![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is dynamic equilibrium |
It occurs when a reversible reactions forward and backward rate are the same, the concentration of the reactants and products are constant. |
|
|
What is le chapeliers principle and what is the 3 conditions of changes? |
Le chateliers principle: if conditions are changed in a reversible reaction, the equilibrium position will shift in order to minimise the change 3 conditions of change: temperature/ pressure/ concentration |
|
|
Equilibrium position shifts by change of increasing tempreture |
In the ENDOTHERMIC direction ( transferring energy from the surroundings, cooling them down) |
|
|
Equilibrium position shifts by change of decreasing temperature |
In the EXOTHERMIC direction ( transferring energy to the surroundings, heating them up) |
|
|
Increasing gas pressure |
In the direction that forms fewer gas (as this reduces pressure) |
|
|
Equilibrium position shifts by change of decreasing gas pressure |
In the direction that forms more gas molecules (as this increased pressure) |
|
|
Equilibrium position shifts by increasing a concentration |
In the direction that uses up the substance that has been added |
|
|
Equilibrium position shifts by decreasing a concentration |
In the direction that forms more of the substance that has been removed |
|
|
The haber process: tempreture |
Increasing the temperature favours the endothermic reaction In the haber process, the reverse reaction is endothermic so the equilibrium will shift to the left, producing more H2 and N2
Increasing the temperature will increase the rate of the forwards and backwards reactions allowing equilibrium to be reached faster A compromise of equilibrium and rate is reached at 450• |
|
|
The haber process: pressure |
Higher pressure favours the side of the reaction with fewer molecules of gas In the haber process, there are fewer molecules of gas in the right hand side, so the equilibrium will shift right, forming more products
Increasing the pressure also increases the rate of the reaction allowing the equilibrium to be reached quicker High pressures are expense to maintain due to equipment cost so a compromise of 200 atmospheres is used. |
|
|
Fertiliser production |
1) fixing nitrogen from the air N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3 2) producing nitric acid NH3 + O2 = HNO3 + H2O |
|
|
What is a half cell? |
It consists of a metal dipped in a solution of that metal If you connect 2 different half cells, there will be a potential difference between them, better know as a voltage |
|
|
What is a daniell cell? |
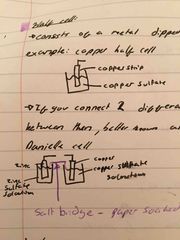
It is a basic example of cells used in everyday life-batteries It consists of 2 half cells joined by a wire and a salt bridge |
|
|
What is a hydrogen fuel cell? |
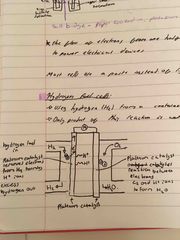
It uses hydrogen from a container and oxygen from the air (so fuel won’t run out) Only product of this reaction is water: no co2 or other harmful gases produced |
|
|
What is a hydrogen fuel cell and the equations of reactions? |
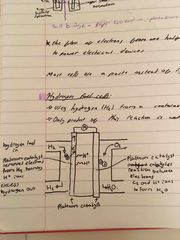
It uses hydrogen from a container and oxygen from the air (so fuel won’t run out) Only product of this reaction is water: no co2 or other harmful gases produced Equations: 2H2 = 4e- + 4H+ 4e- + O2 + 4H+ = 2H2O |
|
|
What is the yield, both theoretical and actual, and how do you calculate percentage yield? |
Theoretical yield: the maximum amount of the product you could make. It is calculated using ‘reacting mass Actual yield: the amount of product made in reality. There are 3 reasons why this may happen: 1) incomplete reactions 2) loss of product due to transfer losses 3) unwanted side reactions %yield= actual yield / theoretical yield x 100 |
|
|
What is the atom economy and how do you calculate it? |
This is a calculation that determines the percentage of reactants that end up in the useful product Atom economy = Mr of useful product/ total Mr of products x 100 |
|
|
Calculating mass and molar concentration |
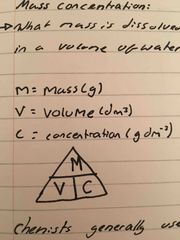
Mass concentration: what mass is dissolved in a volume of water Molar concentration: what number of moles is dissolved in a volume of water |
|
|
Calculating mass and molar concentration |

Mass concentration: what mass is dissolved in a volume of water Molar concentration: what number of moles is dissolved in a volume of water Remember units must be in dm3, if it is in cm3, you must divide by 1000 |
|
|
What is titration used for and what is the calculation used? |
Titrations are used to find the concentration of the solution by reacting a set volume of the above solution with a known concentration of another solution. N C x V |
|
|
What is titration used for and what is the calculation used? |
Titrations are used to find the concentration of the solution by reacting a set volume of the above solution with a known concentration of another solution. N C x V |
|
|
Molar volumes of gases- what is Avogardros law, RTP and STP and the equation used? |
Avogadros law states that at a specific temperature and pressure, I mole of any gas will occupy the same volume RTP: at room temperature and pressure; 1 mol of any gas occupies 24 dm3 - so |
|
|
Molar volumes of gases- what is Avogardros law, RTP and STP and the equation used? |
Avogadros law states that at a specific temperature and pressure, I mole of any gas will occupy the same volume RTP: at room temperature and pressure; 1 mol of any gas occupies 24 dm3 - so Vm would = 24 STP: at Standard tempreture and pressure; 1 mol of gas occupies 22.4 dm3 - so Vm would = 22.4 V Vm x N |
|
|
Molar volumes of gases- what is Avogardros law, RTP and STP and the equation used? |
Avogadros law states that at a specific temperature and pressure, I mole of any gas will occupy the same volume RTP: at room temperature and pressure; 1 mol of any gas occupies 24 dm3 - so Vm would = 24 STP: at Standard tempreture and pressure; 1 mol of gas occupies 22.4 dm3 - so Vm would = 22.4 V Vm x N |

