![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
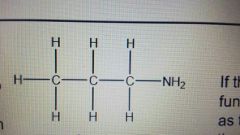
How do you name an amine? Eg. |
Propylamine |
|
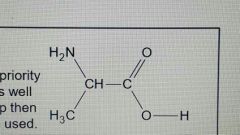
How do you name this amine? Eg |
2-aminopropanoic acid |
|
|
Naming amines: if secondary and tertiary amines have alkyl groups, what do you put in the name? |
Secondary = N- Tertiary= N,N- |
|
|
What are primary, secondary and teriary amines? |

Primary have one alkyl group Secondary have two alkyl group Tertiary have three alkyl groups |
|
|
What is a lewis base? Why? |
Has a lone pair of electrons for donation Ammonia and amines have a lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom, making thrm lewis bases |
|
|
What is a bronsted lowry base? And why are amine this? |
Proton acceptor Lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen is readily available for forming a dative covalent bond with a H+ and so accepting a proton |
|
|
Are primary aliphatics more basic than ammonia? Why? |
Yes Alkyl groups are electron releasing and push electrons towarss the nitrogen atom and so make it a stronger base |
|
|
Why don't primary aromatics form basic solutions? |
Lone pair on electrons on the nitrogen delocalise with the ring of electrons in the benzene ring. The means the N is less able to accept protons |
|
|
What does as amine + acid form? Mechanism details |

Ammonium salt Amine accepts a proton. A covalent bond is formed by the nitrogen atom donating its lone pair ot electrons to the proton to form a dative covalent bond |
|
|
How can we convert ammonium salt back to amine? |
Add NaOH |
|
|
What happens when primary amine reacts with acid (HCl)? What other acids used? |
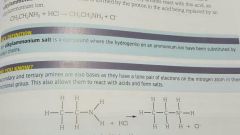
Alkylammonium salt formed. Proton in acid replaced by an alkyammonium ion Other strong acids such as nitric (NO3-) or sulfuric acid ( SO4 2-) can be used |
|
|
Steps to prepare aliphatic amines? |
1) haloalkane + ammonia + ethanol in a close container are heater to make amine Reflux cannot be used as ammonia is volatile and can escape 2) ammonia reacts eith haloalkane to make ammonium salt- nucleophillic substitution 3) ammonium salt reacts with ammonia to form ammonium chloride salt - a reversible reaction 4) first hydrogen substituted with alkyl group and so on until no mre hydrogens. |
|
|
How to prepare aromatic amines? |
Nitroarenes such as nitrobenzene can be reduced to produce as amine. Reducing agent is made by mixture of tin and concentrated HCl. Ruflux 100 degrees 30min later, strong alkali eg naoh added. Neutralises all excess HCl and produce amine. Seperaring aromatic amine involves stean distillation, solvent extraction and further distillation |
|
|
What is the structure of an amino acid? |
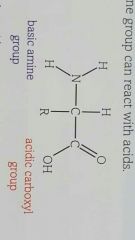
|
|
|
How does amino acid act as a base or acid? |
Carboxylic acid goup is a weak acir and partially ionises in water The nitrogen atom on the amine group has a lone pair of electrons and can act as a base. This means amino acids are amphoteric |
|
|
What are zwitterions in amino acid? How does it work |
Where two functional groups exchange a proton and make an internal salt Carboxylic acid donates a proton to amino group. Two charges cancel out- no overall charge |
|
|
What is an isoelectric point? |
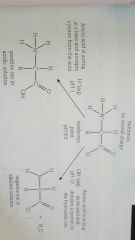
No net electrical charge due to each zeitterion having an internal balance of charge. This means at low PH where there is lots of H+ carboxylic acid becomes COOH and amine group is charged and vice versa |
|
|
Carboxylic acid functional grouo reactions |
All neutralisation reactions Carboxylix acid can react with metal oxide, alkali, carbonates alcohol- not neutralisation forms ester |
|
|
Amine functional group reactions with acid |
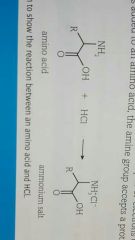
Can act as a base due to lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. When acid is added amine group accepts a proton. Ammonium salt formed |
|
|
Structure of amides |
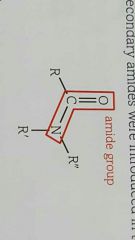
|
|
|
Definition of optical isomerism |
Non- superimposable mirror images of each other. |
|
|
What are enantiomers? |
Each of the two enantiomets look like mirror images of each other, and no matter how hard you try, you cannot lay them exactly on top of each other |
|
|
What is a chiral/ chirality? |
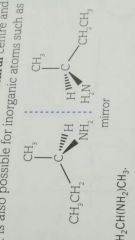
A carbon that has 4 different groups attached to it They do not have a plane of symmetry due to the asymmetrical or chiral carbon. |

