![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
CTR(cathode ray tube) |
A CTR monitor has three color beams (red,green,blue) directed at a phosphorous dot on the back of the monitor tube. The result is a single image on the screen called a pixel, or picture element |

|
|
|
CTR 2 |
Dot pitch is the distance between like-colored phosphorous dots on adjacent dot triads. The lower the dot pitch, the sharper the image |
|
|
|
LCD (liquid crystal display) |
Two glasses substrates have a thin layer of liquid crystal between them. One glass substrate is the color filter, with 3 main colors--that allow millions of colors to be displayed be displayed |
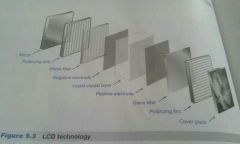
|
|
|
TFT(thin film transistor) (LCD 2) |
The other glass substrate is the TFT array, which has the tech to direct the liquid crystal to block the light |
|
|
|
Backlight (LCD 3) |
A backlight (that can be a fluorescent lamp or LED tech) extends behind the combined glass assembly, and the light is always on. This is why an LCD monitor appears to sometimes glow even if it's off and why crystals are needed to block some of the light to create the intensities of light. |
|
|
|
# LCD |
Liquid crystals are sensitive to temperature changes. Laptop displays may appear distorted in cold or hot temperatures due to liquid crystals |
|
|
|
LED (light emitting diode) |
A low powered, low heat, long lasting electronic device used in many technologies--calculators, home,business, auto lighting, fiber optics, displays. LED displays still use liquid crystals;the displays just use an LED backlight instead of CCFL. LED displays have better color accuracy and are thinner than the LCDs and CCFLs |
|
|
|
OLED (organic LED) |
Does not require backlight like LCDs but has a film of organic compounds placed in rows and columns that can emit light. It is light weight and has a fast response time, low power usage, and a wide viewing angle |
|
|
|
DLP (digital light processing) |
A Texas instrument tech used in projectors and rear projection TVs. DLP has an array of mounted miniature mirrors, one of which is smaller than the width of a human hair and represents one or more pixels |
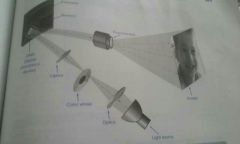
|
|
|
DLP 2 |
The mirrors are used to create a light or dark pixel on a projection surface by being repositioned to different angles to reflect light. A color wheel or LEDs are used for the primary colors red, green, blue |
|
|
|
Plasma |
Displays that work similarly to LCDs except that they have plasma gas in little chambers. When electricity is applied inside the chambers, exciting electrons hit red, green, blue phosphorous dots that glow. |
|
|
|
# LCDs plasma CTR |
LCDs take less energy that CTRs. Many believe plasma displays require less energy than CTR but that's not true |
|
|
|
(1) Accelerometer |
The screen orientations of mobile devices have been greatly enhanced due to accelerometers and gyroscopes
An accelerometer detects the screen orientation and adapts what is shown on the screen based on that orientation |
|
|
|
(2)Gyroscope |
A gyroscope measures and maintains that orientation These technologies allow you to turn an ipad horizontally to better see a picture in wide format |
|
|
|
Resolution |
The maximum number of pixels on the monitor. Two numbers separated by an x (meaning by) describe a monitors resolution, such as 1024x768. First number describes how many pixels can fit horizontally and the second vertically |
|
|
|
Refresh rate |
The monitor refresh rate is for a specific resolution. If the electron beam has to handle more pixels, it will naturally take longer |
|
|
|
Refresh rate |
In CTRs, the maximum times a screen is scanned or redrawn in one second. Measured in hertz (hz). An electron beam continuously sweeps left to right, scanning every row of pixels |
|
|
|
# settings |
Ipad/apple- general settings Android- general settings |
|
|
|
PASSIVE MATRIX/STN (SUPERWRIST NEMATIC) # basic types of LCD |
Passive matrix-cheaper one. Made up of two rows and columns conductors. Each pixel is located at the intersection of a row and a column(cells) current on yhe grid determines whether a pixel us turned on or off. Each pixel has three cells in a color monitor(RGB) |
|
|
|
Active matrix # two basic types of LCD |
Active matrix displays have a transistor for each pixel. The number of transistors depends on the maximum resolution. 1280x80p requires 1,024,000 transistors. This technology provides a higher display. They take more power than passive matrix but both use less than CTR |
|
|
|
Viewable size |
The diagonal length of the LCD screen surface. Sometimes called VIS (viewable image sizes |
|
|
|
Native resolutions |
The optimum setting for LCD, shown as the number of pixels that go across the screen followed by the number of pixels that go up and down the screen. Examples include 1024x768 and 1280x800 |
|
|
|
Aspect radio |
A ratio monitor width to height. Common monitor aspect ratios are 4:3 or 5:4, but newer widescreen formats such as 16:9 or 16:10, are becoming more prevalent |
|
|
|
Contrast ratio |
The difference in light intensity between the brightest white and darkest black, but measured in different ways by manufacturers. A higher contrast ratio such as 800-1 is better than 500-1 |
|
|
|
Lumen |
A measure of light output or brightness--how much visible light is coming out of equipment such as lamps, lighting equipment, or projectors. This measure is important when comparing products for a room that has lots of exposure to sublight, for example |
|
|
|
TN (twisted nematic) (LCD technologies) |
The majority of displays use this technology. Cheapest to make and fastest to display |
|
|
|
VA (vertical alignment) (LCD technologies) |
Better viewing angles, color, and brightness, but response time is not too good |
|
|
|
IPS(in plane switching) (LCD technologies) |
A Hitachi tech that tends to be pricey and can have a slow response time, but these have really good color and viewing angles |
|
|
|
PLS (plane to line switching) (LCD technologies) |
A Samsung technology that has brighter and clearer images,improved viewing angle, and low production costs |
|
|
|
Thunderbolt port |
A new type of Port seen on PCIe cards or apple computers. Looks like mini display port, but it has a lightning bolt beside it. Can provide power to up to 7 daisy chained devices(upto 10.5w) |

