![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
143 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Carbohydrates are produced in plants by __.
|
photosynthesis
|
|
|
Carbohydrates are important sources of __ for animals.
|
energy
|
|
|
Each gram of carbohydrate releases about __ of energy.
|
4 Cal (or 4 kilocalories)
|
|
|
Monosaccharides such as glucose and fructose are simple carbohydrates because they contain a __ sugar unit.
|
single
|
|
|
Disaccharides such as sucrose and lactose consist of 2 monosaccharide units joined through bridging of __ atoms.
|
oxygen
|
|
|
The bridging of oxygen atoms between 2 monosaccharide units is called a __ bond.
|
glycosidic
|
|
|
Monosaccharides such as __ and __ are simple carbohydrates because they contain a single sugar unit.
|
glucose and fructose
|
|
|
Disaccharides such as __ and __ consist of 2 monosaccharide units joined through bridging oxygen atoms; this bridging is a glycosidic bond.
|
sucrose and lactose
|
|
|
Oligosaccharides consist of how many monosaccharide units joined by glycosidic bonds?
|
3-10
|
|
|
Which is the largest and most complex carbohydrate?
|
polysaccharide
|
|
|
Polysaccharides are often __.
|
branched
|
|
|
Name 3 examples of polysaccharides.
|
1. starch 2. glycogen 3. cellulose
|
|
|
Monosaccharides are made of __, __, and __.
|
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
|
|
|
Most monosaccharides have the general formula __.
|
(CH20)n (where n=3-7)
|
|
|
Monosaccharides are named according to their __ __.
|
functional groups
|
|
|
A monosaccharide that has a ketone (C=O carbonyl group) is called __.
|
ketose
|
|
|
If an monosaccharide has an aldehyde, it is an __.
|
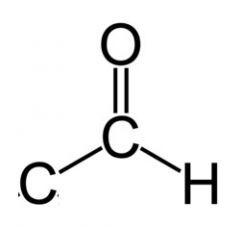
aldose
|
|
|
Monosaccharides contain many __ groups.
|
hydroxyl (-OH)
|
|
|
Monosaccharides can also be named by how many __ atoms are in the main skeleton.
|
carbon
|
|
|
A monosaccharide with 3 carbons in the main skeleton is called a __.
|
triose
|
|
|
A monosaccharide with 4 carbons in the main skeleton is called a __.
|
tetrose
|
|
|
A monosaccharide with 5 carbons in the main skeleton is called a __.
|
pentose
|
|
|
A monosaccharide with 6 carbons in the main skeleton is called a __.
|
hexose
|
|
|
The prefixes D and L found in the complete name of a monosaccharide are used to identify which of its 2 possible __ forms is being used.
|
isomeric
|
|
|
The two isomeric forms of a monosaccharide are called __.
|
stereoisomers
|
|
|
Each member of a pair of stereoisomers must be identical in what 2 ways?
|
1. molecular formula 2. bonding
|
|
|
D and L isomers of monosaccharides differ in the __ arrangement of atoms in the molecule.
|
spatial
|
|
|
The study of the different spatial arrangement of atoms is called ?
|
stereochemistry
|
|
|
What do you call 2 stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other?
|
enantiomers
|
|
|
Molecules that exist in enantiomeric forms are called ?
|
chiral molecules
|
|
|
For every pair of nonsuperimposable mirror image forms (called enantiomers), one is always designated __ and the other __.
|
D and L
|
|
|
A carbon atom that has 4 different groups bonded to it is called an __ carbon.
|
chiral or asymmetric
|
|
|
Large biological molecules typically have more than __ chiral carbon.
|
one
|
|
|
Each member of a pair of stereoisomers will rotate plane polarized light in __ directions.
|
different
|
|
|
Plane-polarized light is light of one wavelength polarized to one __.
|
plane
|
|
|
Large __ molecules typically have more than one chiral carbon.
