![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
DRAM (Dynamic RAM ) |
One of the two types of RAM. Less expensive than SRAM. with DRAM, the 1s and 0s inside the chip must be refreshed. Over time, rhe charge, which represents info inside a DRAM chip,leaks out. (Most memory inside motherboard is DRAM) |
|
|
|
Refreshing |
Information stores in 1s and 0s periodically rewritten to the memory chip through refreshing. The refreshing is accomplished inside the DRAM while other processing occurs. It's why DRAM chips are slower than SRAM |
|
|
|
# |
Most memory in a motherboard Is DRAM, but a small amount of SRAM can be found inside the processor |
|
|
|
Cache memory / SRAM |
Can be found inside processor or its housing or motherboard. Cache memory Holds the most frequently used data so the CPU does not return to the slower DRAM chips to obtain data. |
|
|
|
SO-DIMM (small outline DIMM) |

|
|
|
|
# |
DDR2-800 is a type of DDR2 memory that can run. On a 400Hz front side bus (the number after the DDR2 is divided in half) |
|
|
|
# how parity works |
If |
|
|
|
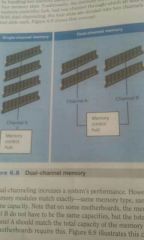
Dual channel |
A duel channel means that the motherboard memory controller chip handles processing of memory requests more efficiently by handling two memory paths simultaneously |
|
|
|
Trippe channel Memory
Quadruple channel Memory |
Three memory modules work together
Increases data transfer rate between the DRAM memory and the memory controller hub by adding more channels of communication between them. |

|
|
|
Acess time |
Describes how fast info goes into a memory chip or is removed from the chip and is measured in nanoseconds(ns) as for MHz or PC ratings, the higher the number is the faster the speed |
|
|
|
CL (column address strobe [CAS] latency) rating |
Is the memory address. RAM is the amount of time (clock cycles) that passes before the processor moves on to the next memory address. |
|
|
|
# |
RAM is made up of Cells where data is held. A cell is the intersection of a row and a column. |
|
|
|
Dual voltage memory |
Motherboards support dual voltage memory, which means the motherboard supports the memory module that runs at the lower 1.35V level. 1.35V memory modules use less power and generate less heat. All memory modules must be 1.35V modules to operate at 1.35 volts |
|
|
|
Virtual memory |
Is a method of using hard disk space as if it were RAM. Virtual memory allows the operating system to run large applications and manage multiple applications that are loaded simultaneously. |
|
|
|
Swap file/page file/paging file |
A block of hard drive space that applications use like RAM. |
|
|
|
Swap file (2) |
Allows your computer's operating system to pretend that you have more RAM than you actually do |
|
|
|
Pages (look at page |
All memory space is a devided into 4KB blocks of memory called pages
A transfer of pages between main memory and auxiliary store, such as a hard disk drive, is referred to as paging or swapping |
|
|
|
PAE (physical address extension) |
A method of converting a computer's memory (RAM) and other virtual memory, into general system memory. This can only be done in systems that are 32-bit, use 86 processors and have more than 4 (GB) |
|
|
|
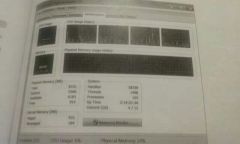
Performance utility5 |
Within task manager, monitors memory usage. Press ctrl, alt, Del to acess task manager |
|
|
|
Total physical memory (Task manager performance tab) |
The amount of RAM installed |
|
|
|
Cached physical memory (Task manager performance tab) |
Memory pages that could be written to disk and be made available |
|
|
|
Available physical memory (Task manager performance tab) |
The amount of memory (physical and paged) for application use |
|
|
|
Free physical memory |
The amount of available RAM |
|
|
|
Paged kernel memory (Task manager performance tab) |
Memory that can be used by applications as needed that can be copied to the paging file (which frees up RAM) |
|
|
|
Non paged kernel memory (Task manager performance tab) |
This memory is only available to the operating system and stays in RAM |
|
|
|
Handles (Task manager performance tab) |
The number of resources the operating system is currently dealing with |
|
|
|
Threads (Task manager performance tab) |
The number of objects contained within currently running processes that are executing program instructions |
|
|
|
Processes (Task manager performance tab) |
A running executable program, such as notepad or a service that is currently running |
|
|
|
Up time (Task manager performance tab) |
How long the system has been up |
|
|
|
Commit (Task manager performance tab) |
A snapshot of virtual memory requests- note that if the commit charge exceeds the total physical memory, the system is probably paging to the hard disk too much. Add more RAM |
|
|
|
NT virtual DOS machine (NTVDM) |
A technology that allows running 16 bit/32 bit DOS and 16 bit windows programs on Intel 80386 or higher when retest already another operating system. It simulates a 486 computer running DOS |
|
|
|
Virtual machine |
Allows you to reduce hardware costs by running multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single computer (without one interfering with the other) |
|
|
|
Flash memory |
A type of non vilotile, solid state memory that holds data even when the power Is off. PCs use flash memory as a replacement for the BIOS chip |
|
|
|
* |
SRAM needs constant power and DRAM need to be refreshed |
|
|
|
Compact flash (CF) |
Has two main standards: compact flash and CF+. Compact flash is a small, 50 pin removable storage device that allows speeds up to 133MBps. Can store up to 137GB |
|
|
|
CF+ |
The CF+ standard allows increased functionality with cards available for ethernet, fax/modem/wireless, and Barcode scanners |
|
|
|
USB FLASH drive/memory bars/sticks/thumb drives |
Allows storage up to 256GB with higher capacities expected |
|

