![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Key Attributes to Security Mgmt |
Access control protects your:CIA The following 4 key attributes should be specified: Who has access to the system What resources or data they have access to What operations are permitted Specify individual accountability |
|
|
Accountability Principle |
Accountability is the ability to trace specific system eventsto a single entity such as a process, a user, or device. You cannot share accountability, avoid group credentials Logging (syslog and event logs) is Technical/Logical Monitoring / Auditing policies are Administrative Preserving and Creating summaries of logs is Operational Retention Policies |
|
|
Accountability Principle Can be established by monitoring: |
System Level Events Application Level Events User Level Events |
|
|
Access policy is based on: |
Separation of duties (SOD) Principle Of Least Privilege (POLP) Need To Know (NTK) Compartmentalization Security Domains |
|
|
Your Access Control Policy should: |
State what are the organization expectations Define Standards such as: -How users are identified and authenticated -How credentials are granted -What level of access will be granted Define your requirements Specify responsibilities Define access according to your business needs Provide a centralize point of control Provide a uniform point of control as well |
|
|
Separation of duties (SOD) |
Helps to prevent fraud and errors Require collusion to defeat access control systems A single person cannot complete a critical task alone A single person cannot gain unauthorized access Separation based on sensitivity of task |
|
|
Principle Of Least Privilege (POLP) |
Give user & process only required privilege Removes opportunity to commit a crime Removes ability to abuse of the system |
|
|
Need To Know (NTK) |
Only what is required to complete tasks & Duties Proper clearance must be in place as well Formal Approval from Management and NDA |
|
|
Compartmentalization |
Separates users into group Information does not flow between groups For example: A team for merger and acquisition – Avoid insider trading problem – General population is not aware of activities |
|
|
Security Domains |
Areas of common processes and security controls Separations between Domains Examples: - All users involved in managing finance for example - All users involved in E-Commerce Based on trust between resources and services - Trust is the context in which a program is operating A user belongs to one or more domains Separation can be Physical or Logical |
|
|
Separation of Duties vs Dual Control |
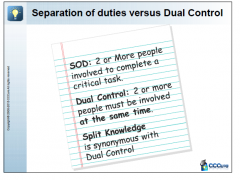
|
|
|
Default Security Stance |
• DENY ALL • PERMIT ALL |
|
|
Deny All |
• Add rules according to business needs • Completely closed by Default • Best choice for security devices |
|
|
Permit All |
• All traffic is allowed • Close unneeded services • You cannot upgrade security • Insecure once, insecure for ever |
|
|
ISSP |
The Information System Security Professionals
Draft polices, standards, procedures, baselines Maintain the documents above Provide guidance on security issues Must be aware of emerging threats Must be aware of legal requirements Must be aware of industry specific regulations Has a good understanding of solutions |
|
|
Data/Information Owners |
Entrusted with company’s information asset Understands risks to information assets
Will define classification on the data Based on criticality, sensitivity, and CIA Will define who has a need to know (NTK) Usually an Executive within the company Ensures the data is properly protected Ensures retention and backup’s are in place Must review classifications at regular interval |
|
|
Data/Information Custodian |
Usually a technical person
Implements controls on behalf of data owners Ensure proper retention and backup Will manage access right to information assets Does not decides who has a need to know Ensures proper maintenance and updates Ensures environmental controls are in place Your system or security administrators |
|
|
Information System Auditors |
Validate compliance with: - Security policies, procedures, standards - Baselines, designs, and requirements Validate appropriateness of controls Act as independent assurance to management Internal and External auditors Their roles are becoming more technical Expect to be able to capture information |
|
|
BCP and DRP Planners |
Develop and Maintain contingency plans Address interruption, disasters, catastrophe Ensures business processes can continue Ensures drills are performed Update the plan as needed Ensure adequacy of alternate site(s) Main point of contact for BCP and DRP |
|
|
Security Administrator |
Manages user’s privileges Creates and Deletes account as required Ensure there is no dormant accounts Ensures minimum level of privileges are given Monitor access aggregation issues Follow the security policies of the company Assist with audits |
|
|
Network/Systems Administrator |
Configures Network and Server Hardware Apply patches and updates Ensure proper testing of updates in the lab first Performs Vulnerability management Is aware of tools related to his tasks Work along with the Security Administrator Operation well done is security |
|
|
Physical Security Staff |
No physical security = No logical security Establish contact with local authorities Maintain and Operate CCTV Ensure physical controls are in good order Burglar Alarms, IDS, Card Readers, etc… Act as a deterrent Must be well trained and competent It is the most effective physical control Validate the service if using outsourcing |