|
biological
|
|
|
Each member of a pair of __ will rotate plane polarized light in different directions.
|
stereoisomers
|
|
|
Some compounds rotate light in a clockwise direction. These are said to be __.
|
dextrorotatory
|
|
|
How are dextrorotatory compounds designated?
|
With a plus sign +
|
|
|
Some compounds rotate light in a counterclockwise direction. They are said to be __.
|
levorotatory
|
|
|
How are levorotatory compounds designated?
|
by a minus sign -
|
|
|
A __ carbon atom bonded to 4 different atoms, or groups of atoms, are the basis of plane-polarized optical activity.
|
tetrahedral
|
|
|
Compounds that rotate light in a clockwise direction are called __.
|
dextrorotatory (+)
|
|
|
Compounds that rotate light in a counterclockwise direction are called __.
|
levorotatory (-)
|
|
|
A 2 dimensional drawing of a molecule that shows a chiral carbon at the intersection of 2 lines with horizontal lines representing bonds projecting out the page and vertical lines representing bonds projecting into the page are called ?
|
Fischer Projections
|
|
|
Do you need to draw in the carbons when drawing a Fischer Projection?
|
no
|
|
|
A mixture of 2 enantiomers is called ?
|
a racemic mixture
|
|
|
True or false: Racemic mixtures rotate light.
|
False. The shifting of light by each enantiomer cancels the other one out.
|
|
|
The position of the __ __ on the chiral carbon that is farthest from the carbonyl group (C=O) that determines whether a monosaccharide is in the D or L configuration.
|
hydroxyl group (-OH)
|
|
|
If the hydroxyl (-OH) group is on the right side of the carbohydrate molecule, the molecule is in which position? (D or L?)
|
D
|
|
|
Almost all carbohydrates in living systems are members of which family? (Are they in the D or L position?)
|
D
|
|
|
If the hydroxyl (-OH) group is on the left side of the carbohydrate molecule, the molecule is in which position? (D or L?)
|
L (L=left)
|
|
|
What is the most important sugar in the human body?
|
glucose
|
|
|
What are 3 other names for glucose?
|
1. dextrose 2. grape sugar 3. blood sugar
|
|
|
Glucose is broken down by __ and other pathways to release energy for the body.
|
glycolysis
|
|
|
What is the molecular formula for glucose?
|
C6H12O6
|
|
|
Glucose is an __.
|
aldohexose
|
|
|
The cyclic form of glucose exists because the carboxyl group at (which carbon?) reacts with the hydroxyl group at (which carbon?)
|
C1 - C5
|
|
|
The cyclic form of glucose is six member ring, or a cyclic __ __.
|
intramolecular hemicetal
|
|
|
Which is more stable: the cyclic or linear forms of glucose?
|
cyclic
|
|
|
2 isomers of D-glucose are called ?
|
alpha and beta
|
|
|
The isomers of D-glucose differ in the location of the -OH (hydroxyl group) attached to the __ __.
|
hemiacetal carbon (or the C-1 carbon)
|
|
|
The alpha and beta isomers of D-glucose are called __.
|
anomers
|
|
|
Where is the C-1 hydroxyl located in an alpha anomer of D-glucose?
|
below the ring
|
|
|
Where is the C-1 hydroxyl located in a beta anomer of D-glucose?
|
above the ring
|
|
|
What is the sweetest of all sugars?
|
fructose
|
|
|
Fructose is known by what other names?
|
1. Levulose 2. fruit sugar
|
|
|
Fructose is a __.
|
ketose
|
|
|
The cyclic form of fructose is an __ __ and a hexose.
|
intramolecular hemiketal
|
|
|
Galactose is a hexose or an aldose?
|
It is both a hexose and an aldose.
|
|
|
True or false: The cyclic form of fructose is a hexose.
|
True
|
|
|
Galactose is a component of the disaccharide __.
|
lactose
|
|
|
Ribose is a component of __.
