![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Lewis diagram |
A structural formula in which valence electrons are represented by dots or crosses. |
|
|
Define valence electron |
The electrons in the highest energy level of an atom in which there are electrons. |
|
|
Define a chemical bond |
A mutual attraction between two atoms resulting from the simultaneous attraction between their nuclei and outer electrons. |
|
|
Which is smaller: energy of two bonded atoms or energy of individual atoms? What does this result in? |
The energy of the combined atoms is smaller. This results in higher stability in bonded atoms. |
|
|
How do atoms make more than 4 bonds? |
One of the electrons in a lone pair in a 3s or 3p orbital can move to the 3d orbital. |
|
|
Give an example of: 1) an element that can form 5 bonds and 2) an element that can form 6 bonds. |
1) phosphorus (5 bonds) -e.g. PCl5 2) sulphur (6 bonds) -e.g. SF6 |
|
|
What is the difference between a single bond and multiple bonds? |
Atoms joined by single bonds can rotate around the bond, whereas atoms joined by multiple bonds are held in a fixed position. |
|
|
Give examples of atoms that cam form: 1) double bonds and 2) triple bonds |
1) oxygen 2) nitrogen |
|
|
Give the formula and couper diagram for hydrogen cyanide. |
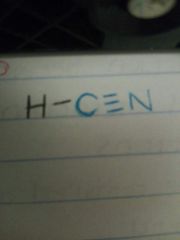
HCN |
|
|
How are dative covalent bonds formed? |
Dative covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of a filled orbital containing a lone pair with the empty orbital of another atom or ion. |
|
|
Give two examples of when dative covalent bonds are formed. |
When an H+ ion joins to a water molecule to form H3O+. When an H+ ion joins to an ammonia molecule to form the ammonium ion, NH4+. |
|
|
Show, by means of a Lewis diagram, how H3O+ is formed. |
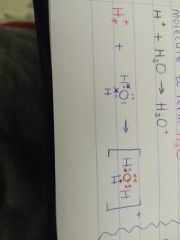
|
|
|
Show, by means of a Lewis diagram, how the ammonium ion is formed. |
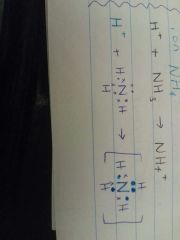
|
|
|
Define a covalent bond |
The sharing of electron between two atoms to form a molecule. |
|
|
Define a molecule. |
A group of two or more atoms covalently bonded and that function as a unit. |
|
|
Why can two He atoms not form a chemical bond? |
Different atoms with paired valence electrons (lone pairs) cannot share these 4 electrons to make a bond, according to the rules of bond formation. |
|
|
Define a bonding pair |
A pair of electrons that is shared between two atoms |
|
|
Define a lone pair |
A pair of electrons in the valence shell of an atom that is not shared with another atom. |
|
|
What does the shape of a molecule depend on? |
The number of bonding electron groups and lone pairs on the central atom. |
|
|
What shape, bond angle, and symmetry (yes/no) will a molecule with 1 bonding pair have? |
Linear, 180°, asymmetrical |
|
|
What shape, bond angle, and symmetry (yes/no) will a molecule with 2 bonding pairs have? |
Linear, 180°, symmetrical |
|
|
What shape, bond angle, and symmetry (yes/no) will a molecule with 3 bonding pairs have? |
Trigonal planar, 120°, symmetrical |
|
|
What shape, bond angle, and symmetry (yes/no) will a molecule with 4 bonding pairs have? |
Tetrahedral, 109°, symmetrical |
|
|
What shape, bond angle, and symmetry (yes/no) will a molecule with 5 bonding pairs have? |
Trigonal bi-pyramid, 120° in the plane and 90° at top and bottom, symmetrical |
|
|
What shape, bond angle, and symmetry (yes/no) will a molecule with 6 bonding pairs have? |
Octahedral, 90°, symmetrical |
|
|
What shape, bond angle, and symmetry (yes/no) will a molecule with 3 bonding pairs and one lone pair have? |
Pyrammidal, 107,5°, asymmetrical |
|
|
What shape, bond angle, and symmetry (yes/no) will a molecule with 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs have? |
Angular, 109°, asymmetrical |
|
|
Define electronegativity |
A measure of the tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract bonding electrons |
|
|
Define non-polar bond |
A bond in which the electron density is shared equally between the two atoms. |
|
|
Define polar covalent bond |
A bond in which the electron density is shared unequally between the two atoms |
|
|
In which region of difference in electronegativity will a bond be ionic? |
EN > 2,1 |
|
|
In which region of difference in electronegativity will a bond be polar covalent? |
EN > 1 |
|
|
EN < 1 |
Very weakly polar covalent |
|
|
EN = 0 |
Pure covalent / non-polar covalent |
|
|
2 vases for non-polar molecules |
When there are non-polar bonds (EN = 0) When there are polar bonds, but the molecule is symmetrical |
|
|
Define bond energy |
The energy needed to break one mole of compound's molecules into separate atoms. |
|
|
Define bond length |
The average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms. |
|
|
What is the relationship between bond energy and bond length? |
Bonds with a shorter bond length require more energy to break then bonds with a longer bond length. (As bond length increases, bond energy decreases.) |
|
|
What is the relationship between the strength of a chemical bond and the length of the bond between two atoms? |
If the force if attraction between two atoms is strong, the nuclei will come very close together, resulting in a short bond length. |
|
|
What is the relationship between the strength of a chemical bond and the size of the bonded atoms? |
The bond length between larger atoms is longer than the bond length between smaller atoms. Therefore, larger atoms will have weaker bonds. |
|
|
What is the relationship between the strength of a chemical bond and the number of bonds between the atoms? |
Bond strength increases as the number of bonds between atoms increases. |
|
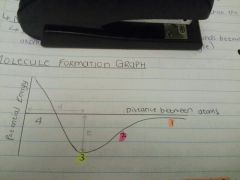
What is happening at point 1? |
The atoms are far apart, there is no interaction between them and the potential energy is almost zero. |
|
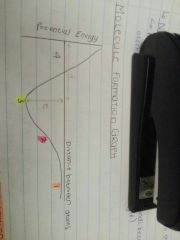
What is happening at point 2? |
As the atoms approach, the potential energy decreases because the nucleus from one atom attracts the electron cloud from the other. |
|
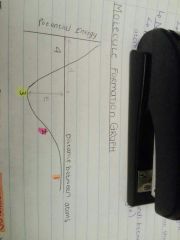
What is happening at point 3? |
The lowest energy level value means this is the most stable position and the atoms bond by sharing electrons. |
|
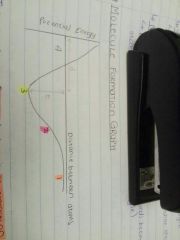
What is happening at point 4? |
The atoms approach too closely. There is repulsion between the nuclei; the potential energy rises, so this is not a stable position. The atoms return to position 3. |
|
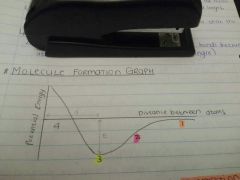
What do d and E represent? |
d - bond length E - bond energy |

