![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why Firms Compete |
1. To create a customer base 4. To achieve product superiority 6. To maximize profits |
|
|
Difference Between Price and Non Price Competition |
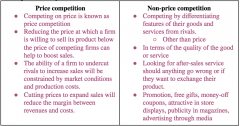
|
|
|
Is competition good or bad for the customer |
It is good in that prices might go down and the quality may increase but excessive advertising and packaging can also lead to higher prices for compensation |
|
|
What is a market share? |
The percentage of how much a certain company has/controls of a specific market |
|
|
How is a market share determined? |
It is calculated by taking the companies sales over a period of time and divide it by the total sales the company has made. |
|
|
Competitive Pricing Strategies |
1. Penetration Pricing 2. Expansion Pricing 3. Market Skimming 4. Price Wars |
|
|
Perfect Competitive Market + Example |
There are so many consumers and producers that no one alone can influence the market price. Ex: Orange market because orange prices are all about the same, and if they increase their prices they will most likely go out of business |
|
|
Price Taker & Price Maker |
Price Taker: In perfect competitive market, consumers and producers are all price takers; no one alone can influence the market price Price Maker: A monopoly is a price maker because it can restrict market supply to force up the price market |
|
|
Market Structure |
Describe how a market is organized in terms of how much competition there is, usually on the supply side. Competition between firms encourage the best use of scarce resources |
|
|
The amount of competition in a market is determined by |
- The amount of control a firm has over the market supply and output - Amount of influence the firm has over market price - Freedom new suppliers have to enter the market - Barriers to entry that restrict new competition |