|
RNA
|
|
|
Ribose is a 5-carbon __.
|
aldose
|
|
|
DNA contains 2 __.
|
deoxyribose
|
|
|
In DNA, the OH group at C-2 of ribose has been replaced with a __.
|
hydrogen (it lost an oxygen; this is reduction)
|
|
|
All monosaccharides and disaccharides except sucrose are __ sugars.
|
reducing
|
|
|
Reducing sugars can be oxidized by __ __ to produce a carboxylate anion.
|
Benedict's reagent
|
|
|
All monosaccharides and disaccharides except __ are reducing sugars.
|
sucrose
|
|
|
Reducing sugars can be oxidized by Benedict's reagent to produce a __ __.
|
carboxylate anion
|
|
|
The cyclic forms of monsaccharides are __ or __.
|
hemiacetals or hemiketals
|
|
|
When a hemiacetal reacts with an alcohol, the product is a __.
|
ketal
|
|
|
When acetals or ketals are formed, they are given the general name __.
|
glycosides
|
|
|
The C-O bonds of glycosides are called __ bonds.
|
glycosidic
|
|
|
Another name for maltose is ?
|
malt sugar
|
|
|
Maltose is composed of 2 __ molecules.
|
D-glucose
|
|
|
Lactose is also called ?
|
milk sugar
|
|
|
Lactose is made from 1 __ molecule and an __ or __ D-glucose.
|
beta-D-galactose, alpha or a beta-
|
|
|
The bond between the 2 monosaccharides is a __ glycosidic bond.
|
Beta (1-4)
|
|
|
Who established the field of biochemistry?
|
Emil Fischer
|
|
|
Sucrose is also called ?
|
table sugar, cane sugar, or beet sugar
|
|
|
Sucrose is an important carbohydrate in plants, but can it be synthesized in animals (including humans)?
|
no
|
|
|
Sucrose is a monosaccharide or a disaccharide?
|
disaccharide
|
|
|
Sucrose is a disaccharide of __ joined to __.
|
alpha-D-glucose joined to a beta-D-fructose
|
|
|
The glucose and fructose that form a sucrose are joined by a __ bond.
|
glycosidic (alpha1-beta2)
|
|
|
Why is sucrose NOT a reducing sugar?
|
it lacks a hemiacetal group.
|
|
|
Will sucrose react with a Benedict's reagent?
|
no
|
|
|
Most carbohydrates found in nature are large polymers of __.
|
glucose
|
|
|
What is the major transport form of sugar in plants?
|
sucrose
|
|
|
What is the principal storage form of sugar in plants?
|
starch
|
|
|
Starch is a heterogenous material composed of the glucose polymers __ and __.
|
amylose and amylopectin
|
|
|
Amylose accounts for about __% of the starch in a plant cell.
|
20%
|
|
|
A single chain of amylose can contain about __ glucose units.
|
4000
|
|
|
Amylopectin is a highly __ amylose.
|
branched
|
|
|
Each branch of amylopectin contains __-__ glucose untis.
|
20 - 50
|
|
|
What is the major glucose storage molecule in animals?
|
glycogen
|
|
|
The structure of glycogen is similar to __.
|
amylopectin
|
|
|
Glycogen differs from amylopectin in that it has __ branches and the branches are __.
|
more, shorter
|
|
|
What is the most abundant polysaccharide in the world?
|
cellulose
|
|
|
A molecule of cellulose typically contains about __ glucose units, but can have as many as __..
|
3000, 26,000
|
|
|
Cellulose is the __ component of the plant cell wall.
|
structural
|
|
|
Why can't cellulose be digested by humans?
|
We lack the enzyme "cellulase" (NOTE: this isn't what it's really called, but it's what he wants on the test.)
|
|
|
Lipids are a collection of organic molecules of varying chemical composition grouped together on the basis of their __ and on being __ solvents.
|
solubility, nonpolar
|
|
|
Name the 4 main groups of lipids.
