![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Molecular orbital =
|
interaction of orbitals between different atoms
|
|
|
Atomic orbital =
|
orbitals on the same atom interact
|
|
|
Sigma Bonding
Between two s orbitals |
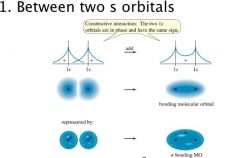
|
|
|
Sigma Bonding --
Between one s orbital and end of p orbital |
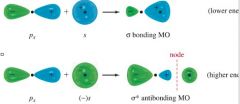
|
|
|
Sigma Bonding --
Between the ends of two p orbitals |

|
|
|
Pi Bonding
Between two p orbitals, side-by-side |
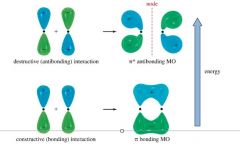
|
|
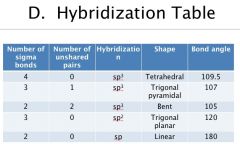
|
Hybridization Table
|
|
|
Isomers =
|
compounds with the same formula
|
|
|
Constitutional isomers =
|
same formula, different point of attachment
|
|
|
Stereoisomers =
|
same formula, different orientation in space
|
|
|
Dipole-dipole interactions =
|
intermolecular forces resulting from the attraction of the positive and the negative ends of the polar molecule
|
|
|
London dispersion forces =
|
attraction between nonpolar molecules
|
|
|
Hydrogen bonding =
|
bonding between the H attached to O, N, or F with another O, N, or F of another molecule
|
|
|
Polar solute dissolves in polar solvent
|
Polar solute does not dissolve in nonpolar solvent
|
|
|
Nonpolar solute dissolves in nonpolar solvent
|
Nonpolar solute does not dissolve in polar solvent
|
|
|
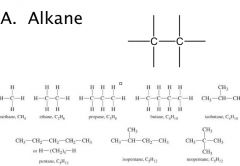
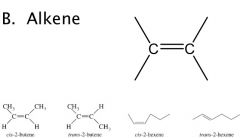
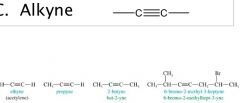
General Structures
|
R = alkane — H
X = halogen (F, Br, Cl, I) |
|
|
carbonyl =
|
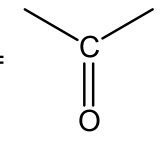
|
|
|
|
|
|
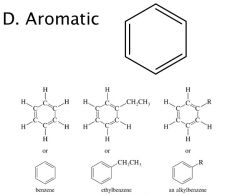
|