|
|
Administrative Assistant/Secretary |
Plays a very important role Must be trained on security engineering issues Act as a gateway sometimes for visitors Front Desk, Reception Area Must enforce the policy Must take their role seriously Often time trained to help at all cost The customer is always right |
|
|
Help Desk Administrator & Staff |
Must be trained on Social Engineering Issues Solves users problems and issues May identify security problems Must be aware of Incident Response Must be aware of proper escalation procedures Reset passwords Resynchronize tokens Reinitialize Smart Card |
|
|
Control Frameworks |
Ensures Security & Privacy requirements are met NIST SP 800-53 ISO 270001 - Code of Practice for Information SecurityManagement COSO - Committee Of Sponsoring Organizations COBIT - Control Objectives for Information &Related Technology, and ITIL - Information Technology InfrastructureLibrary And many others… |
|
|
Liability |
Determine based on lack of: Due Diligence (identifying risks – Do Detect) & Due Care (taking action – Do Correct) |
|
|
Due Diligence |
-Preemptive efforts made to prevent undue harm -Following Best practices & Standards -Following Consensus of experts -Doing further Research and Analysis |
|
|
Due Care |
Prudent man rule – The care that an ordinarily reasonable and prudent person would use under the same or similar circumstances Determine legal duties What are you doing about it. |
|
|
Main Areas of Knowledge (1 of 6) |
A. Understand and apply concepts of Confidentiality,Integrity, and AvailabilityB. Apply Security Governance Principles through:B.1 Alignment of Security Function to Strategy, Goals,Mission, and objectivesB.2 Organizational processes (acquisitions, divestitures,governance committees).B.3 Security Roles and ResponsibilitiesB.4 Control FrameworksB.5 Due CareB.6 Due DiligenceC. ComplianceC.1 Legislative and Regulatory ComplianceC.2 Privacy Requirements Compliance |
|
|
Legislative & Regulatory Compliance |
Law, Regulations, and compliance must be met You must understand the law of your country You must understand regulations as well They are an important driver to your security Is there any “Safe Harbor” clause A clause that protects you against litigation Or a clause protecting you against penalties Ignorance of the law is not an excuse When needed talk to your legal counsel |
|
|
Privacy Requirements Compliance |
PII – Personally Identifiable Information - Names, CC, Phone Numbers, Address Information is used only for the purpose it was collected Collect only as much and for as long as it is needed Information is properly protected User can review their own information User can get it corrected if inaccurate User MUST consent to sharing with others Beware of penalties if you do not follow the law Have a Privacy Policy on your web site Identify, Classify, Secure, Audit |
|
|
Main Areas of Knowledge (2 of 6) |
D. Understand legal and regulatory issues that pertains toinformation security in a global contextD.1 Computer CrimesD.2 Licensing and Intellectual Property (copyrights, digitalrights management)D.3 Import/Export controlsD.4 Trans-border data flowD.5 PrivacyD.6 Data breachesE. Understand Professional EthicsD.1 Exercise (ISC)2 Code of Professional EthicsD.2 Support organization’s code of ethicsF. Develop and Implement documented security policy,standards, procedures, and guidelines |
|
|
Computer Crimes |
Who commits them? Why are they committed? How are they committed? |
|
|
Why Crimes are Committed – M.O.M. |
Motivations
Opportunities
Means
|
|
|
Motivations |
Who commits these crimes and why What do they get out of these acts |
|
|
Opportunities |
Where do opportunities exist for computer crimes When would someone take advantage of these opportunities |
|
|
Means |
Who has the capabilities to commit these types of crimes |
|
|
Computer Crime Characteristics |
Criminal Profiles Lack of Basic Protection Problems Prosecuting Computer Crimes: |
|
|
Criminal Profiles
|
Hackers and crackers Business competitors Friendly allies and spying Political opponents |
|
|
Lack of Basic Protection |
Lack of awareness Inadequate safeguards Insufficient security staff, skill, resources Lack of incident response capability Companies do not press charges |
|
|
Problems Prosecuting Computer Crimes: |
Complex legal definitions and technical definitions Cross-jurisdiction problems Lack of understanding and skill New types of crimes Private sector lack of reporting Setting appropriate punishments Intangible evidence Not viewed as “serious” crimes |
|
|
Attack Types |
Grudge Terrorist International Warfare Financial Business “Fun” Salami Data Diddling Password Sniffing IP Spoofing Dumpster Diving Masquerading Wiretapping Social Engineering Information Warfare |
|
|
Grudge |
“Get back” at a company Disgruntled employees Political reasons |
|
|
Terrorist |
Using technology to assist in attacks Causing harm against another country |
|
|
International Warfare |
Countries attacking eachother |
|
|
Financial |
E-commerce and banking on-line may experience Loss of funds or financial information |
|
|
Business |
Competitive intelligence through computer relatedattacks |
|
|
“Fun” |
Joy riding attacks |
|
|
Salami |
Skimming a small amount of money with the hopes ofnot being noticed Series of minor computer crimes that are part of a largercrime |
|
|
Data Diddling |
Altering data before it is input into a program or after it isoutput |
|
|
Password Sniffing |
