![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does addition polymerisation occur? |
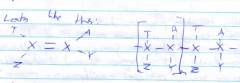
With many monomers close together under the influence of heat, an initiator and pressure. |
|
|
How are polyesters made? |
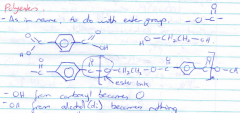
Polyesters are made from the condensation reaction between a diol and a dicarboxylic acid. |
|
|
How are polyamides made? |

Polyamides are made from the condensation reaction between a diamine and a dicarboxylic acid. |
|
|
What is known about the bond strength between polymer chains? |
- Increases as the length of the chain increases. - Polymers with just dispersion forces are soft, flexible and non-elastic. - Low melting points, can be reshaped; good for recycling. |
|
|
What are cross-links? |
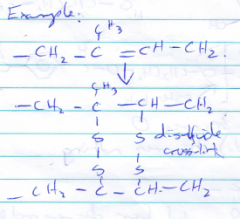
Cross-links are covalent bonds and increase the rigidity. They act like in addition reactions as seen in the image of disulfide cross-links. |
|
|
What are thermoplastics are thermosets? |
Thermoplastics: - Reversible. - Only secondary interactions exist between molecules. - Suited for recycling. Thermosets: - Not softened when heated. Char. - Not reversible. - Not recyclable. - Cross links are strong and when heat breaks this, decomposition products are created. |
|
|
How do you find the charge on aluminosilicate ions? |

|
|
|
What are aluminosilicates? |
- Aluminium substitutes silicon in a silicate structure. - Feldspar and zeolites are the two most important groups of aluminosilicates. - Clays are formed from the weathering of rocks. |
|
|
What is the equation for the cation exchange on the surface of soil silicates? |
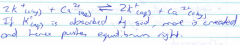
|
|
|
What is the equation for the cation exchange and acid rain? What happens because of this? |

|
|
|
What is the equation for the cation exchange and zeolites? What happens because of this? |

|
|
|
How do soaps work? |
- The long non-polar hydrocarbon chains of the soap are attracted to the grease where the ionic head stick out. - When agitated, grease is released and form micelles. - Micelles have a constant negative charge around and hence repel each other, allowing for grease to be washed away. |
|
|
What is the equation for saponification? |

|
|
|
What is the disadvantage of soaps? |

The creation of scum from dissolved calcium and magnesium ions. The equation is shown in the image. |
|
|
What are the main differences between soaps and detergents? |
Soaps are made from carbonates while detergents are made from suflates |
|
|
How do bleaches work? |
Bleaches work by oxidising coloured stains as to create colourless ones. |
|
|
How do chlorine bleaches work? |

They contain an oxidising agent, known as hypochlorous acid. |
|
|
How do oxygen bleaches work? |

Hydrogen peroxide acts as the oxidising agent. |
|
|
How can stains be removed? |
- A coloured stain can be oxidised by a bleach - A food stain can be broken down with an enzyme. - Rust can be removed with a substance that reactswith the rust. - Acidic and basic stains can be removed byneutralisation with mild alkalis and acids. |

