![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

|
Cycladic Woman
Marble 2400 - 2100 BCE |
doesn't have an actual name
|
|

|
Bull Leaping Fresco
Minoan Crete 1450 - 1375 |
the region appeared peaceful.
|
|

|
Snake Goddess or Priestess
Minoan Faience Crete 1500 BCE |
When discovered it was headless. The cat is an original piece but was found else where.
|
|

|
Grand Staircase in the Temple of Knossos
Crete 1500 BCE |
East Wing, Palace complex at Knossos
|
|

|
Vaphio Cup
Gold Sparta 1650 - 1450 |
|
|

|
Lion Gate
Mycenaean Limestone 1300 BCE |
Said to be built by Cyclopse, the lionesses are carved on a triangle of stone that relieves the weight of the massive doorway from the lintel. the original heads, made of brinze have never been found. They we're attached to the bodies with dowels.
|
|

|
Funerary Mask (Mask of Agamemnon)
Gold Ripoussé Mycenae 1600 - 1550 |
Predates the Trojan War by some 300 years. Scholars suggest Schliemann (discoverer) added the handlebar mustache and large ears, perhaps to make the mask appear "heroic".
|
|

|
Treasury of Atreus
Mycenae 1250 BCE |
Shaped like a beehive, Mycenaeans would bury kings in this tholos
|
|

|
Warrior Vase
Ceramic Mycenae, Greece 1300 - 1100 BCE |
|
|

|
Botkin Class Amphora
Archaic Black - figure cecoration on Ceramic Greek 540 - 530 BCE |
Possibly used as a propaganda piece, embodying the concept of areté, this amphora used to store wine and oil, illustrates two warriors battling. The difference in shields shows which warrior is fighting for which polis.
|
|

|
The Blinding of Polyphemus
Spartan Ceramic |
Illustrating Odysseus and his men offering Polyphemus a drink that inebriates him, Odysseus blinds him with a pointed pole after one of his men were eaten by the Cyclops.
|
|

|
Temple of Hera (I & II)
Archaic 460 BCE |
Dioric order. Rebuilt to be better and longer lasting for Magne Gracia (greater Greece)
|
|

|
The Athenian Treasury, Delphi
510 BCE |
Industry of Greek architecture. Worshipped Apollo. Bigger by standard and the wealthiest of all greek treasuries.
|
|

|
The Panathenaic Vase
Black - figure amphora Terra cotta 530 BCE |
Panathenaic Games in Athens
|
|

|
New York Kouros
Archaic Marble 600 BCE |
Lifesize. Style taken from Egyptian construction. Positioned in a frontal view, the frontal flatness, hair and Archaic smile fail to display a naturalistic appearance.
|
|
|
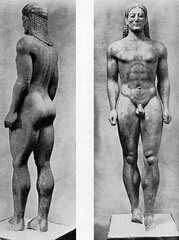
Anavysos Kouros
Archaic Marble Athens 525 BCE |
Invites you to walk around the sculpture due to the naturalism and detailed muscular body structure. Used as commemorative goods among the gods.
|
|

|
Peplos Korea
Archaic Marble Athens |
Presumed her hand was extended as an offering. Votive of offering to Athena.
|
|

