![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Electron microscope |
Microscope that focuses a beam of electrons through a specimen or onto its surface. Downside is that the specimen has to be dead. |
|
|
Cytosol |
Jelly-like semifluid found in all cells that holds all subcellular components. |
|
|
Nucleus (cell) |
In a eukaryotic cell, it is a (double) membrane-enclosed organelle in which most DNA is stored. |
|
|
Nucleoid (cell) |
Region (not membrane-enclosed) in prokaryotic cells that holds most of the DNA. |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Interior of a cell. In eukaryotic cells, this does not include the nucleus. |
|
|
Prokaryotic cells are usually __________ than eukaryotic cells. |
Smaller |
|
|
Nuclear envelope |
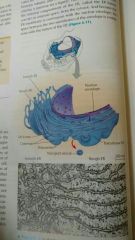
Double membrane that encloses the nucleus and separates it from cytoplasm. |
|
|
Nuclear lamina |
Net-like array of protein filaments that lines the inside of the nuclear membrane and maintains the shape of the nucleus. |
|
|
Chromosome |
DNA structures that carry genetic info. Each contains one long DNA molecule associated with many proteins, some of which help coil the DNA molecule of the chromosome to help it fit into the nucleus. |
|
|
Chromatin |
Complex of DNA and proteins that make up chromosomes. |
|
|
Nucleolus |
Structure within the nucleus consulting of chromosomal regions containing ribosomal RNA genes along with ribosomal proteins imported from cytoplasm; site of rRNA synthesis and ribosomal subunit assembly. |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Complexes made of rRNA and protein; cellular components that carry out protein synthesis. |
|
|
Endomembrane system |
System in cell containing nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, various vesicles and vacuoles, and the plasma membrane. |
|
|
Vesicles |
Membranous sacs in eukaryotic cells |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) |
Network of membranes in eukaryotic cells, continuous with the outer nuclear membrane and composed of ribosome-studded (rough) and ribosome-free (smooth) regions. |
|
|
Functions of smooth ER |
Lipid synthesis, metabolism of carbs, drug/poison detox, and calcium ion storage. |
|
|
Functions of rough ER |
Protein synthesis and transport |
|
|
Transport vesicles |
Vesicles that move from one part of the cell to the other. |
|
|
Glycoproteins |
Proteins that have carbohydrates covalently bonded to them. Make up most secretory proteins. |
|
|
Golgi apparatus |
Warehouse for receiving, sorting, shipping, and manufacturing of different products such as proteins and Polysaccharides. |
|
|
Lysosome |
Membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that an animal cell uses to digest macromolecules. |
|
|
Phagocytosis |
Type of endocytosis where small substances are taken up by the cell it is carried out by some protists and buy certain immune cells of animals. |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Sites of cellular respiration, the metabolic process that uses O2 to generate ATP by extracting energy from sugars, fats, and other fuels. |
|
|
Vacuoles |
Large vesicles derived from ER and Golgi apparatus. Food vacuoles (phagocytosis), contractile vacuoles (pumps out excess water), central vacuole (in mature plants made of smaller vacuoles). |
|
|
Chloroplast |
Found in plants and algae; sites of photosynthesis. Convert solar energy into chemical energy. |
|
|
Endosymbiont theory |
Theory stating that an early eukaryotic cell engulfed a prokaryotic cell and evolved into a eukaryotic cell with a mitochondrion |
|
|
Cristae |
Inner foldings of a mitochondrion. Divides cell into two parts. |
|
|
Mitochondrial matrix |
Mitochondrial compartment enclosed by the inner membrane; contains enzymes, DNA, and ribosomes. |
|
|
Thylakoids |
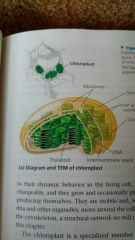
Flattened, interconnected sac in chloroplast. |
|
|
Granum |
Stacks of thylakoids in chloroplast. |
|
|
Stroma |
Fluid outside the thylakoids; contains DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes. |
|
|
Peroxisome |
Specialized metabolic compartment bounded by a single membrane; contain enzymes that remove hydrogen atoms from various substrates and transfer them to oxygen, producing hydrogen peroxide as a by-product. |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm. |
|
|
Motor proteins |
Protein that interacts with cytoskeletal elements and other cell components, producing movement of the whole cell or parts of the cell. |
|
|
Microtubules |
Hollow rods (25nm in diameter, 200+ nm in length) found in eukaryotic cells. |
|
|
Centrosome |
Region near nucleus; "microtubule-organizing center" |
|
|
Centriole |
Structure made of microtubules. |
|
|
Flagellum |
Long, cellular appendage for locomotion. Made of microtubules. |
|
|
Cilia |
Short microtubule-containing projections used for locomotion or moving things past a cell. |
|
|
Dyneins |
Proteins responsible for bending movement of a cell. |
|
|
Microfilaments |
Solid rods about 7 nm in diameter built from actin molecules. |
|
|
Cortex |
Outer cytoplasmic layer of a cell. |
|
|
Myosin |
Type of motor protein that associates into filaments that interact with actin filaments to cause cell contraction. |
|
|
Pseudopodia |
Cellular extensions ("false foot") used by amoeba to move. |
|
|
Cytoplasmic streaming |
Circular flow of cytoplasm within a cell. |
|
|
Cell wall |
Extracellular structure of plant cells that protects them, maintains their shape, and prevents excessive intake of water. |
|
|
Middle lamella |
Polysaccharide glue that keeps plant cells together. |
|
|
Collagen |
Most abundant glycoprotein (40% of all protein in human body) in ECM (extracellular matrix); forms strong fibers outside cells. |
|
|
Proteoglycans |
Large molecule consisting of a small core protein with many carb chains attached, found in extracellular matrix of animal cells. Up to 95% carb. |
|
|
Fibronectin |
Glycoproteins that attach some cells to the ECM. |
|
|
Integrins |
Cell-surface receptor proteins built into the plasma membrane. |
|
|
Plasmodesmata |
Membrane-lined channels filled with cytoplasm; perforate cell walls. |

