![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Red Blood Cells Alternative name? Function? Life span? |
Erythrocytes To carry oxygen 120 days |
|
|
|
White Blood Cells Alternative Name? Function? Life Span? |
Leucocytes Remove dead or injured cells and invading micro organism Few mins-few years |
|
|
|
Platelets Name? Function? Life Span? |
Thrombocytes Normal blood clotting 7 days |
|
|
|
Plasma Name? Function? Life span? |
Transport dissolved substances and plasma proteins and hormones and wastes Life time |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
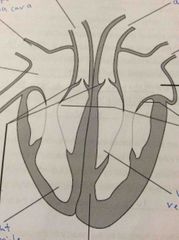
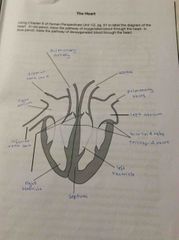
Left hand side valve? |
Bicuspid |
|
|
|
Right side valve? |
Tricuspid |
|
|
|
Heart is surrounded by membrane |
Pericardium prevents heart from overstretching |
|
|
|
Valve in at entrance of arteries? |
Semi-lunar valves |
|
|
|
What artery goes to Lungs? |
Pulmonary artery |
|
|
|
Artery that goes to body? |
Aorta |
|
|
|
Movement of blood around body? |
Circulation |
|
|
|
pulmonary circulation begins where? |
Movement of blood goes to lungs from right ventricle to left ventricle |
|
|
|
Systemic circulation? |
Supply blood to rest of body from left ventricle to right ventricle |
|
|
|
Artery? |
Carries blood away from heart Forced into arteries by powerful elastic thick walled ventricles that cope with pressure Arteries divide into smaller ones called arterioles |
|
|
|
Capillary? |
Microscopic blood vessels carry blood close to every cells Thin walled (one cell thick) so diffusion of nutrients |
|
|
|
Veins? |
Capillaries join to form slightly larger blood vessel called venules. Venules join together to form veins. |
|
|
|
Superior vena cava? |
Veins from arms heads neck |
|
|
|
Inferior vena cava? |
Veins from legs torso and internal organs |
|
|
|
Vein that comes from lungs? |
Pulmonary vein |
|
|
|
Vasoconstriction |
When circular muscle in artery wall contracts reducing diameter of artery and reduce blood flow and heat |
|
|
|
Systole |
Contraction of chamber Pumping phase |
|
|
|
Diastole |
Relaxation of chamber Filling phase |
|
|
|
Cardiac cycle? |
Contraction of both atria (Atrial Systole) pumps blood to ventricles 0.1 secs 2nd part of heartbeat Contraction of ventricles (ventricular systole) pumps blood to arteries 0.3 secs final part Relaxation of all four chambers (diastole) 0.4 secs |
|
|
|
Blood clotting? |
Formation of threads of insoluble fibrin which form meshwork that traps blood cells, platelets and plasma. Mesh + trapped materials = clot Clot retraction Threads become denser and stronger pulling edges of damaged blood vessels together. Serum squeezed out then clot dries and forms scab preventing entry of infecting microorganism |
Clot retraction |
|
|
Explain the Lymphatic system |
Consists of lymph capillaries, lymph vessels, lymph nodes. Arterial end of blood capillary, fluid (lymph) leaks due to high pressure Lymph pushed along the vessel via contraction action of skeletal muscles whilst valves prevent backflow of lymph Lymph nodes (lymph glands) defend against diseases Neck armpit groin Shaped like beans and contain framework of lymph tissue containing cells (lymphocytes, macrophages) and plasma. Lymph traps nodes large particles (bacteria) are trapped in meshwork of fibres and destroyed by macrophages (process is Phagocytosis) |
Define? Consists? How? Where? Structure? Function? |
|
|
Define Lymphatic system |
Lymphatic system is a one way system which carries fluid away from tissues and returns the fluid back to circulatory system |
|
|
|
Oxyhaemoglobin |
Oxygen carrying molecule Haemoglobin + oxygen <-> oxyhaemoglobin 3% blood plasma 97% red blood cells |
|
|
|
Carbaminohaemoglobin |
Haemoglobin + CO2 <-> carbaminohaemoglobin 8% plasma 22% red blood cells 70% hydrogen carbonate ions Co2 + h2o <-> h2co3 <-> h(+) + HCO3(-) |
|
|
|
Circulatory system |
Responsible for transporting substances to the cells while at the same time be removing waste products. |
|
|
|
Substance to cells |
Oxygen Amino acids Glucose Vitamins Minerals Fatty acids Glycerol Hormones |
|
|
|
Wastes removed for cells |
CO2 Urea Utica acid Drugs (antibiotics) |
|
|
|
Vasodilation |
When circular muscle in artery wall relaxes and blood pressure increasing diameter of artery and increase blood flow and heat |
|
|
|
Universal recipient |
AB+ No antibodies to A B or Rh |
|
|
|
Universal Donor |
O- No A B or Rh antigens |
|
|
|
What would happen if person A was given blood transfusion of B- |
Die as they are incompatible and cause erythrocytes to clump together (agglutination) Foreign cells clump together and then disintegrate |
|
|
|
Group A Red blood cell type? Antibodies in plasma? Antigens in blood cell? |
A Anti - B A antigen |
|
|
|
Group B Red blood cell type? Antibodies in plasma? Antigens in blood cell? |
B Anti - A B- antigen |
|
|
|
Group AB Red blood cell type? Antibodies in plasma? Antigens in blood cell? |
AB none A+B antigen |
|
|
|
Group O Red blood cell type? Antibodies in plasma? Antigens in blood cell? |
O Anti - A+ B None |
|
|
|
Define Blood transfusion |
Blood transfusion can be given to a person suffering from excessive blood loss some types of ill conditions |
|
|
|
Rh |
Based on antigens that occur on surface of red blood cells Rh negative person ca produce antiRh antibody |
|
|
|
Antigen |
Substance that is capable of stimulating formation of specific protein (antibody) |
|