|
|
|
KVM switch (keyboard, video, mouse) |
The ability to use the same monitor for two or more different computers.
Allows at least one mouse, one keyboard and one video output to be used by two or more pcs |

|
|
|
Composite video |
Normally a yellow port (Labeled video) the audio RCA ports are normally red and white |
|
|
|
Component/RGB video |
Analog ports are normally colored red, green, and blue and have symbols Y (brightness) Pr Pb(color difference signals) above them |
|
|
|
Privacy filter Privacy screen |
Distorts the display output for anyone except for the person looking directly at the screen |
|
|
|
GPU (graphics processing unit) Video processor Video compressor Video accelerator |
Some video adapters have their own processor called GPU.
The GPU assists in video communication between the adapter and system processor. Commonly have fans and heat sinks. Found in smartphones,gaming, tablets,laptops. 64-128 bit processors |

|
|
|
TV tuner card |
A specialized of video is with TV tuner and video capture cards. Allows TV signals to be brought into the computer and output to the monitor. Some TV tuner cards have the ability to record video. |

|
|
|
Video capture card |
Has specialized software that allows video to be captured from a camara, tape, VCR, game console, TV channel, optical media, recorder, or live audio and video and manipulated in presentation, archive file, document, streamed online. |
|
|
|
Shared system memory Shared video memory |
When motherboard ram is being used in addition to video card ram.The amount of motherboard RAM being used. |
|
|
|
Artifact |
An artifact is something that appears on your screen that should not appear, such as green dotted or vertical lines, tiny glitters, unusual patters. Caused by overheating GPU, insufficient air flow, bad video driver, intergrated chip going bad |
|
|
|
Paper transport (Printer subsystem) |
Pushes or rolls paper through printer. Can be done using a belt, tractor feed, rollers, duplexer(Allows printing on both sides) |
|
|
|
Marking(engine) (Printer subsystem) |
Parts responsible for placing the image on the paper. This Includes ribbons,ink,cartridges,toner cartridges, any moving parts inside these, and anything else needed to print the image |
|
|
|
Print engine (Printer subsystem) |
Brains of the operation. Accepts data and commands stomach the computer and translates these commands into motion. Redirects feedback to the computer |
|
|
|
Print server |
A printer can attach to a device called an external print server, and the print server attaches to the network |

|
|
|
Impact(dot matrix printer) (Printer categories) |
Good for text printing of multiple copies and can produce limited graphics. Uses ribbons, which keeps costs down. The only printer that can do multiple part forms and supports 132 column paper |
|
|
|
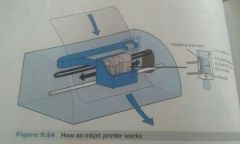
Ink jet (Printer categories) |
Quiet,light,higher quality graphics than dot matrix (impact) uses print cartridge that holds ink used($10-$60) can print 100-200 pages. Best for color printing |
|
|
|
Laser (Printer categories) |
Produces highest quality output at fastest rate. Cartridge cost ($20-$350) common in corporate network environment. Used for graphic design & computer generated art. Some produce color output, but at much higher cost. Some have stippling capabilities |
|
|
|
Thermal (Printer categories) |
Uses special paper that is sensitive to heat. Image is created where the heat is applied. Commonly used during as ticket printers or receipt printers. |
|
|
|
Print head |
Impact printers are commonly called dot matrix printers because of the way they create an image on a paper. Such printer has a print head that holds tiny wires called print wires |

