![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
_____ is an infection involving the endothelial layer of the heart. It mostly affects the _____, however it can effect the lining of heart and the great vessels. |
Infective endocarditis Valves |
|
|
Infective endocarditis is caused by a pathogen introduced to circulation via oral cavity, upper respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, girls whooha, skin or circulatory system causing _____ (Most common) or ______ (least common) |
Bacterium fungemia |
|
|
What is a classic manifesting of IE? |
Vegetation |
|
|
Veg are usually attached to cardiac structures that are____, particularly areas of _____ blood flow. |
Damaged Turbulent |
|
|
The majority of organisms attach to the ______ side of the valves. The ____ side of AV valves and the ____ side of the semi lunar valves. |
Flow Arial Ventricular |
|
|
Two types of Infective endocarditis are _____, and____ |
Acute IE Subacute IE |
|
|
Acute IE is by highly virulent pathogens with sudden onset and rapid destruction of cardiac tissues. It often involves a normal valve and typically caused by the bacteria _____. |
Staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
Subacute IE may be sub-clinical for as long as 8 weeks and has a SUBtle presentation. It often involves invasion of an abnormal valve and typically caused by the bacteria streptococcus viridans . Patient will complain of feeling ____ |
Run down |
|

High risk IE |

Intermediate risk and low risk for IE |
|

Greatest risk |
. |
|
|
Complications of IE are embolism, haemodynamic changes such as stenosis, regurg, flail/ruptured leaflet, aneurysm, perforation, fistula, prosthetic valve dehisence. Abcess, heart failure due to severe regurg. |
Treatment= Antibiotics, oral or intravenous Antibiotics can be required up to 6 weeks ¤Sign and symptoms of IE page 217 |
|
|
IE in a 2D echo may appear thickened, _____, swinging or peduculated. |
Shaggy |
|
|
Vegs vary in size. The veg must be > ____mm to be seen by TTE. With TEE usually detects a vegs as small as > ___mm |
>2-3mm >1mm |
|
|
With IE, LV function is usually ____ or _______. With acute IE it cause severe regurg which causes the LV to have a ____ overload pattern resulting in dilatation and a hyperdynamic state. The ____ _____ ____ explains this best, the more blood that enters the ventricle during diastole= the greater the quantity of blood pumped during systole. |
Normal Hyperdynamic Volume Frank-Starling principle |
|
|
You may notice the patient has a _____ in the 2D echo when IE is present. |
Pericardial effusion |
|
|
With IE, what is the cause of heart failure? |
Severe, acute regurgitation |
|

AI due to IE |

Measure veg, zoom, freeze, calipers or planimetry |
|
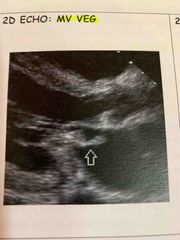
MV veg |
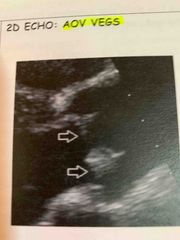
AOV veg |
|
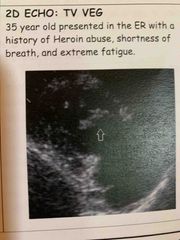
TV veg |
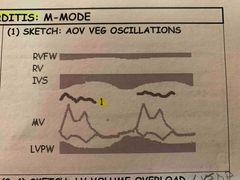
1. Oscillations from veg may be detected. AOV veg oscillations may be detected in LV |
|
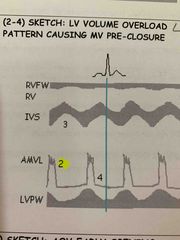
2. AI due to AOV veg may cause flutter of AMVL 3. LVEDP increase from regurg cause MV closure to be early (4) and may cause AOV to open early. |
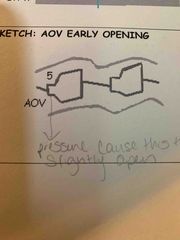
AOV opening early due to pressure. |
|

Front (Term) |
Page 219 DeWitt |

