![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
LLNL Energy Flow Diagram
|
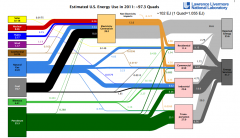
|
|
|
Primary components of a steam driven power plant
|
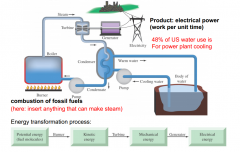
|
|
|
Carnot efficiency equation
|

-
|
|
|
Calculate efficiency using the LLNL Energy
|
-
|
|
|
Combustion reaction
|
-
|
|
|
How to calculate octane rating
|
-
|
|
|
What is a nuclear reaction (fission/fusion)
|
-
|
|
|
How does a nuclear reactor differ from a fossil fuel power plant
|
-
|
|
|
Pros/cons of nuclear energy
|
Pros:
1. No CO2 emissions 2. Can operate at any time (i.e., solar energy requires daylight, wind energy requires wind) Cons: 1. Expensive setup 2. radioactive waste 3. security concerns 4. only produces electricity |
|
|
Balancing fission reactions
|

-
|
|
|
Mass and Atomic Number
|
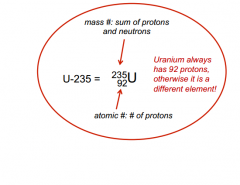
-
|
|
|
Primary renewable resources (Pros and cons/Energy balance associated with both
|
-
|
|
|
General structures of each biofuel and their sources
|
-
|
|
|
Forms of Solar Energy
|
-
|
|
|
Energy Summary (slide 38)
|
-
|
|
|
Potential energy
|
stored energy/energy of position
|
|
|
Kinetic energy
|
Energy of motion
|
|
|
1st Law of Thermodynamics
|
Energy is neither created or destroyed
|
|
|
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
|
Entropy always increases
|
|
|
How an electric generator works
|
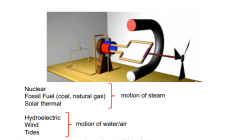
|
|
|
Coal
|
Pros:
1. Abundant 2.Distributed throughout the globe Cons: 1.Solid 2.Lower energy content than petroleum 3. More CO2 emission per unit 4. Difficult and dangerous to obtain 5. Environmentally disruptive to obtain and utilize Obtained through mining |
|
|
Natural gas
|
Obtained through fracking
Cons: 1.Possible ground water contamination 2. Fracking fluids and products can be carcinogenic 3. Opens many new sites for gas extraction 4. Waste/produced water may overwhelm water treatment facilities |
|
|
Oil
|
Obtained through oil refineries
Cons: 1. Oil spills |
|
|
Cracking
|
process of breaking down long chain
hydrocarbons into smaller molecules |
|
|
Thermal cracking
|
process of breaking down long chain
hydrocarbons into smaller molecules requiring high temperatures |
|
|
Catalytic cracking
|
a catalyst reduces the
activation energy required to start the cracking process |
|
|
Octane rating
|
higher numbers
indicate less propensity for engine knocking; gasoline with rating = 87 has the same knocking characteristics as 87% isooctane + 13% n-heptane |
|
|
Radioactivity
|
The spontaneous emission of radiation
|
|
|
Wind Energy
|
Obtained through wind
Pros: 1. Wind is free 2. No CO2 emissions from operation Cons: 1. Blocks views 2. Wind doesn't blow all the time 3. Transmission losses 4. Energy storage 5. Environmental/ecological (i.e., bird migration) 6. Requires energy and resources to make windmills |
|
|
Solar Energy
|
Obtained through the sun
Pros: 1. No shortage of energy 2. Carbon neutral Cons: 1. Sun doesn't shine all the time 2. transmission losses 3. Land usage issues 4. Energy cost of implementation |
|
|
Concentrated Solar (Solar Thermal)
|
Use solar radiation to generate steam for turbine to generate electricity
|
|
|
Photovoltaics
|
Directly convert photons into electricity
|
|
|
Solar fuels
|
Generate H2 by splitting water with solar photons
|
|
|
Alpha decay (α)
|
A. 4/2 He
B. Gives off helium atoms with alpha radiation C. Blocked by skin (dangerous ingestion) |
|
|
Beta decay (β)
|
A. 0/-1 e
B. Give off electron from the nucleus C. Blocked by Plexiglas and distance |
|
|
Gamma decay (γ)
|
A. 0/0 γ
B. Ionizes water C. Leaves behind H2O Radical cation D. Radical + Cation = react with other molecules Pro: Rapidly divides cells susceptible for cancer cells Con: Rapidly divides cells susceptible for healthy cells (bone marrow, skin, etc) |
|
|
Peak Oil
|
The concern we are rapidly running out of petroleum worldwide
|

