![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
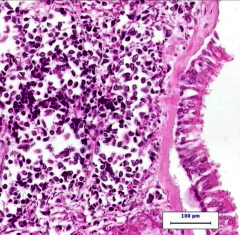
Describe what you see.
Diagnosis? |
--Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium (falling off = artificial) on thickened basement membrane
--Infiltrate of small cells with inconspicuous cytoplasm with larger than normal nuclei (nuclei too large and irregular to be lymphocytes). Diagnosis = small cell carcinoma |
|

What does this patient have?
What is this an important symptom of? |
Nausea
Hypercalcemia of malignancy |
|
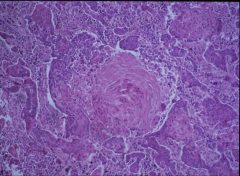
What is the circular structure in the middle?
Where is the neoplasia? What is the diagnosis? What is the most common lung cancer type to cause hypercalcemia? |
Keratin pearl
Dark colored fibrinous looking tissue around the outside of the keratin pearl. Squamous cell carcinoma SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA |
|
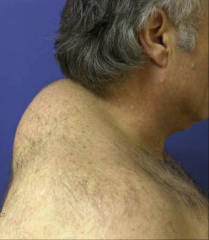
What is this?
What disorder is it commonly seen with? |
A "buffalo hump" fat deposit.
Cushing syndrome |
|
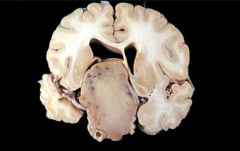
What is this?
How does it relate to Cushing's syndrome? What malignancy is Cushing syndrome also associated with? |
Pituitary adenoma
Most common source of ACTH causing Cushing syndrome Small cell carcinoma of the lung |
|
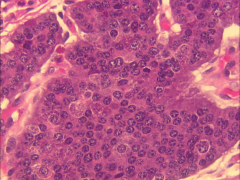
What does this show?
|
Coalescing NESTS of intestinal carcinoid.
"Endocrine pattern" = nests, trabeculae, or spindled cells separated by thin-walled vessels. Uniformity of cells and nuclei, normal nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio, small nucleoli, stippled chromatin No necrosis |
|
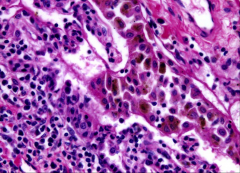
What is this an image of?
Diagnose. Etiology? |
Bronchiole --nectrotizing inflammation, infiltration by lymphocytes, accumulation of macrophages with finely granular brown and black pigment (SMOKER'S MACROPHAGES)
Diagnosis = respiratory bronchiolitis Etiology = smoking |
|
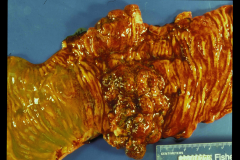
What was happening to the colon?
|
Bile stain on the left side behind obstructing colon cancer.
|
|
|
What is this diagnosis?
A 65-year-old white male car dealer with a history of smoking comes to your ER with cough productive of a small amount of blood and a 20-lb. weight loss over 3 months. He has also had some dyspnea, mild dull chest pain, malaise and fatigue. His temperature is 38, pulse 90, blood pressure 110/60 and respirations 24. He has a few pulmonary crackles, but physical examination is otherwise normal. |
Classic clinical scenario for LUNG CANCER
|
|
|
What is the most common symptom of lung cancer?
What is the second most common symptom? Third most common? Other two common symptoms? |
Cough
Hemoptysis Dyspnea Chest pain and weight loss |
|
|
What is the lung cancer most likely to causes a paraneoplastic syndrome? Why?
|
Small cell carcinoma
It is a neuroendocrine tumor |
|
|
What is a paraneoplastic syndrome?
What percent of patients does it occur in? Does is include cachexia? |
Symptoms not attributable to direct effects of tumor (or hormones native to the primary tumor organ)
10% of patients Does not include cachexia (it's in a class by itself) |
|
|
What are three characteristics of paraneoplastic syndromes?
|
1. Can be the earliest manifestation of occult tumor
2. Can be sickening, even fatal by themselves 3. May mimic metastatic disease |
|
|
What are the three paraneoplastic syndromes to know? Which one is the most common?
|
1. Hypercalcemia (most common)
2. Cushing syndrome (ACTH) 3. Carcinoid syndrome (serotonin) |
|
|
What are the common symptoms of hypercalcemia?
