is the total protein of a dog |
5.4-7.5 g/dL |
|
|
|
What is the total protein of a cat |
5.7-7.6 g/dL |
|
|
|
What is the total protein of a horse |
5.4-7.9 g/dL |
|
|
|
What is the total protein of a cow |
6.0-7.5 g/dL |
|

