![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cations |
-Lose electrons
-Positive + (ca-+-ions)
-METAL |
|
|
Anions |
-Gain electrons
-Negative A Negative Ion
-Ending -ide -Non metals |
|
|
Ionic bond |
Bond that forms between ions of opposite charge through transfer of electrons. (Metal and non) |
|
|
Molecule and example |
Atoms held by covalent bond 2 or more different substance chemically combine.
Oxygen, water, nitrogen, chlorine |
|
|
Compounds and example |
2 or more different elements held together by chemical bond with the exact propotion
Water and carbon dioxide |
|
|
Mixtures |
2 or more substance not chemically combined together which can be easily seperated by physical method Water sand |
|
|
Ions |
When atoms lose or gain electrons to be stable |
|
|
Formula bond to remeber |
1.if it's 1 don't put 1 =Li2O1 X Li2O ✔️
2.Dont put the charge (cuz it's neutral) Li2+O- ❌ LiO✔️ |
|
|
Example of ionic compound |
Sodium chloride NaCl (salt) Sodium fluoride NaF (toothpaste) Sodium bicarbonate NaHC03 (baking soda) |
|
|
Describe the formation of ..... |
Element: electron configuration ---lose/gain--→ion electron configuration Na:2,8,1 ---loses--→2,8 |
|
|
Why don't group 8 form ions /bond? |
They're already stable . |
|
|
Ionic compound other name |
Cubic unit cell / Ionic lattice / Giant 3D structure / regular lattice structure |
|
|
Symbol |
NaCl,Cas |
|
|
Word equation |
Lithium fluoride, Sodium chloride |
|
|
Draw a diagram how this atom gain a stable outershell. |

|
|
|
When group A react with group B draw the diagram. |
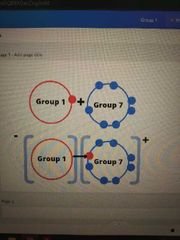
|
|
|
When element A react with B |
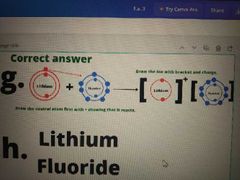
Draw the neutral atom (combined by +) first then the ion (bracket + charge). |
|
|
Covalent bond |
When element share electron to be stable. (Non metal and non metal) |
|
|
Example of covalent bonding |
Carbon dioxide Co2 (soft drink) Water H2O Meghan CH4 (Fuel) |
|
|
How many covalent bond for ..... |
So for this one just count how many electron the element need. Example: fluorine need 1 so it will make 1 bond. Oxygen need 2 so it will make 2 bond. Or Divide the electrons used in the bonding with 2. For example Na is 1 Cl is 1 = 2/2=1 |
|
|
Covalent diagram |
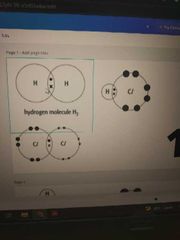
Use dot and cross only outer shell isoke. Make sure each element have 8 electron |
|
|
Ionic diagram |
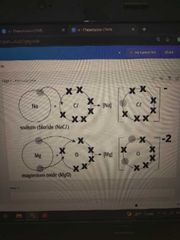
Another question will be like this. So draw the neutral atom first than the ion like ionic |
|
|
What inert noble gas structure does .... Atom have? |
This means kalo atom itu jadi ion dia bakal mirip siapa. Misalnya Carbon itu 2,6 kalo dia jadi ion jadi 2,8 yaitu sama kek neon 2,8. |
|
|
Metal |
High mp. Good conductor solid and liquid. |
|
|
Ionic compound |
Good conductor in liquid only (Because in solid the ion cannot move it vibrate) Soluble High MP and BP (Strong force to break between ions) |
|
|
Molecular= |
Macromolecule |
|
|
Electron distribution for ion |
Ion = stable configuration (2/2,8/2,8,8) |
|
|
What do you think about the distribution? |
....gain....lose |
|
|
Is molecule Ionic or covalent? |
ITS COVALENT |
|
|
One bond = .... Electron |
2 electron |
|
|
Molecule meaning |
A group of Atoms held together by covalent bonds |
|
|
Stable meaning |
Full outer shell |
|
|
1 st 2 nd 3 rd Shell electrons |
288 |
|
|
Ionic compound formula charge trick |
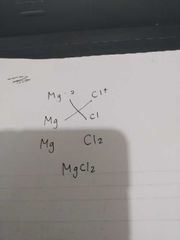
Cross em |
|
|
Molecule / simple molecular substance |
Low melting point (Weak covalent bond between molecule) Don't conduct electricity (No free electrons and no electric charge) |
|
|
Giant covalent structure |
Regular repeating structure
Strong High MP and BP (Strong covalent bonds between molecule) Don't conduct electricity (No free electrons and no electric charge) except graphite |
|
|
Properties of graphite |
Soft and slippery (Slide between layers because weak attraction) Can conduct electricity and heat (Have free electrons) High MP and BP (Strong force between molecule) |
|
|
Mettalic bonding |
Atoms in a regular pattern Hard High MP and BP (Strong force between free electrons and cation.) Conduct electricity and heat (Free electrons) Malleable Ductile (Make into thin wire) (Layers can slide) |

