![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
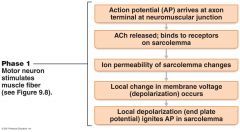
What is this?
|
Phase 1
|
|
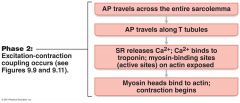
What is this?
|
Phase 2
|
|
|
Motor Neurons
|
Stimulate muscle cells to contract, found in brain and spinal chord.
|
|
|
Motor axons
|
long, thread-like extensions of neurons within the nerves to the muscle cell.
|
|
|
Neuromuscular junction
|
axon ending (terminal) on a single muscle fiber
|
|
|
Synaptic cleft
|
microscopic space separating axon terminal from the muscle fiber
|
|
|
Synaptic vesicles
|
small membranous sacs filled with neurotransmitter (acetycholine)-ACh
|
|
|
Motor end plate
|
folded region of sarcolemma under axon terminal which contain ACh
|
|
|
Acetylcholinesterase
|
enzyme that breaks down ACh to prevent over stimulation of muscle fiber
|
|
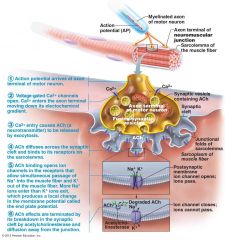
Study this, what is it
|
muscle fiber stimulation
|
|
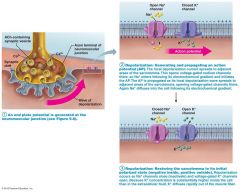
Study this, what is it?
|
Generation of sarcolemma action potential
|
|
|
Depolarization
|
sarcolemma becomes less negative
|
|
|
Repolarization
|
restoration of initial polarized state
|
|
|
Refractory period
|
period where a cell cannot be stimulated again, usually during repolarization.
|
|
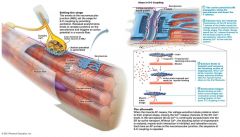
E-C coupling
|
Excitation-contraction
|
|
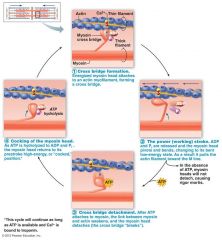
what is this?
|
muscle fiber contraction
|
|
|
Muscle tension
|
force exerted on an object by muscle contraction
|
|
|
load
|
force exerted on a muscle by the weight of an object
|
|
|
isometric contraction
|
muscle does not change in length
|
|
|
isotonic contraction
|
muscle tension does not change but length does
|
|
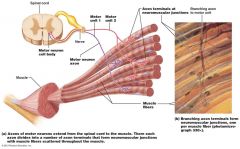
What is this?
|
Motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it supplies
|
|
|
myogram
|
graphic recording of contractile activity
|
|
|
muscle twitch
|
response of a motor unit to a single action potential
|
|

latent period
|
e-c coupling, beginning of muscle contraction
|
|

period of contraction
|
from onset of contraction to peak tension
|
|

period of relaxation
|
calcium reentry in SR
|
|
|
wave summation
|
adding twitch contraction from rapid stimulation of the muscle
|
|
|
unfused(incomplete) tetanus
|
rapid stimulation created a sustained and quivering contraction
|
|
|
fused(complete) tetanus
|
stimulation is fast enough for all evidence of muscle relaxation to disappear
|
|

function
|
to create smooth continuous contractions
|
|
|
recruitment
|
multiple motor unit summation
|
|
|
threshold stimulation
|
stimulus where contraction is observable
|
|
|
maximal stimulus
|
all muscle's motor units recruited
|
|
|
size priciple
|
motor units recruited in order from smallest muscle fibers to largest muscle fibers
|
|
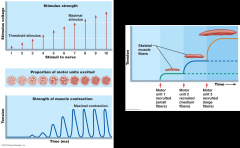
whats the left?
what the right? |
recruitment
size principle |
|
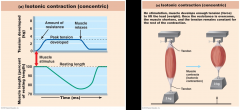
what kind of contraction is this?
|
isotonic
|
|
|
concentric
|
muscle shortens
|
|
|
eccentric
|
muscle lengthens
|
|
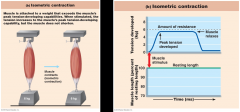
what contraction is this one?
|
isometric
|
|
|
muscle metabolism
|
ATP provide
|

