![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Common-ion effect |
Weak electrolyte and strong electrolyte together with a common ion, weak one ionizes less than it would if it were alone This effects acid base equilibrium and solubility |
|
|
Example common ion |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Example cont |

A |
|
|
More practice |

A |
|
|
Buffer |
Solutions of weak conjugate acid-base pair that resist drastic changes in pH These solutions contain relatively high concentrations of both the acid and base Concentrations are approximately equal |
|
|
Ways to make a buffer |
1. Mix a weak acid an a salt of its conjugate base or a weak base and a salt of its conjugate acid 2. Add strong acid and partially neutralize a weak base or add strong base and partially neutralize a weak acid |
|
|
How a buffer works |

Buffets resist change in pH Adding a small amount of acid or base only slightly neutralize one component of the buffer
|
|
|
Henderson-hasselbach equation |

A |
|
|
Buffer capacity |

Amount of acid or base the buffer can neutralize before pH begins to change Using Henderson-hasselbach equation, pH will be the same for a conjugate acid-base pair of 1 M each or .1M; however the buffer which is 1 M can neutralize more acid or base before pH changes |
|
|
Adding strong acid or base to a buffer |
1. Adding strong acid or base neutralizes (neutralization rxn) Strong acid reacts w c. Base and strong base reacts w weak acid 2. Use HH equation to find pH |
|
|
Example |
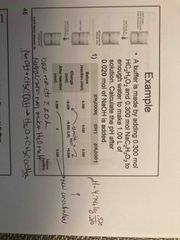
A |
|
|
Equivalence point |
Amount of acid = amount of base In titration |
|
|
4 types of titration |
Strong acid, strong base Strong base, strong acid Weak acid, strong base Weak base, strong acid |
|
|
Strong acid, strong base titration |
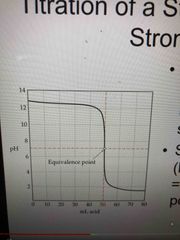
pH = 7 at the equivalence point Just before and after the equivalence pt, pH rises rapidly As more base is added, pH again levels off |
|
|
Titration of a weak acid with a strong base |
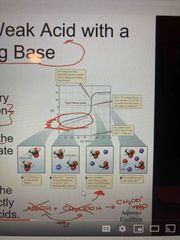
Use Ka to find pH Find pH in the buffer region using stoichiometry and then HH equation At equivalence pt pH is going to be greater than 7. Use the c. Base of weak acid to determine pH As more base i as added the pH levels off (same as strong acids) |
|
|
Weak acid differs from strong in that |
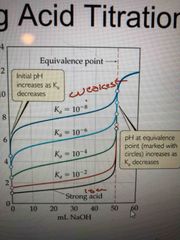
1. Solution of weak acid has higher initial pH than strong 2. The pH change near equivalence pt is smaller for a weak acid 3. pH at equivalence pt is > 7 for a weak acid |