|
|
|
Print wires |
The wires individually strive a ribbon hard enough to create a dot on the paper. The dots collectively form letters or images. |
|
|
|
CPS (characters per second |
The speed at which the print head can place characters on a page is its CPS rating. The number if print wires on the print head determines the quality of the printing;the more print wires, the better the print quality |

|
|
|
DPI |
number of dots per inch a printer outputs. The memory Higher the DPI, the better the quality of ink jet or laser printer output |
|
|
|
#? Fuser cleaning pad Fuser roller |
A fuser cleaning pad above the the top fusing roller lightly coats the roller with silicon oil to prevent the paper from sticking to the roller, which is often coated with teflon. |
|
|
|
Processing/ Faster image processing (Laser printer processor steps) |
Gets data ready to print. Laser printer converts data from the printer language such a *HPPCL (hewlett-packyard printer control language) *Adobe postscript, *Microsoft openXPS (open XML paper specification) into a bitmap image. Made up of very closely spaced dots. Each row of dots is a scan line |
|
|
|
Charging/conditioning (Laser printer processor steps) |
Gets the drum ready for use. Before any info goes into the drum, the entire drum must have the same voltage level. |
|
|
|
Conditioning roller/primary corona (Charging/conditioning 2) |
Has up to 6000VDC applied to it. A primary control grid located behind the corona wire or conditioning roller that controls the amount of voltage applied to the drums surface (approx -6000to-1000 volts ) the drum gets a uniform electrical charge |
|
|
|
Exposing/writing phase (Laser printer processor steps) |
Puts 1s and 0s on the drum surface. Wether the printer uses a laser beam or an LED array, the light reflects to the drum surface in the form of 1s and 0s. Everyplace the beam touches, the drum's surface voltage reduces to approx -100V (from the very high negative voltage level). The image on the drum is nothing more than dots of electrical charges |
|
|
|
Developing (Laser printer processor steps) |
Gets toner on the drum(develops the image) a developing cylinder (developing roller) us inside the toner cartridge and contains a magnet that runs the length of the cylinder. When the cylinder rotates, toner is attracted to the cylinder because the toner has iron particles in it. The toner receives a negative electromagnetic charge. The magnetic charge is a voltage level between -200 and -500 volts. The magnetized toner particles are attracted to the places on the drum where the light beam strikes |
|
|
|
Density controller blade |
Controls the amount of toner allowed through the drum. The image Is no longer transparent on the drum. The image is black on the drum surface |
|
|
|
Transferring (Laser printer processor steps) |
Transfers an image to paper. A transfer corona (roller/pad) is located at the bottom of the printer. It places a positive charge at the back of the paper. The positive charge is strong enough to attract the negatively charged toner particles from the drum. The particles leave the drum and go onto the paper. At this point, the image is on the paper, but the particles are held only by their magnetic charge |
|
|
|
Fusing (Laser printer processor steps) |
Melts the toner onto the paper. Her pressure make the image permanent on the paper. The paper, with the toner particles clinging to it, immediately passes through fusing rollers or a belt that apply pressure to the toner. The top roller applies intense heat (350F) to the toner and paper that literally squeezes and Melts the toner into paper fibers |
|
|
|
Cleaning (Laser printer processor steps) |
Wipes off any toner left on the drum. Continuous cycle. During the cleaning stage a wiper blade or brush clears the photosensitive drum of any excess toner.then an erase lamp neutralizes any charges left on the drum so the next printed page begins with a clear drum |
|
|
|
Feed assembly |
Used to move the thermal paper through the printer |
|
|
|
Print driver |
Piece or software specifically written for a particular printer when that printer is attached to a computer running a specific opera system |
|
|
|
Print spooler Print manager |
Software program that intercepts an applications request to print. Instead of going directly to the printer, data goes the hard drive |
|
|
|
# |
The printing hardware subsystem consists of the printer,cable,and communications port. If something is wrong with the hardware, the problem is normally in one of these aread |
|
|
|
# a USB cable can be rated as superspeed, hi-speed, low speed |
The super speed and hi-speed cables have more shielding and can support higher speeds. If a superspeed or hi-speed device attaches to a low speed cable, the device operates at the lower speed |
|

