![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Trapezius |
Extends neck & adduced scapula |
|
|
Latissimus dorsi |
Extends & adducts humerus |
|
|
Erector spinae |
Extends the back |
|
|
Quadratus lumborum |
Flexes the spine laterally; extends spine |
|
|
Deltoid |
Abducts humerus |
|
|
Triceps brachii |
Extends elbow |
|
|
Flexor Capri radialis |
Flexes wrist & abducts hand |
|
|
Flexor carpi ulnaris |
Flexes wrist & adducts hand |
|
|
Flexor digitorium superficialis |
Flexes wrist & fingers |
|
|
Extensor carpi radialis |
Extends wrist & abducts hand |
|
|
Extensor digitorium |
Extends fingers and wrist |
|
|
Gluteus maximus |
Extends hip (when forceful extension is required) |
|
|
Gluteus medius |
Abducts thigh; steadies pelvis during walking |
|
|
Hamstring muscles |
Flex knee & extend hip |
|
|
Gastrocnemius |
Plantar flexes foot & flexes knee |
|
|
Soleus |
Plantar flexes foot |
|
|
Frontalis orbicularis occuli |
Raises eyebrows, blinks and closes eyes |
|
|
Orbicularis oris |
Closes & protrudes lips |
|
|
Temporalis |
Closes jaw |
|
|
Zygomaticus |
Raises corners of mouth |
|
|
Masseter |
Closes jaw |
|
|
Buccinator |
Compressed cheeks as in whistling & sucking; holds food between teeth during chewing |
|
|
Sternocleidomastoid |
Flexes neck; rotates the head |
|
|
Platysma |
Pulls corners of the mouth inferiorly |
|
|
Pectoralis major |
Adducts & flexes humerus |
|
|
Rectus abdominis |
Flexes vertebral column |
|
|
External oblique |
Flexes & rotates vertebral column |
|
|
Biceps brachii |
Flexes elbow & supinate forearm |
|
|
Brachialis |
Flexes elbow |
|
|
Deltoid |
Abducts arm |
|
|
lliopsoas |
Flexes hip |
|
|
Adductor muscles |
Adducts thigh |
|
|
Sartorius |
Flexes thigh on hip |
|
|
Quadriceps |
All extend knee; rectus femoris also flexes hip on thigh |
|
|
Tibialis anterior |
Doriflexes & inverts foot |
|
|
Extensor digitorium longus |
Extends toes & dorsiflexes foot |
|
|
Fibularis muscles |
Plantar flex & evert foot |
|
|
Gluteus medius, Vastus lateralis, deltoid |
Muscles where injections can be administered |
|
|
Adduction |
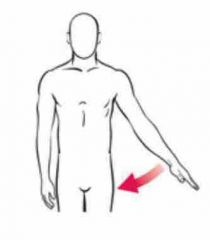
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Abduction |
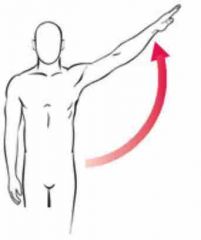
|
|
|
Flexion & extension |
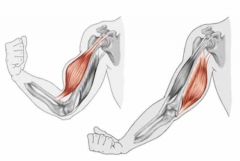
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Circumduction |
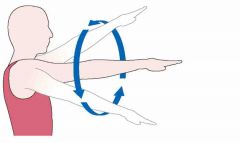
|
|
|
Dorsiflexion |
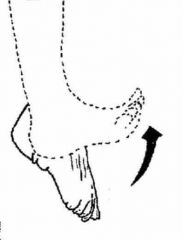
|
|
|
Plantar flexion |
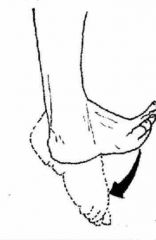
Back (Definition)
|
|
|
Supination |
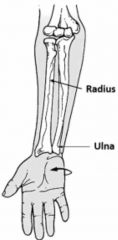
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Pronation |
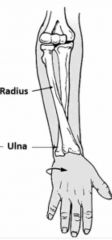
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth |
3 types of muscles |
|
|
Motor neuron |
Skeletal muscles must be stimulated by ____ to contract |
|
|
Motor unit |
One motor neuron & all the skeletal cells stimulated by that neuron |
|
|
Neuromuscular junction |
Association site of axon terminal if the motor neuron & muscle |
|
|
Walls of hollow organs |
Smooth muscle is usually found in... |
|
|
Synaptic cleft |
Gap between the nerve and muscle |
|
|
Neurotransmitter |
Chemical released by nerve upon arrival of nerve impulses |
|
|
Acetylcholine |
Neurotransmitter for skeletal muscle |
|
|
Bones, cartilages, connective tissue coverings |
Sites of muscle attachment |
|
|
Excitability |
Ability to receive & respond to stimulus |
|
|
Contratibility |
Ability to shorten when an adequate stimulus is received |
|
|
Extensibility |
Ability of muscle cells to be stretched |
|
|
Elasticity |
Ability to recoil & resume resting length after stretching |
|
|
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth |
3 types of muscles |
|
|
Motor neuron |
Skeletal muscles must be stimulated by ____ to contract |
|
|
Motor unit |
One motor neuron & all the skeletal cells stimulated by that neuron |
|
|
Neuromuscular junction |
Association site of axon terminal if the motor neuron & muscle |
|
|
Walls of hollow organs |
Smooth muscle is usually found in... |
|
|
Synaptic cleft |
Gap between the nerve and muscle |
|
|
Neurotransmitter |
Chemical released by nerve upon arrival of nerve impulses |
|
|
Acetylcholine |
Neurotransmitter for skeletal muscle |
|
|
Bones, cartilages, connective tissue coverings |
Sites of muscle attachment |
|
|
Excitability |
Ability to receive & respond to stimulus |
|
|
Contratibility |
Ability to shorten when an adequate stimulus is received |
|
|
Extensibility |
Ability of muscle cells to be stretched |
|
|
Elasticity |
Ability to recoil & resume resting length after stretching |
|
|
Graded responses |
Different degrees of skeletal muscle shortening |
|
|
Frequency of muscle stimulation, # of cells being stimulated at one time |
Graded responses can be produced by changing ________. |