|
Kore from Acropolis
Archaic Marble Athens 520 BCE |
Shinton type of dress. A bit more realistic compared to the Peplos Kore
|
|
|
Minoans
|
Lived on Crete. Peaceful people who lived in unfortified towns and battle scenes were nonexistent in their art. Abandoned Knossos in 1450 BCE. Three possible reasons for leaving their city would consist of deforestation, the volcanic eruption on Thera or the Mycenaean army overwhelming the island.
|
|
|
|
Mycenaeans
|
First ones to actually speak Greek. After sending an army to Crete, fortified towns were built. Warriors who lived and died by the sword had their scenes illustrated within their art. They were motivated by trade
|
|
|
|
Agora
|
A large open area in acient Greek cities that served as a public meeting place, marketplace and civic center.
|
|
|
|
Acropolis
|
Literally "top of the city"; the natural citadel of a Greek city that served as a fortification or religious center.
|
|
|
|
Agora
|
An open place used for gathering or as a market.
|
|
|
|
Amphora
|
A Greek jar with an egg shaped body and two curved handles that was used for storing oil and wine.
|
|
|
|
Archaic Style
|
A style in early Greek art (600 - 480 BCE) marked by increased naturalism, seen especially in the period's two predominant sculptural types, Kouros and Korai.
|
|
|
|
Bard
|
A singer of songs about the deeds of heroes and the way of the gods.
|
Example: Homer
|
|
|
Black - figure
|
A style in Greek pottery decoration composed of black figures against a red background.
|
Example: Women at a Fountain House
|
|
|
Buon Fresco
|
The technique of applying pigment mixed with water onto wet plaster so that the paint is absorbed by the plaster and becomes part of the wall when dry.
|
Example: Bull Leaping Fresco
|
|
|
Capital
|
A sculpted block that forms the upper most part of a column.
|
|
|
|
Cella
|
The principal interior of a Greek building, especially a temple, also called a naos.
|
|
|
|
Column
|
A vertical element that serves as an architectural support, usually consisting of a capital, shafts and base.
|
|
|
|
Corinthian Order
|
The most elaborate of the Greek architectural orders distinguished by a capital decorative with acanthus leaves.
|
|
|
|
Cyclopean Masonry
|
Walls made of huge blocks of rough-hewn stone ; so called because of myth that a race of monsters known as Cyclopse built them.
|
Example: Lion Gate (1300 BCE)
|
|
|
Democracy
|
Ruled by the people.
|
|
|
|
Doric Order
|
The oldest and simplest of the Greek architectural orders characterized by a heavy column that stands directly on a temple's stylobate.
|
|
|
|
Elavation
|
The arrangement, proportions, and appearance of a temple foundation, column and lintels.
|
Example: Temple of Hera
|
|
|
Engaged Column
|
A half-column that projects from a wall but serves no structural purpose.
|
|
|
|
Entasis
|
The swelling of the shaft of a column.
|
|
|
|
Faience
|
A type of earthenware ceramic, can decorated with glazes.
|
Example: The Snake Godess
|
|
|
Feudal
|
A system of political organization based on ties of allegiance between a lord and those who owed their well fare to him.
|
|
|
|
Geometric Style
|
A style of early Greek ceramics characterized by circles, rectangles, highlighting and triangles arranged in parallel bands.
|
Example: Dipylon Vase
|
|
|
Hubris
|
Exaggerated pride and self confidence.
|
|
|
|
Ionic order
|
One of the Greek architectural orders (second) characterized by plums either of caryatids or with scrolled capitals.
|
|
|
|
Kore
|
A freestanding sculpture of a standing maiden.
|
Dxample: Peplos Kore
|
|
|
Kouros
|
A freestanding sculpture of a nude male youth.
|
Example: Anavysos Kouros
|
|
|
Naturalism
|
A style in art that seeks to represent forms, including the human body.
|
Kouros and Kore
|
|
|
Order
|
In Classical Greek architecture, the relationship of an elevation's three vertical elements.
3 orders - Doric, Ionic, Corinthian |
Example: Platform, column, entablature
|
|
|
Pediment
|
The triangular area over a porch.
|
|
|
|
Polis
|
The Greek city - state that formed the center of cultural life.
|
Example: Athens
|
|
|
Red - figure
|
A style in Greek pottery decoration composed of red figures against a black background.
|
Example: Death of Sarpedon (515 BCE)
|
|
|
Repoussé
|
A metalworking technique of creating a design in relief by hammering or pressing on the reverse side.
|
Dxample: Mask of Agamemnon
|
|
|
Shaft Grave
|
A deep vertical pit enclosed in a circle of stone slabs.
|
Example: The Treasury of Atreus
|
|
|
Symposium
|
In Ancient Greece, a gathering of men initially for the purpose of sharing poetry, food and wine.
|
|
|
|
Tholos
|
A round building.
|
Treasury of Atreus
|
|
|
Volute
|
A scroll - like motif on a column's capital.
|
|

