![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ALPHONSE BERTILLION
|
created the first systematic attempt at personal identification in 1883
|
|
|
FRANCIS GALTON
|
published the textbook entitled "Finger Prints". Discussed the anatomy and suggested methods of recording them. Showed that no two prints are the same.
|
|
|
DR. JUAN VUCETICH
|
created a classification system that is still used in Spanish speaking countries.
|
|
|
SIR EDWARD HENRY
|
devised another classification system used in most English speaking countries.
|
|
|
UNITED STATES vs. BYRON C. MITCHELL
|
defendant's attorney argued that fingerprints cannot be proven unique. Judge said: human friction ridges are unique and permanent and that human friction ridge skin arrangements are also unique and permanent.
|
|
|
FINGERPRINTS
|
a reproduction of friction skin ridges found on the palm side of the fingers and thumbs.
|
|
|
FINGERPRINT PRINCIPLES
|
1. a fingerprint is an individual characteristic because no two are alike.
2. a fingerprint will remain unchanged during a person's lifetime. 3. fingerprints have general ridge patterns that permit them to be classified. |
|
|
MINUTIAE
|
ridge characteristics of fingerprints
|
|
|
COMMON RIDGE CHARACTERISTICS
|
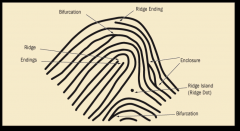
ridge ending, bifurcation, and ridge island
|
|
|
FRICTION SKIN GLANDS
|
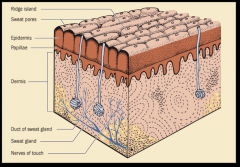
|
|
|
FINGERPRINT CLASSES
|
loops, arches, and whorls (L.A.W)
|
|
|
LOOP FINGERPRINT
|
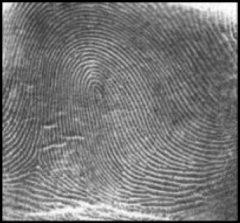
must have one or more ridges entering from one side of the print.
|
|
|
ARCH FINGERPRINT
|
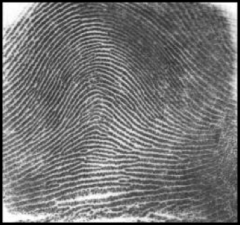
arches do not have type lines, deltas, or cores.
|
|
|
WHORL FINGERPRINT
|
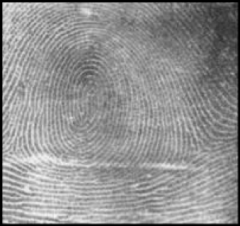
all whorl patterns have type lines and a minimum of two deltas.
|
|
|
AFIS
|
digitally encodes, classifies, and retrieves fingerprints
|
|
|
VISIBLE PRINTS
|
created when fingers touch a surface after the ridges have been in contact with a colored material.
Examples: blood, paint, or grease |
|
|
PLASTIC PRINTS
|
ridge impressions that are left on a soft material.
Examples: putty, wax, or soap. |
|
|
LATENT PRINTS
|
when a finger touches a surface and body oils from the finger are transferred to that surface.
|
|
|
RUVIS
|
aids in detecting latent fingerprints without chemicals or powder using ultraviolet light.
|

