![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The functional group of a carboxylic acid is a _________ group, which can be represented in any one of three ways
|
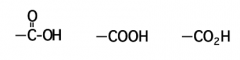
carboxyl |
|
|
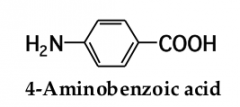
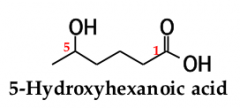
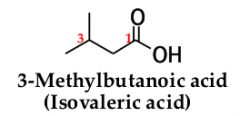
for an acyclic carboxylic acid, take longest carbon chain that contains the carboxyl group as the parent alkanedrop the final -e from the name of the parent alkane and replace it by _____ _____ |
-oic acid. number the chain beginning with the carbon of the carboxyl groupbecause the carboxyl carbon is understood to be carbon 1, there is no need to give it a number |
|
|
|
|
|
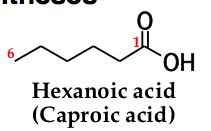
|
|
|
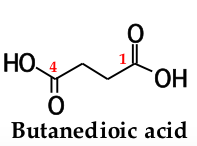
to name a dicarboxylic acid, add the suffix ______ _______ to the name of the parent alkane that contains both carboxyl groups |
-dioic acid |
|
|
the numbers of the carboxyl carbons are not indicated because: |
they can be only at the ends of the chain |
|
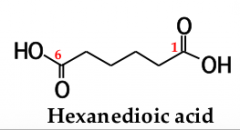
|
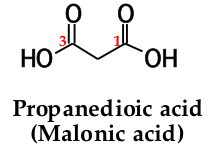
|
|
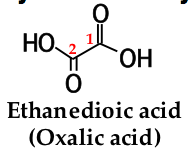
|
|
|
|
carboxylic acids are more soluble in water than are alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, and ketones of comparable molecular weight |
carboxylic acids have significantly higher boiling points than other types of organic compounds of comparable molecular weight |
|
|
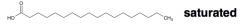
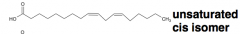
an unbranched-chain carboxylic acid derived from hydrolysis of animal fats, vegetable oils, or membrane phospholipids = ? |
fatty acid |
|
|
|
|
|
an ester of glycerol with three fatty acids = ? |
Triglyceride |
|
|
Hardening = ? |
reduction of some or all of the carbon-carbon double bonds of an unsaturated triglyceride using H2/catalyst |
|
|
Natural soaps are prepared by boiling lard or other animal fat with NaOH, in a reaction called _______________ |
saponification |
|
|
Carboxylic acids are (strong/weak) acids |
weak |
|
|
Reactions with bases. All carboxylic acids, whether soluble or insoluble in water, react with NaOH, KOH, and other strong bases to form water-soluble salts |

|
|
|
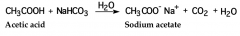
like inorganic acids, carboxylic acids react with sodium bicarbonate and sodium carbonate to form water-soluble sodium salts and carbonic acid. carbonic acid then decomposes to give water and carbon dioxide, which evolves as a gas |
|
|
|
in Fischer esterification, a carboxylic acid is reacted with an ________ in the presence of an acid catalyst, such as concentrated sulfuric acid |
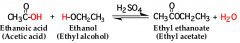
alcohol
|
|
|
At equilibrium the forward rate is equal to the reverse rate. RF [A] = RR [C] So if we increase the concentration of A, the forward rate ________ and shifts the equilibrium to the ______. |
increases; right |
|
|
If we decrease the concentration of A, the forward rate ________ and shifts the equilibrium to the _____. |
decreases; left |
|
|
Increasing a compound on one side of the equilibrium, shifts the equilibrium (toward/away from) that compound. This causes any other compound on the side side to be _______ and compounds on the opposide side to ________. |
away; decreased; increase |
|
|
Decreasing a compound on one side of the equilibrium, shifts the equilibrium (toward/away from) that compound. This causes any other compound on the side side to be _______ and compounds on the opposide side to ________. |
toward; increased; decrease |

