![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Equilibrium |

It is a state of a reaction where the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the back reaction. The reaction mixture contain reactants and products in equilibrium concentrations. |
|
|
Equilibrium Constant K |

|
|
|
Equilibrium Constant Shifting |

|
|
|
Equilibrium Partial Pressure |

|
|
|
Relationship between Kc and Kp |
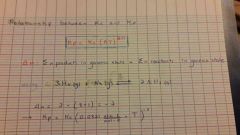
|
|
|
Multiple Equilibrium |

|
|
|
How Balancing Affects Kc |
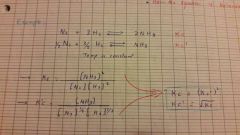
|
|
|
Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations from Initial Concentrations and Kc |
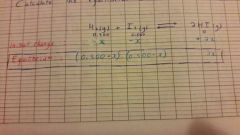
With these variable concentrations, make an equation using Kc and calculate x. Once calculated, calculate each equilibrium concentration. |
|
|
How Changes in Concentration Affect Equilibrium |

|
|
|
How Increasing Pressure Affects Equilibrium |

|
|
|
How Decreasing Pressure Affects Equilibrium |

|
|
|
How Changing Temperature in Exothermic Reactions Affects Equilibrium |

|
|
|
How Changing Temperature in Endothermic Reactions Affects Equilibrium |

|
|
|
Electrochemistry |
When spontaneous redox reactions are used to produce electricity. |
|
|
Balancing a Redox Reaction in an Acidic Medium |

|
|
|
Balancing a Redox Reaction in an Basic Medium |

|
|
|
Galvanic Cell |

|
|
|
Galvanic Cell Illustration |
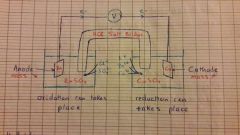
|
|
|
Salt Bridge |

|
|
|
Cell Diagram |

|
|
|
Standard Conditions |

|
|
|
Cell Potential |

If E°cell > 0, the rxn is spontaneous. If E°cell < 0, the rxn is non-spontaneous. E°cathode is always > 0 |
|
|
Reading a Table of Standard Reduction Potentials |

|
|
|
Some Notes on Standard Reduction Potentials |

|
|
|
Gamma-Rule |

|
|
|
Reduction Potential is Intensive |

|
|
|
Non-Standard Conditions |

|
|
|
Nernst's Equation |

|
|
|
E°cell, Ecell, and Quotient |

|
|
|
Heat of The Reaction at Constant Pressure |

|
|
|
Enthalpy |

|
|
|
Addinh Heat to a Reaction |

|

