![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
AMPHIPATHIC |
Molecules for which solubility is dictated by both hydrophilic and hydrophobic bonds. The length of the Hydrocarbon chain is determinant. See surfactant & detergents (282) |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
The pont at which the pressure in a bubble (within a liquid) equals the atmospheric pressure pushing down from above.
(270) |
|
|
CONDENSATION |
Term for the Phase Change from gas to liquid. (269) |
|
|
DENSITY |
The mass of ice, water, or any other substance squeezed into a given volume. The mass unit divided by a volume unit. For example mg/mL. (283) |
|
|
DETERGENT |
amphipathic molecules that contain polar heads and hydrocarbon tails (285) |
|
|
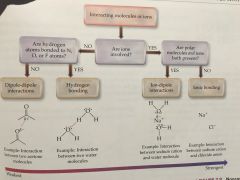
DIPOLE-DIPOLE INTERACTION |
A type of non-covalent interaction when two polar molecules interact and there is no full charge involved. |
|
|
EVAPORATION |
Term for the Phase Change from liquid to gas. (269) |
|
|
FREEZING POINT |
The temperature at which any liquid turns into a solid. (264) |
|
|
HYDROGEN BOND |
A type of dipole-dipole interaction. It is stronger than traditional d-d interactions. It involves the partial positive charge of the Hydrogen atoms of one molecule with the strong pull of the oxygen atom on another. (259) |
|
|
HYDROPHILIC |
Molecules that dissolve readily in water.
This happens by virture of dipole-dipole reactions and electronegativity (280) |
|
|
HYDROPHOBIC |
Highly non-polar substances that avoid water.
(281) |
|
|
IMMISCIBLE |
(of liquids) not forming a homogeneous mixture when added together.
|
|
|
MELTING POINT |
The temperature at which any solid becomes liquid. (264) |
|
|
MICELLE |
Three dimentional, spherical structure of amphipathic molecules with 1 hydrocarbon tail.
(285) |
|
|
NUCLEATION CENTER |
Phenomena at the beginning of freezing. The first few joined -together molecules. The begging point of the lattice. (264) |
|
|
PHASE |
|
|
|
SPECIFIC HEAT |
The amount of heat absorbed by 1 gram of a substance as its temperature increases by 1° Celcius
(270) |
|
|
SURFACE TENSION |
the magnigtude of gravitational force pulling an object down in relation to the force between [water] molecules on the surface. (262) |
|
|
SURFACTANT |
Amphipathic molecules with
1 very polar head and 2 hydrocarbon tails Found in Lungs (282) |
|
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
The pressure exerted by water vapor in the air above liquid water when the two are in equillibrium.
This happens at a specified temperature, and in sealed container, such as a flask. (273) |
|
|
WATER VAPOR |
The gaseous form of water. |
|
|
Non-covalent interactions |