What does the mechanism involve? Treatment? |
NAUSEA, vomiting, constipation, polyuria, disorientation, lethargy, seizures
Mech: parathyroid hormone Treatment: hydration, biphosphates |
|
|
What are some common symptoms associated with Cushing syndrome?
|
Weight gain, central obesity, moon face (FAT DEPOSITION), weakness, hirsutism, hypertension, glucose intolerance, depression, psychosis, broad red abdominal striae, buffalo hump dorsal neck fat deposition, plethora, osteoporosis, menstrual irregularity, muscle wasting, etc.
|
|
|
What are some common symptoms associated with carcinoid syndrome?
|
Attacks of cutaneous FLUSHING (deep red erythema of face and neck) --> may become persistent or cyanotic, diarrhea, cramps, nausea, vomiting, cough, etc.
|
|
|
A young non-smoker develops lung cancer. What is this most likely from?
|
Radon
|
|
|
What is the order of contributors to lung cancer for non-smokers?
|
Radon gas>passive smoking>asbestos>autoimmunity>asthma
|
|
|
How long does it take for smoking to cause lung cancer?
|
40 years
A non-smoker may have had poor DNA repair, poor p53 function, or some other congenital predisposition to neoplasia to cause cancer at such a young age. |
|
|
A 75-year-old black male retiree comes to your clinic with mild lower back pain, mild perineal discomfort, urinary hesitancy, intermittent urinary stream, decreased force of stream and a 5-pound weight loss over 3 months. His temperature is 37, pulse 80, blood pressure 140/90 and respirations 16. He has a firm irregular nodular prostate; physical examination is otherwise normal.
Diagnosis? |
Classical clinical scenario of
PROSTATE CANCER (metastatic) |
|
|
The proportion of prostate cancer patients with symptoms at the time of diagnosis is most likely...
What does diagnosis usually follow? What proportion of lung cancer patients have symptoms at the time of diagnosis? |
30%
PSA screen or rectal examination 90% |
|
|
What is the curative treatment for prostate cancer?
What are the adverse effects of the curative treatment? What are alternative treatments for prostate cancer? What treatment would you advise for this patient? Is the blood level of PSA a sensitive test for prostate cancer? Is the blood level of PSA a specific test for prostate cancer? |
Look up
|
|
|
A 64-year-old white female comes to your clinic with a breast lump. She also has mild upper back pain, mild right upper quadrant abdominal pain, anorexia and mild dyspnea. Her temperature is 37, pulse 80, blood
pressure 120/80 and respirations 20. She has a rock hard, immovable breast nodule with irregular borders and erythema, thickening and dimpling of the overlying skin. She firm enlarged lymph nodes palpable in the axilla, but physical examination is otherwise normal. DIAGNOSIS? |
Breast cancer (metastatic)
|
|
|
What percent of women have no symptoms at the time of diagnosis and is detected by mammography screening?
What percent are diagnosed with mammographically occult cancer? What percent present with a breast mass in the interval between mammograms? |
55%
15% 30% |
|
|
What are the important risk factors for breast cancer?
|
Family history, older age, estrogen, race (white>black, both > Asian), early menarche, late menopause, obesity, fewer pregnancies, later pregnancies, not breast feeding, eating red meat, dietary fat, testosterone level, smoking, moderate alcohol, radiation, nocturnal light exposure, antibiotic use, not exercising, height.
|
|
|
What are 5 direct effects of tumors?
|
Impingement of adjacent structures
Obstruction Functional activity (hormones) Surface ulceration (+/- bleeding, +/- infection) Infarction (+/- rupture) |
|
|
What is tumor state?
What is tumor grade? |
Anatomic extent of tumor (primary tumor size, extent of lymph node and distant metastases)
Qualitative assessment of the differentiation of a tumor (extent to which it resembles normal tissue at primary site) |

