![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Energy that travels thru space at the speed of light as oscillating waves |
Electromagnetic radiation |
|
|
|
Number of wave cycles passing a stationary point in one second |
Hertz |
|
|
|
Amount of energy required to remove a valence electron from an atom or ion in the gaseous state |
Ionization energy |
|
|
|
A rule stating that electrons are distributed in orbitals of the same energy in such a way as to give the maximum number of unpaired electrons |
Hund |
|
|
|
A description of the distribution of electrons in an atom’s sublevels |
Electron configuration |
|
|
|
An inner electron that is not a valence electron |
Core electron |
|
|
|
A region in space where an electron is likely to be found |
Orbital |
|
|
|
A spectrum that consists of all the wavelengths of visible light |
Visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum |
|
|
|
Having the same number of electrons |
Isoelectric |
|
|
|
The distance between 2 corresponding points on a wave |
Wavelength |
|
|
|
The smallest packet of energy of a specific type of electromagnetic radiation |
Photon |
|
|
|
A measure of the size of an atom measured from the nucleus to the outer edge of the atom |
Atomic radius |
|
|
|
A rule stating that a maximum of 2 electrons can occupy an orbital and that the electrons must have opposite spin |
Pauli exclusion principle |
|
|
|
An electron that occupies the highest principle energy level |
Valence electron |
|
|
|
The lowest energy electron configuration |
Ground state |
|
|
|
An energy level consisting of orbitals of the same type and energy |
Valence level |
|
|
|
A spectrum of an element or molecule which uniquely identifies it |
Line spectrum |
|
|
|
Having only specific allowed values |
Quantized |
|
|
|
List 3 types of electromagnetic radiation that have longer wavelengths than visible light |
Microwave, Infrared, radio |
|
|
|
The number of levels in the S orbital |

One |
|
|
|
The shape of the P orbital and the number of orbitals in the P sublevel |
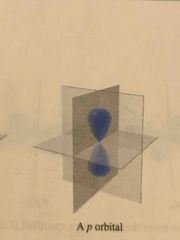
Three shaped like a dumbell |
|
|
|
Rule which states that electrons fill orbitals starting with the lowest energy orbitals first |
Aufbau principle |
To build up |
|
|
The lowest energy state of an atom |
Ground state |
|
|
|
The maximum number of electrons found in any main energy level can be determined by the formula 2n^2 where n is the? |
Principle energy level |
|
|
|
A region of space in which one or two electrons are found |
Orbital |
|
|
|
For n = 2 the total number of electrons would be? |
8 |
2 (2^2) |
|
|
Symbols by which sub levels are indicated |
S P D F |
|
|
|
What does the symbol 4S^2 represent? |
Energy level 4 (period 4) Sublevel S number of electrons (2) |
|
|
|
Sub level that contains 5 orbitals |
D Sublevel |
|
|
|
Electron configuration for iron (Fe) |
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 |
|
|
|
Elements that tend to form mono atomic ions by gaining one or more electrons |
Non metals |
|
|
|
Which subatomic particles are involved in the production of light? |
Electrons |
|
|
|
The lowest energy state of an atom |
Ground state |
|
|
|
A particle of light is called a |
Photon |
|
|
|
What type of energy is light? |
Electromagnetic radiation Radiant |
|
|
|
Using ROYGBIV, which has the longest wavelength? |
Red |
|
|
|
Using ROYGBIV which has the highest energy? |
Violet |
|
|
|
Using ROYGBIV which has the lowest frequency? |
Red |
|
|
|
Visible spectrum wavelengths range from violet nm? To red nanometers? |
400 to 750 |
|
|
|
What is the atomic number for 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 |
20 |
Add the superscripts |
|
|
Delta energy = |
E(final) - E(initial) |
|
|
|
Which transition has the highest energy? 4 -> 2 4 -> 1 1 -> 4 2 -> 4 |
4-1 because 4 minus one is three. Also we are measuring transition energy where the electron is falling from a higher level to a lower level |
|
|
|
When an electron occupies an energy level higher than the lowest energy level it is in what state? |
Excited state |
|
|
|
Using ROYGBIV, which has the longest wavelength? |
Red |
|
|
|
Subshell |
All the orbitals of one type within a shell |
|
|
|
Symbols by which sub levels are kndicated |
S P D F |
|
|
|
Visible spectrum wavelengths range from violet nm? To red nanometers? |
400(violet) 750 (red) |
|
|
|
Sub level that contains 5 orbitals |
P Sublevel |
|
|
|
Delta energy = E(final) - E(initial) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Elements that tend to form mono atomic ions by gaining one or more electrons |
Non metals |
|
|
|
Periodic trend of atomic radii |
Top to bottom increasing. Right to left increasing. Runs counterclockwise. |
|
|
|
Ionization energy trend |
Bottom to top increasing Left to right increasing. Runs clockwise |
|
|
|
What is the abbreviated electron config for Al3+ ion |
Al 3+ = [Ne]3s2 3p1 Minus 3 electrons Becomes [Ne] |
|
|
|
Which element has greater ionization energy, F or C |
F because it is further to the right of carbon and it also has a higher electronegativity |
|
|
|
Ionization energy increases from ? To ? And ? To ? |
Left to right and bottom to top |
|
|
|
The size of an atom is described in terms of its ? |
Atomic radius |
|
|
|
The lithium ion in terms of atomic size is smaller/larger than the lithium atom? |
Smaller because it loses an electron and contracts |
|
|
|
The fluorine ion becomes smaller/larger than the fluorine atom? |
Larger because fluorine gains an electron thus it expands |
|
|
|
What is the speed of light in a vacuum? |
3.00x10^8 meters per second |
|
|
|
For any isoelectronic series as the number of ___ increases the ion size ___ |
Protons Decreases |
|
|
|
Ionization energy trend |
Bottom to top increasing Left to right in reading. Runs clockwise |
|
|
|
Ionization energy factors |
Charge Distance (of electron from nucleus) Shielding (valence electrons) More protons |
|
|
|
Valence level (shell) |
The last occupied principle energy level |
|
|
|
Order atoms by their size |
Periodic trend is counterclockwise. Starting from lower left largest to upper right smaller. Also each group runs smallest from top of group to largest at bottom of group |
|
|
|
S block elements are groups __ And___. They are known as ___metals and ____metals |
1 and 2 Alkali metals Alkali earth metals |
|
|
|
P block elements contain groups ___,___,___,___,___,___ And consist of _____, _____ and ____ |
IIIA , IVA, VA, VIA, VIIA, VIIIA metals, metalloids and non metals. |
|
|
|
Group 8 elements |
Are noble gases Don’t mix, |
|
|
|
Group 7 elements |
Are halogens Non metals |
|
|
|
Group 6 elements |
Non metals, metalloids and metals |
|
|
|
What is an ion? |
An atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons |
|