|
1. fatty acids 2. glycerides 3. nonglyceride lipids 4. complex lipids
|
|
|
What are the 8 functions of lipids in the human body?
|
1. energy source 2. energy storage 3. cell membrane structure (lipid bilayer) 4. hormones 5. vitamins (A,D,E,K) 6. vitamin absorption 7. protection 8. insulation
|
|
|
Fatty acids are long-chain __ acids.
|
monocarboxylic
|
|
|
Fatty acids generally contain an __ number of carbon atoms.
|
even
|
|
|
The esterification of glycerol with a fatty acid produces a __ __.
|
neurtral glyceride
|
|
|
Esterification may occur at 1, 2, or all 3 positions, producing __, __, or __.
|
monoglycerides, diglycerides, or triglycerides
|
|
|
What are the main components of fat cells?
|
triglycerides
|
|
|
The principal function of riglycerides is to store __.
|
energy
|
|
|
An __ agent aids in the suspension of triglyerides in water.
|
emulsifying
|
|
|
Lecithin is __.
|
amphipathic
|
|
|
Amphipathic means a molecules possesses a __ head and __ tail.
|
polar head, nonpolar tail
|
|
|
__ is a common steroid found in the membranes of most animal cells.
|
Cholesterol
|
|
|
Complex lipids are lipids bonded to other types of __.
|
molecules
|
|
|
What are the 2 most important complex lipids?
|
plasma and plasma lipoproteins
|
|
|
Plasma lipoproteins transport other __ in the body.
|
lipids
|
|
|
What are the 4 major classes of human plasma lipoproteins?
|
1. chylomicrons 2. VLDL 3. LDL 4. HDL
|
|
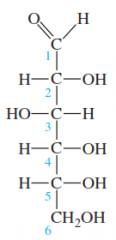
|
Open chain form of D-Glucose
|
|
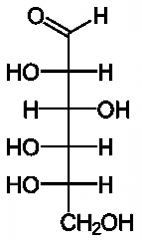
|
Open chain form of L-Glucose
|
|
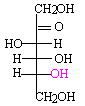
|
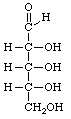
Open chain form of D-fructose.
|
|
|
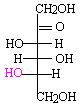
Open chain form of L-fructose.
|
|
|
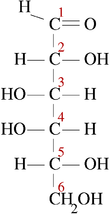
Open chain form of D-galactose.
|
|
|
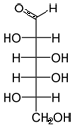
Open chain form of L-galactose.
|
|
|
Open chain form of D-ribose.
|
|
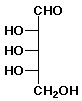
|
Open chain form of L-ribose. (Hydrogens would be on the right)
|
|
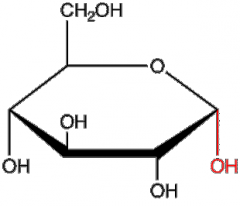
|
a-D-glucose
|
|
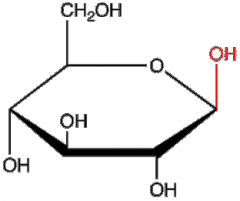
|
B-D-glucose
|
|
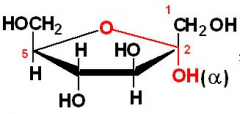
|
a-D-fructose
|
|
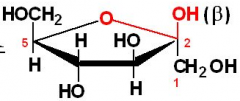
|
B-D-fructose
|
|
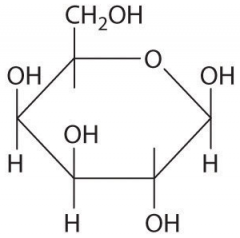
|
B-D-galactose
|
|
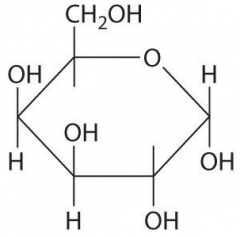
|
a-D-galactose
|

