![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the organization of living matter?
|
cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism
|
|
|
What is the smallest living entity?
|
cell
|
|
|
What are the 4 basic tissue types in the body?
|
epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue
|
|
|
What is all matter made up of with tiny partials?
|
atom
|
|
|
What are charged elements?
|
ions
|
|
|
What are molecules that contain carbon atoms and are found in living or once living things?
|
organic molecules
|
|
|
What molecules are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and is the most abundant biological molecule on earth, which include sugar, starch, and cellulose?
|
carbohydrates
|
|
|
What molecule is composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, but have less oxygen than carbohydrates do, are important building blocks in cell membranes?
|
lipids
|
|
|
What molecules contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen, and is the most abundant and diverse molecules in the body?
|
proteins
|
|
|
What molecules generally do not contain carbon atoms?
|
inorganic molecules
|
|
|
What is the smallest unit of life?
|
the cell
|
|
|
All cells share 3 structural features in common: what are they?
|
1. a cell or plasma membrane that forms an outer envelope of the cell, 2. a nucleus that serves as the control or command center of the cell, 3. the cytoplasm, which is the watery fluid (cytosol) of the cell and the various organelles and cytoskeletal scaffolding dispersed in the fluid.
|
|
|
What is the very thin membranous structure that bounds each cell?
|
plasma membrane or cell membrane
|
|
|
What are the 4 general functions of the cell membrane?
|
1. mechanical barrier, 2. selective gate keeper, 3. chemical receptor sites, 4. identify self from non self for immune function.
|
|
|
What is the largest single organized cellular component?
|
nucleus
|
|
|
What are the 2 nucleus functions?
|
1. control center that directs protein synthesis, 2. location of DNA, that directs cell replication.
|
|
|
What is the portion of the cell interior not occupied by the nucleus?
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
What does the cytoplasm contain?
|
highly organized structures -the organelles- dispersed within the cytosol; a complex gel like mass.
|
|
|
What is the complex, gel like mass containing enzymes, ribosomes, transports vesicles, and various filaments and microtubules?
|
Cytosol
|
|
|
What is an elaborate fluid-filled membranous system distributed extensively throughout the cytosol that functions primarily as a protein - manufacturing factory?
|
Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
What are the 2 distinct types of endoplasmic reticulum?
|
the smooth ERIC and the rough ER
|
|
|
What organelles specialize in modifying, packaging, and distributing proteins?
|
Golgi complex
|
|
|
What organelles are viewed as "the recycling centers" that break down old, damaged, or dead cell parts or extracellular materials that have been engulfed by the cell?
|
Lysosomes
|
|
|
What is the organelles that detoxify various toxic wastes produced within the cell?
|
Peroxisomes
|
|
|
What are the energy organelles or "power plants" of the cell?
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
What part of the cell moves material on the cell surface forward?
|
cilia
|
|
|
What is a single, long, whip - like appendage of the cell membrane?
|
Flagella
|
|
|
What part of the cell is very slender, long, hollow, unbranched tubes composed primarily of tubulin, they help the cell maintain its shape? |
Microtubules
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of molecular movement across the cell membrane in a passive movement?
|
1. Diffusion
2. Osmosis |
|
|
What is the movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration of water molecules to an area of low concentration of water molecules?
|
Osmosis
|
|
|
What is the 2 active movements of molecules across the cell membrane that requires the cells to expend energy?
|
1. Carrier mediated transport
2. Vesicular transport- endocytosis/exocytosis |
|

What 2 molecular movements is this?
|
1. Diffusion
2. Osmosis |
|

What active molecular movement is this?
|
Carrier mediated transport
|
|
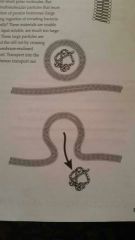
What active molecular movement is this?
|
Vesicular transport- endocytosis/exocytosis
|
|
|
What energy is produced in cells?
|
ATP
|
|
|
What is the energy production cycle in the cytosol called?
|
Glycolysis
|
|
|
Where does glycolysis occur?
|
Within the cytosol of the cell
|
|
|
What energy production can occur without the presence of oxygen?
|
Anaerobic energy
|
|
|
How many ATP molecules are produced with glycolysis?
|
Produces 2 ATP
|
|
|
What are the 2 roles that glycolytic does?
|
1. degrades glucose to produce ATP
2. it provides building blocks for the cell |
|
|
What energy production cycle takes place in the mitochondria?
|
Tricarboxylic acid cycle or Kreb's cycle or Citric acid cycle
|
|
|
How many ATP molecules are produced in the mitochondria?
|
36 ATP
|
|
|
Which energy production cycle requires oxygen to proceed?
|
aerobic energy production
|
|
|
What energy production cycle also serves as a source of building blocks for biosynthesis?
|

Kreb's cycle
|

