![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Open circulatory system |
A circulatory system in which fluid called hemolymph bathes the tissues and organs directly and there is no distinction between the circulatory fluid and the interstitial fluid
Ex. Found in arthropods and molluscs |
|
|
|
Closed circulatory system |
A circulatory system in which blood is confined to vessels and is kept seprrate from the interstitial fluid heart |
|
|
|
Heart |
A muscular pump that uses metabolic energy to elevate the hydrostatic pressure of the circulatory fluid (blood or hemolymph). |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular system |
A closed circulatory system with a heartlands branching network of arteries, capillaries, veins. This system is a Characteristic of Vertebrates |
|
|
|
Artery |
A vessel that carries blood away from the heart to organs throughout body |
|
|
|
Artery |
A vessel that carries blood away from the heart to organs throughout body |
|
|
|
Arterioles |
a vessel that conveys blood between an artery and a capillary bed |
|
|
|
Capillary bed |
A network of capillaries in a organ |
|
|
|
Capillary |
A microscopic blood vessel that penetrates the tissues and consist of a single layer of endothelial cells that allow exchange between the blood and interstitial fluid |
|
|
|
Venules |
A vessel that conveys blood between a capillary bed and a vein |
|
|
|
Vein |
A vessel that carries blood toward the heart |
|
|
|
Hepatic portal vein |
Carries blood from capillary bed in digestive system to capillary beds in the liver |
|
|
|
Hepatic portal vein |
Carries blood from capillary bed in digestive system to capillary beds in the liver |
|
|
|
Hepatic vein |
Once the blood from the digestive system reached the liver, the blood from the liver than passes into the hepatic vein, which conducts blood toward the heart |
|
|
|
Atria |
Chamber that receives blood from body |
|
|
|
Atria |
Chamber that receives blood from body |
|
|
|
Ventricle |
Chamber that's responsible for pumping blood it of heart to the body |
|
|
|
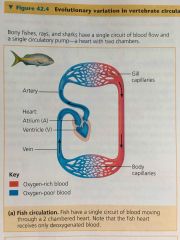
Single circulation |
A circulatory system consisting of a single pump and circuit, in which blood passes from the sites of gas exchange to the rest of the body before returning to the heart Ex. Fish |
|
|
|
Double circulation |
A circulatory system consisting of separate pulmonary and systemic circuits, in which blood passes through the heart after completing each circuit |
|
|
|
Systemic circuit |
The branch of the circulatory system that supplies oxygenated blood to and carries deoxygenated blood away from organs and tissues throughout the body |
|
|
|
Pulmonary circuit |
The branch of the circulatory system that supplies the lungs |
|
|
|
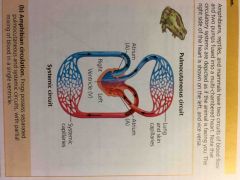
Pulmocutaneous circuit |
A circulatory system in many amphibians that supplies the lungs and skin |
|
|
|
Cardiac cycle |
The alternating contractions and relaxations of the heart |
|
|
|
Systole |
Contraction of heart |
|
|
|
Systole |
Contraction of heart |
|
|
|
Diastole |
Relaxation phase of heart |
|
|
|
Cardiac output |
The volume of blood pumped power minute by each ventricle of the heart |
|
|
|
Systole |
Contraction of heart |
|
|
|
Diastole |
Relaxation phase of heart |
|
|
|
Cardiac output |
The volume of blood pumped power minute by each ventricle of the heart |
|
|
|
Heart rate |
Frequency of heart contraction in beats per minute |
|
|
|
Stroke volume |
Amount of blood pumped by a ventricle in a single contraction. About 70mL.
