![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
5 functions of the skeletal system |
Support, Protection, Movement, Storage, Hematopoiesis |
|
|
Storage |
Strong enough to hold the weight, yet flexible enough to withstand twisting forces. Internal framework of the body. |
|
|
Protection |
Protects the soft tissue |
|
|
Movement |
Bones and muscles make movement possible. |
|
|
Storage |
Store calcium |
|
|
Hematopoiesis |
Blood cell formation |
|
|
Types of Bones |
Long, Short, Flat, Irregular |
|
|
Osterblasts |
"remodeling" growing |
|
|
Osteoclasts |
Bone-resorbing cells |
|
|
endochondral ossification |
"formed within cartilage" |
|
|
epiphyseal plate |
layer of cartilage, between epiphysis and diaphysis, growth continues |
|
|
Two Divisions of the skeleton |
Axial and Appendicular |
|
|
Axial |
skull, spine, chest |
|
|
Appendicular |
shoulder, arms, wrists, hands |
|
|
Frontal, Maxillary, Sphenoid, Ethmoid bones |
Paranasal Sinuses |
|
|
Mastoiditis |
inflammation of the air spaces within the mastoid portion of the temporal bone, can produce serious helath problems. |
|
|
Fontanels |
"soft spots", 2 years |
|
|
Cervical number of bones |
7 |
|
|
Thoracic number of bones |
12 |
|
|
lumbarnumber of bones |
5 |
|
|
sacrum number of bones |
1 |
|
|
coccyxnumber of bones |
1 |
|
|
How Many True Ribs and where/what are they |
7 upper seven attached |
|
|
How Many False Ribs and where are they
|
3 lower attached |
|
|
How Many Floating Ribs and where are they
|
2 front NOT attached |
|
|
Lordosis |
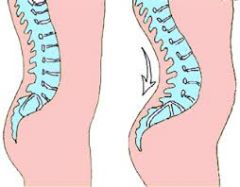
Swayback |
|
|
Kyphosis |
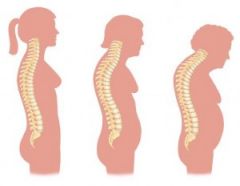
hunchback |
|
|
scoliosis |
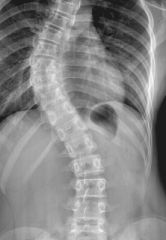
side to side |
|
|
Synarthroses |
NO movement; |
|
|
Amphiarthroses |
SLIGHT movement; |
|
|
Diarthroses |
any movement; |
|
|
Hinge Joint |
Elbow |
|
|
Pivot Joint |
Neck/Head |
|
|
Saddle Joint |
Wrist |
|
|
Condyloid Joint |
Jaw |
|
|
Ball-And-Socket |
Hip |
|
|
Gliding Joint |
Spine |
|
|
Osteosarcoma |
Most common and devastating malignant neoplasm of bone |
|
|
Chondrosarcoma |
cancer of the skeletal hyaline cartilage tissue & is the 2nd most common cancer affecting bones |
|
|
Osteoporosis |
Bone Cancer; Not enough Calcium |
|
|
Rickets |
bo-legged, Lack of vitamin D |
|
|
paget disease |
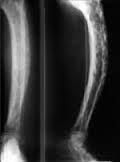
weakened and irregular cancellous bone overgrowth in the femur |
|
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta |
affect 1 and 30,00 births and is also called "brittle bone disease" |
|
|
Osteomyelitis |
Bacterial infections of bone and marrow tissue |
|
|
Open Fractures |
Compound; pierce the skin |
|
|
Closed Fractures |
Simple; do not pierce the skin |
|
|
Osteoarthritis |
most common noninflammatory disorder of movable joints |
|
|
Strain |
muscle |
|
|
Sprain |
bone |
|
|
Arthritis (3 Types) |
Rheumatoid, Gout, Infectious |
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis |
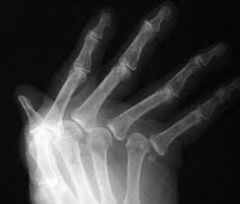
AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE chronic inflammation of connective tissues |
|
|
Gouty arthritis-- Gout |
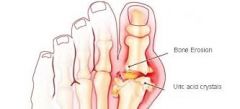
metabolic condition in which uric acid, a nitrogenous waste, increases in the blood,. Excess uric acid id deposited as sodium urate crystals in distal joint and other tissues. |
|
|
Infectious Disease |
Lyme disease; carried by ticks |

