![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cranial nerves
|
2. Optic 3. Occulomotor 4. Trochlear 5. Trigeminal 6. Abducens 7. Facial 8. Auditory 9. Glossopharangeal 11. Spinal accessory 12. Hypoglossal |
|
|
How to inspect eyes (8)
|
2. Eyebrows 3. Eyelids 4. Lacrimal apparatus 5. Conjunctiva/ Sclerae 6. Cornea, Lens 7. Iris 8. Pupils |
|
|
How to test CNII (3 tests)
|
2. Visual fields - if defect, test one at a time 3. View retina |
|
|
Describe defects of CNII
|
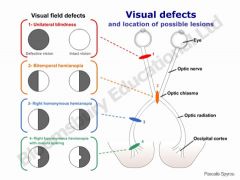
2. Legally blind = 20/200 3. Anopsia - know lesion sites |
|
|
CN II/III tests + what do abnormals mean.
|
2. Pupillary (concensual) reaction to light. If flashed only gets smaller = CNIII lesion. If opposite eye constricts, CNII lesion. 3. Near response |
|
|
Innervation of eye muscles. How to test??
|
LR6, SO4 Rest are III Hit 6 cardinal directions (H shape), lid elevation. |
|
|
Abnormals of occulomotor/CNIII
|
1. Down and out = Superior oblique, Lateral rectus only left. CNIII paralysis. 2. Ptosis. (NOT lid lag) 3. Mydriasis. |
|
|
CN IV abnormalities
|
1. Vertical diplopia, esp. when reading 2. "UP and IN" appearance - SO lesioned |
|
|
How to detect CN6 lesion
|
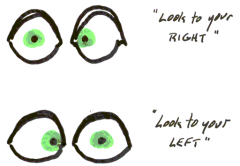
Abducens Lateral deviation |
|
|
How to inspect iris
|
2. Look for crescentic shadow 3. If seen, indicates glaucoma |
|
|
Pupil - 3 abnormalities, clinical correlate
|
1. Miosis: constricted 2. Mydriasis: prolonged dilation 3. Anisocoria : if >5mm, <3mm, or unequal. PS contricts, sympathetic dilates. Argyll Roberson Pupils: Constricts w/focus on near object (near reaction) BUT not with light (concensual light reflex). CAUSES: Neurosyphilis, brain trauma, mitral regurgitation, thiamine (B1) deficiency |
|
|
Horner's syndrome signs
|
1. Miosis, anisicoria, ptosis, anhydrosis (decreased pupil size, pupil size difference, ptosis, sweating on one side) Common causes: CVA, tumor/spinal cord injury, carotid,neck injury, LUNG CANCER, idiopathic, migraines, heterochromia if congenital PANCOAST TUMOR: in apices of lung, can insult autonomic nervous system --> horner's. |
|
|
Marcus Gunn Pupil
|
Use swinging flashlight test Unhealthy eye will constrict less OR, if severe, dilate when shined on |
|
|
Adie's pupil (Tonic - presentation, cause)
|
PARASYMP. denservation. Loss of knee/ankle DTRs. |
|
|
Describe types of strabismus (4) + How to test
|
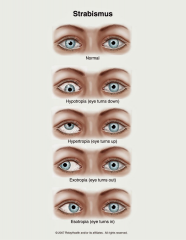
Cover affected eye. When uncovered, affected eye drifts back center. Cover unaffected eye. Unaffected will drift. |
|
|
Nystagmus - presentation, meaning
|
2. Normal in extreme lateral gaze, slightly 3. Seen in neurological disorders |
|
|
Disorders seen under ophtalmoscope (2)
|
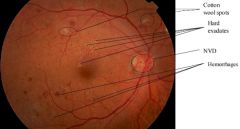
1. Corneal arcus - normal aging, young African americans. Usually benign. White right. 2. Cataract: Clouded appearance in lens. 3. Diabetic retinopathy 4. Hypertensive retinopathy |
|
|
Hypertensive retinopathy presentation
|
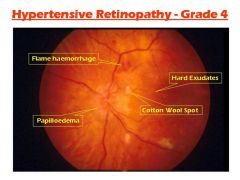
|
|
|
Other abnormalities
|
2. Subconjunctival hemorrhage - harmless |
|
|
Label normal fundus
|
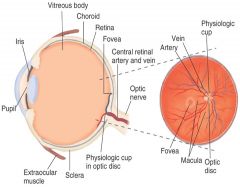
|