Capture passwords as they travel over a network |
|
|
IP Spoofing |
Use a bogus IP address to hide identity |
|
|
Dumpster Diving |
Go through trash in hopes of finding useful information |
|
|
Masquerading |
Hiding one’s identity or origin of attack |
|
|
Wiretapping |
Eavesdropping on a conversation – passive attack |
|
|
Social Engineering |
Pretending to be someone else to uncover information |
|
|
Information Warfare |
Attacking the information infrastructure of a nation |
|
|
Phreakers |
Telephone fraud 2600 Club Captain Crunch- cereal toy whistle |
|
|
Phone Attacks |
Red Boxing Blue Boxing Black Boxing |
|
|
Red boxing |
Simulating coins dropped in a pay phone |
|
|
Blue Boxing |
Tones used to trick phone company’s system |
|
|
Black Boxing |
Manipulating line voltage |
|
|
Liabilities – who is at fault? |
Did management fail to execute Due Care and/or DueDiligence? Prudent Man Rule -Perform duties that prudent people would exercise insimilar circumstances Downstream Liabilities (when a partner connects to your company or vice versa and partner sues because they get compromised by you) Integrated technology with other companies can extendone’s responsibility outside the normal bounds |
|
|
Legal Liability |
Legally Recognized Obligation Proximate Causation Violation of Law Violation of Due Care Violation of Privacy |
|
|
Legally Recognized Obligation |
A standard exists that outlines the conduct expected ofa company to protect others from unreasonable risks |
|
|
Proximate Causation |
Fault can actually be proven Can prove that he clipped me running down the stairs which caused my injury |
|
|
Violation of Law |
Regulatory, criminal, or intellectual property |
|
|
Violation of Due Care |
Stockholders suits |
|
|
Violation of Privacy |
Employee suits |
|
|
Privacy Issues – Employee Monitoring |
Notify employees of monitoring that may be used Ensure monitoring is done properly according to laws Banner and security awareness Ensure that monitoring is lawful Do not target individuals in monitoring Monitor work-related events: Keystroke Cameras Badges Telephone |
|
|
Personal Data Passed Internationally |
Transborder Information Flow Movement and storage of data by automatic meansacross national or federal boundaries Many European countries have strong restrictions onflow of personal and financial data Bank statements, personal records, mailing lists Know laws before transmitting data through differentareas Route data through other routes, if necessary |
|
|
Types of Common Laws |
Civil Law (tort law- wrongdoing) Criminal Law Administrative Law Intellectual Property Law |
|
|
Civil Law |
Also called tort (harm done to someone) Wrongs against individuals or companies that result indamage or loss No jail time defamation |
|
|
Criminal Law |
Violation of government law that was developed to protect the public Can include jail time assault, battery, theft, DUI |
|
|
Administrative Law |
Violation of a regulatory standard that regulates theperformance and conduct of a business Different types of companies have different industryregulations they must abide by |
|
|
Intellectual Property Law |
Protecting products of the mind Company must take steps to protect resources coveredby these laws or these laws may not protect them purchasing license for all software |
|
|
Intellectual Property |
Trade Secret Copyright Trademark Patent |
|
|
Trade Secret |
Resource must provide competitive value Protect from unauthorized use or disclosure Proprietary to a company and important for survival Something that gives you a competitive advantage. example: Pepsi ingredient was going to be leaked |
|
|
Copyright |
Protects expression of ideas rather than the ideas themselves Author to control how work is distributed, reproduced,used Protects the expression of the resource instead of theresource itself **anything you write yourself is copyrighted. must have notes so people cant say I did not know |
|
|
Trademark |
Protect word, name, symbol, sound, shape, color orcombination used to identify product to distinguish fromothers Protect from someone stealing another company’s “look and feel” |
|
|
Patent |
Protection for those who have legal ownership of aninvention Invention must be novel and non-obvious Owner has exclusive control of invention for 20 years - Cryptographic algorithm |
|
|
(ISC)2 Code of Ethics |
Protect society, the commonwealth, and the infrastructure Act honorably, honestly, justly, responsibly, and legally Provide diligent and competent service to principals Advance and protect the profession |
|
|
Internet Activities Board – RFC 1087 |
Committee for Internet design, engineering, & management Internet use is seen as a privilege Deemed unethical: - Purposely seeking to gain unauthorized access toInternet resources - Disrupting the intended use of the Internet - Wasting resources through purposeful actions - Destroying the integrity of computer-based information - Compromising the privacy of others - Involving negligence in the conduct of Internet-wideexperiments |
|
|
Program/Corporate Security Policy |
A high-level document stating management’s intentionsregarding security. It contains information on company culture, goals,objectives, and indicate what is acceptable withindifferences areas of the company. Policies might be to meet compliance (mandatory), legal, orregulatory requirements and obligations. Enforcement is the key, do not use the CYA approach Policies should focus on desired results Standards, Procedures, Guidelines, and Baselines will bederived from the policy. |