72 beats per minute |
|
|
|
Atrioventricular valve |
Lies between each atriumand ventricle |
|
|
|
Atrioventricular valve |
Lies between each atria and ventricle |
|
|
|
Seminar valve |
Located at the two exits of the ventricle |
|
|
|
Lymphatic system |
A system of vessels and nodes, separate from the circulatory system, that returns fluid, proteins, and cells to the blood. |
|
|
|
Lymph |
The colourless fluid, derived from interestrial fluid, in the lymphatic system of Vertebrates. |
|
|
|
Plasma |
The liquid matrix of blood in which blood cells are suspended. 90% water |
|
|
|
Platelets |
Fragments of cells from a bone marrow cell involved in blood clotting |
|
|
|
Erythrocyte |
A blood cell that contains hemoglobin, an iron containing protein, which transports oxygen. Also called a red blood cell |
|
|
|
Leukocytes |
A blood cell that functions in fighting infections. Also called a white blood cell. |
|
|
|
Thrombus |
A clot that forms in a blood vessel and blocks the flow of blood |
|
|
|
Gas exchange |
The uptake of molecular oxygen from the environment and discharge of CO2 into the environment |
|
|
|
Partial pressure |
The pressure exerted by a particular gas in a mixture of gases(for instance, the pressure exerted by oxygen in air ) |
|
|
|
Ventilation |
The flow of air or water over a respiratory surface |
|
|
|
Countercurrent exchange |
The exchange of a substance or heat between two fluid flowing in opposite directions Ex. Blood in a fish gill flows in the opposite direction of water padding over the gill, maximizing diffusion of oxygen into and CO2 out of the blood |
|
|
|
Tracheal system |
In insects, a system of branched, air filled tube that extend throughout the body and carries oxygen directly to Cells |
|
|
|
Lungs |
An infolded respiratory surface of a terrestrial vertebrate, that connects to atmosphere by narrow tubes.found in open circulatory systems. Functions for gas exchange. |
|
|
|
Larynx |
Containing the vocal cords. Above trachae |
|
|
|
Trachea |
After larynx the trachae extends to the bronchi (wind pipe) |
|
|
|
Bronchi |
Trachae branches into two bronchi, one leading to each lung. |
|
|
|
Bronchi |
Trachae branches into two bronchi, one leading to each lung. |
|
|
|
Bronchioles |
Bronchi branched into finer tubes that transport air to alveoli |
|
|
|
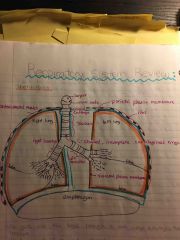
Alveoli |
Air sacs clustered at the tip of the bronchioles |
|
|
|
Surfactant |
A substance secreted by alveoli that decrease surface tension in the fluid that coats the alveoli |
|
|
|
Ventilation |
|
|
|
Breathing |
Process that ventilates lungs. Alternating inhalation and exhalation of air |
|
|
|
Positive pressure breathing |
A breathing system in which air is forced into lungs. Amphibians use this method
Ex.frogs |
|
|
|
Parabronchi |
Gas exchange In bird lungs by tiny channels. Requires two cycle of inhalation and exhalation |
|
|
|
Negative breathing pressure |
Found in mammals. A breathing System in which air is pulled into lungs |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
A sheet of muscle that forms the the bottom of thoracic cavity. Contraction of diaphragm pulls air into lungs |
|
|
|
Inspiration |
Thoriac cavity moves up and out and the diagram moved down. Breathing in |
|
|
|
Inspiration |
Thoriac cavity moves up and out and the diagram moved down. Breathing in.
Active and requires work |
|
|
|
Expiration |
Causes the interstitial muscles to relax which allows the thoriac cavity (rib cage) to fall down and in and the diagram moved up.
Passive |
|
|
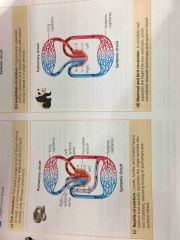
Front (Term) |
Variations in vertebrate |
|
|
|
Respiratory pigments |
A protein that transports oxygen in blood or hemolymph. They increase the amount of oxygen that can be carried in the circulatory fluid. Consist of a distinctive colour and a protein bound to a metal |
|
|
|
Bohr shift |
A lowering of hemoglobin for oxygen, caused by a drop in pH. It facilitates the release of oxygen from hemoglobin in active tissue |
|

