![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
London dispersion forces
|
Weakest of all molecular interactions.
Attractions resulting from the constant motion of electrons and the creation of instantaneous dipoles |
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bonds
|
Strongest of the intermolecular forces.
Formed between the hydrogen end of one dipole and a fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen atom on another dipole. Hydrogen bonding always involves hydrogen. |
|
|
|
Dipole Dipole Forces
|
Forces of attraction between polar molecules.
A polar molecule can induce a dipole in a non polar molecule. |
|
|
|
Metallic bonding
|
Metal atoms are loosely held.
Atoms don't lose their valence electrons they release them into a sea of electrons. Thermal and electrical conductivity due to mobile valence electrons. Malleability and ductility. |
|
|
|
Diatomic Molecules
|
Occur when any two atoms of the same element form covalent bond.
*N2 O2 H2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2* |
Dia
|
|
|
Sigma bond
|
A covalent bond resulting from the formation of a molecular orbital by the end-to-end overlap of atomic orbitals.
|
|
|
|
Pi Bond
|
A covalent bond resulting from the formation of a molecular orbital by side-to-side overlap of atomic orbitals along a plane perpendicular to a line connecting the nuclei of the atoms
|
|
|
|
Double Covalent Bonds
|
Has one sigma bond and one pi bond.
Carbon & Hydrogen = sigma Carbon & Carbon= Pi |
|
|
|
VSPER code
|
A is the central atom
B is the outside atoms E is the lone pairs on the central atom |
|
|
|
VSPER code
|
A is the central atom
B is the outside atoms E is the lone pairs on the central atom |
|
|
|
VSPER code
Linear |
AB or AB2
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
|
A is the central atom
B is the outside atoms E is the lone pairs on the central atom |
|
|
|
VSPER code
Linear |
AB or AB2
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Planar |
AB3
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
|
A is the central atom
B is the outside atoms E is the lone pairs on the central atom |
|
|
|
VSPER code
Linear |
AB or AB2
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Planar |
AB3
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Tetrahedral |
AB4
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
|
A is the central atom
B is the outside atoms E is the lone pairs on the central atom |
|
|
|
VSPER code
Linear |
AB or AB2
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Planar |
AB3
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Tetrahedral |
AB4
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Pyramidal |
AB3E
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
|
A is the central atom
B is the outside atoms E is the lone pairs on the central atom |
|
|
|
VSPER code
Linear |
AB or AB2
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Planar |
AB3
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Tetrahedral |
AB4
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Pyramidal |
AB3E
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Bent |
AB3E2
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
|
A is the central atom
B is the outside atoms E is the lone pairs on the central atom |
|
|
|
VSPER code
Linear |
AB or AB2
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Planar |
AB3
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Tetrahedral |
AB4
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Pyramidal |
AB3E
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Bent |
AB3E2
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Bipyramidal |
AB5
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
|
A is the central atom
B is the outside atoms E is the lone pairs on the central atom |
|
|
|
VSPER code
Linear |
AB or AB2
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Planar |
AB3
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Tetrahedral |
AB4
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Pyramidal |
AB3E
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Bent |
AB3E2
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Trigonal Bipyramidal |
AB5
|
|
|
|
VSPER code
Octahedral |
AB6
|
|
|
|
Structural formula
|
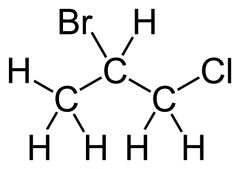
|
|
|
|
Electronegativity Chart
|
0 > .3 = nonpolar covalent
.4 - 1.8 = polar covalent > 1.9 = ionic |
|
|
|
Exception to the octet rule
|
Hydrogen- only 2 electrons.
Boron- 3 electrons. Phosphorous/Sulfur- combine with fluorine, oxygen, and chlorine |
|
|
|
Ionic bond
|
Electrical attraction of cations and anions
|
|
|
|
Ionic bond
|
Electrical attraction of cations and anions
|
|
|
|
Covalent bond
|
Sharing of electron pair between two atoms
|
|

